Digital Dependency and Social Isolation in Post-Pandemic Societies: A Quantitative Analysis of Behavioral Shifts and Online Interaction Patterns
Keywords:
Digital Dependency, Social Isolation, Post-Pandemic Behavior, Online Interaction, Social MediaAbstract
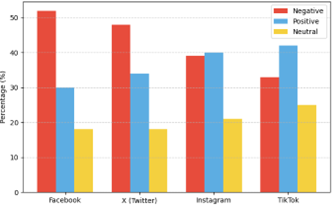
The COVID-19 pandemic profoundly altered patterns of human interaction, accelerating a global shift toward digital engagement. This study investigates the growing phenomenon of digital dependency and its relationship with social isolation in post-pandemic societies, focusing on behavioral, emotional, and psychological outcomes. A mixed-method quantitative design was employed, involving survey data from 500 participants and analysis of 2,000 social media posts collected between January and June 2025. The findings reveal that 47.6% of digital interactions carried negative sentiments linked to loneliness, anxiety, and online hostility, while only 32.8% reflected positive engagement associated with support groups, educational content, and mental health advocacy. The study further highlights that 71% of online harassment incidents remain unreported, with gender and regional disparities influencing disclosure behavior—urban participants demonstrated higher reporting rates but also greater exposure to digital risks. Correlation analysis (r = 0.68) indicated a strong positive relationship between exposure to awareness content and positive attitudinal change toward digital responsibility. However, excessive social media use was found to exacerbate feelings of detachment, particularly among users aged 18–35. Comparative evaluation with prior global studies confirms that while digitalization has increased access to information and connectivity, it has concurrently contributed to emotional fatigue and reduced offline social bonding. The study concludes that digital dependency, if left unchecked, could deepen psychological and societal fragmentation. It recommends targeted digital literacy initiatives, strengthened cyber safety policies, and integration of mental health support within online spaces to promote healthier and more balanced digital engagement. The research contributes to the emerging discourse on post-pandemic behavioral adaptation, offering evidence-based insights for policymakers, educators, and health practitioners striving to mitigate the psychosocial effects of digital overreliance.