The Impact of Follower Status on Parasocial Relationships and Advertising Effectiveness in Social Media Influencer Marketing
Keywords:
Social Media Influencers, Parasocial Relationships, Influencer Credibility, Advertising EffectivenessAbstract
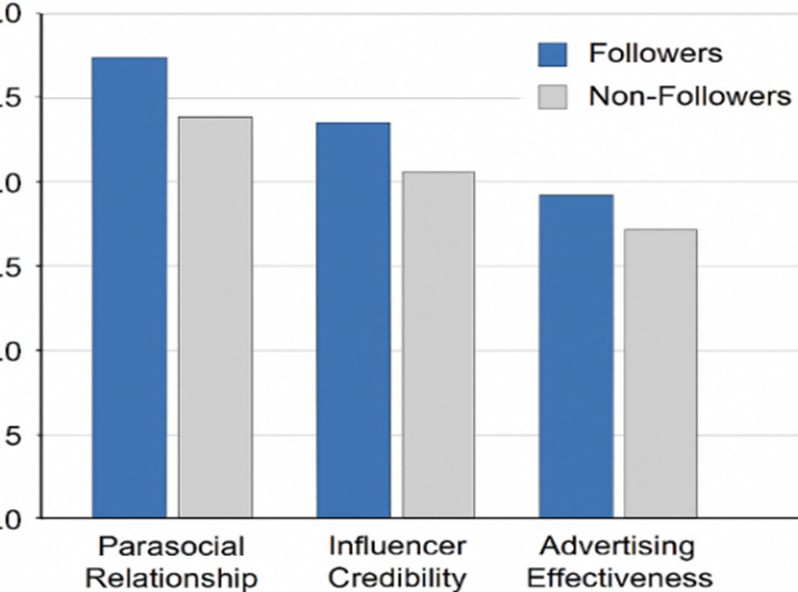
This study explores the psychological mechanisms underlying social media influencer (SMI) marketing effectiveness by examining how follower status impacts parasocial relationships (PSRs) with SMIs and how product involvement moderates this effect. Additionally, the study investigates the mediating role of influencer credibility in the relationship between PSRs and advertising effectiveness, including brand attitudes and purchase intentions. Data were collected from 350 participants, comprising both followers and non-followers of a selected SMI on Instagram. Results indicate that followers develop significantly stronger PSRs and perceive higher influencer credibility than non-followers. Product involvement amplifies the effect of follower status on PSRs, which in turn positively influences advertising effectiveness through increased credibility perceptions. Furthermore, PSRs and credibility significantly predict electronic word of mouth (eWOM) intentions, suggesting that parasocial bonds motivate active sharing of influencer content. The findings highlight the importance of considering follower engagement and product relevance in designing effective influencer marketing campaigns. This study contributes to a deeper understanding of the trans-parasocial processes that drive consumer behavior in digital environments and offers practical implications for brands seeking to optimize influencer partnerships.