Machine Learning for Detecting Social Media Addiction Patterns: Analyzing User Behavior and Mental Health Data
Keywords:
Social Media Addiction, Machine Learning Framework, Random Forest Classifier, User Behavior Analysis and Mental Health Impact.Abstract
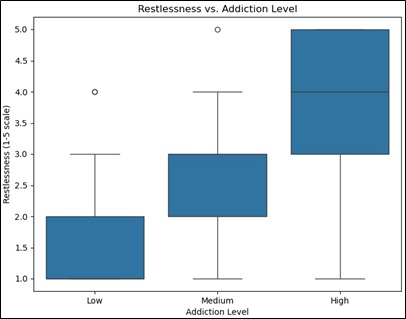
In the modern world, communication through social networks has become the norm, and people have started to worry about the possible addictive properties of social networks and their influence on mental states. This research aims to propose a Machine Learning (ML) framework for examining patterns of Social Media (SM) addiction, while also acknowledging the dearth of research on developing appropriate detection tools. We obtained data for the research through surveys, which led to the creation of a larger dataset that included aspects of user behavior, mental health parameters, and social media statistics. We use a Random Forest Classifier to predict different levels of addiction, including low, medium, and high levels, while considering behavioral and psychological characteristics. Further analysis of the research findings shows that the more hours spent on social media, especially, are associated with higher levels of distractions, irritation, and other forms of emotional problems among the SM users. Additionally, the feature importance analysis reveals that indicators such as emotional comparisons and the need for self-validation also contribute to addiction. Therefore, these results indicate a high, critical level of awareness and require the development of intervention programs associated with social media addiction while considering the close connection between user behavior and mental health. Lastly, the study adds knowledge on social media addiction and helps to open the next stage in research to identify the prevention of negative impacts on mental health due to addiction to social networks.
References
A. M. Khalaf et al., “The Impact of Social Media on the Mental Health of Adolescents and Young Adults: A Systematic Review,” Cureus, vol. 15, no. 8, Aug. 2023, doi: 10.7759/CUREUS.42990.
“Social Media Usage Patterns and Differences Among Generations The Case of Northern Cyprus.” Accessed: Oct. 21, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337051166_Social_Media_Usage_Patterns_and_Differences_Among_Generations_The_Case_of_Northern_Cyprus
D. B. Seo and S. Ray, “Habit and addiction in the use of social networking sites: Their nature, antecedents, and consequences,” Comput. Human Behav., vol. 99, pp. 109–125, Oct. 2019, doi: 10.1016/J.CHB.2019.05.018.
F. Karim et al., “Social Media Use and Its Connection to Mental Health: A Systematic Review,” Cureus, vol. 12, no. 6, Jun. 2020, doi: 10.7759/CUREUS.8627.
P. Best, R. Manktelow, and B. Taylor, “Online communication, social media and adolescent wellbeing: A systematic narrative review,” Child. Youth Serv. Rev., vol. 41, pp. 27–36, Jun. 2014, doi: 10.1016/J.CHILDYOUTH.2014.03.001.
X. Qi, S. K. Malone, Y. Pei, Z. Zhu, and B. Wu, “Associations of social isolation and loneliness with the onset of insomnia symptoms among middle-aged and older adults in the United States: A population-based cohort study,” Psychiatry Res., vol. 325, p. 115266, Jul. 2023, doi: 10.1016/J.PSYCHRES.2023.115266.
A. K. Przybylski and N. Weinstein, “Digital Screen Time Limits and Young Children’s Psychological Well-Being: Evidence From a Population-Based Study,” Child Dev., vol. 90, no. 1, pp. e56–e65, Jan. 2019, doi: 10.1111/CDEV.13007.
V. Schønning, G. J. Hjetland, L. E. Aarø, and J. C. Skogen, “Social Media Use and Mental Health and Well-Being Among Adolescents – A Scoping Review,” Front. Psychol., vol. 11, p. 542107, Aug. 2020, doi: 10.3389/FPSYG.2020.01949/BIBTEX.
M. Boer et al., “Cross-national validation of the social media disorder scale: findings from adolescents from 44 countries,” Addiction, vol. 117, no. 3, pp. 784–795, Mar. 2022, doi: 10.1111/ADD.15709.
A. A. Rabaa’, N. A. i, H. Bhat, and S. A. Al Maati, “Theorising social networks addiction: an empirical investigation,” Int. J. Soc. Media Interact. Learn. Environ., vol. 6, no. 1, p. 1, 2018, doi: 10.1504/IJSMILE.2018.092363.
M. A. Al-Garadi, G. Mujtaba, M. S. Khan, N. H. Friday, A. Waqas, and G. Murtaza, “Applications of big social media data analysis: An overview,” 2018 Int. Conf. Comput. Math. Eng. Technol. Inven. Innov. Integr. Socioecon. Dev. iCoMET 2018 - Proc., vol. 2018-January, pp. 1–5, Apr. 2018, doi: 10.1109/ICOMET.2018.8346351.
N. Çiftci and M. Yıldız, “The Relationship Between Social Media Addiction, Happiness, and Life Satisfaction in Adults: Analysis with Machine Learning Approach,” Int. J. Ment. Health Addict., vol. 21, no. 5, pp. 3500–3516, Oct. 2023, doi: 10.1007/S11469-023-01118-7/METRICS.
B. A. Primack et al., “Social Media Use and Perceived Social Isolation Among Young Adults in the U.S.,” Am. J. Prev. Med., vol. 53, no. 1, pp. 1–8, Jul. 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2017.01.010.
D. J. Kuss and M. D. Griffiths, “Internet Gaming Addiction: A Systematic Review of Empirical Research,” Int. J. Ment. Health Addict., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 278–296, Apr. 2012, doi: 10.1007/S11469-011-9318-5/METRICS.
C. Berryman, C. J. Ferguson, and C. Negy, “Social Media Use and Mental Health among Young Adults,” Psychiatr. Q., vol. 89, no. 2, pp. 307–314, Jun. 2018, doi: 10.1007/S11126-017-9535-6/METRICS.
M. Akter, K. F. Ritu, M. T. Habib, M. S. Rahman, and F. Ahmed, “A Machine Learning Approach To Predict Social Media Addiction During COVID-19 Pandemic,” Proc. - Int. Conf. Appl. Artif. Intell. Comput. ICAAIC 2022, pp. 401–405, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ICAAIC53929.2022.9793193.
R. G. Awopetu, B. A. Olabimitan, S. O. Kolawole, R. T. Newton, A. A. Odok, and A. V. Awopetu, “The Systematic Review of Social Media Addiction and Mental Health of Nigerian University Students: The Good, The Bad and The Ugly,” Eur. J. Theor. Appl. Sci., vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 767–788, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.59324/EJTAS.2024.2(1).69.
“The efficacy of violence prediction: A meta-analytic comparison of nine risk assessment tools.” Accessed: Oct. 21, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://psycnet.apa.org/doiLanding?doi=10.1037/a0020473
R. Plackett, A. Blyth, and P. Schartau, “The Impact of Social Media Use Interventions on Mental Well-Being: Systematic Review,” J. Med. Internet Res., vol. 25, no. 1, p. e44922, Aug. 2023, doi: 10.2196/44922.
Y. Hou, D. Xiong, T. Jiang, L. Song, and Q. Wang, “Social media addiction: Its impact, mediation, and intervention,” Cyberpsychology J. Psychosoc. Res. Cybersp., vol. 13, no. 1, p. 4, Feb. 2019, doi: 10.5817/CP2019-1-4.
S. Kumar, R. Zafarani, and H. Liu, “Understanding User Migration Patterns in Social Media,” Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell., vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 1204–1209, Aug. 2011, doi: 10.1609/AAAI.V25I1.8089.
R. J. J. M. Van Den Eijnden, J. S. Lemmens, and P. M. Valkenburg, “The Social Media Disorder Scale,” Comput. Human Behav., vol. 61, pp. 478–487, Aug. 2016, doi: 10.1016/J.CHB.2016.03.038.
“A Historical Overview of Uses and Gratifications Theory - CORE Reader.” Accessed: Oct. 21, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://core.ac.uk/reader/236299260
M. Savci, A. Tekin, and J. D. Elhai, “Prediction of problematic social media use (PSU) using machine learning approaches,” Curr. Psychol., vol. 41, no. 5, pp. 2755–2764, May 2022, doi: 10.1007/S12144-020-00794-1/METRICS.
“Social comparison: Contemporary theory and research.” Accessed: Oct. 21, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://psycnet.apa.org/record/1991-97036-000
L. Jin, Y. Chen, T. Wang, P. Hui, and A. V. Vasilakos, “Understanding user behavior in online social networks: A survey,” IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 51, no. 9, pp. 144–150, 2013, doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2013.6588663.
S. Choudhury, J. P. Deb, S. Biswas, and A. Pramanik, “Social Media Disorder Scale: Structure, Reliability and Validity in Indian Context,” Int. J. Exp. Res. Rev., vol. 41, no. Spl Vol, pp. 290–304, Jul. 2024, doi: 10.52756/IJERR.2024.V41SPL.024.
“Machine learning to fight addiction using social media | Request PDF.” Accessed: Oct. 21, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329337172_Machine_learning_to_fight_addiction_using_social_media
K. K. Mak, K. Lee, and C. Park, “Applications of machine learning in addiction studies: A systematic review,” Psychiatry Res., vol. 275, pp. 53–60, May 2019, doi: 10.1016/J.PSYCHRES.2019.03.001.
L. Y. Lin et al., “ASSOCIATION BETWEEN SOCIAL MEDIA USE AND DEPRESSION AMONG U.S. YOUNG ADULTS,” Depress. Anxiety, vol. 33, no. 4, pp. 323–331, Apr. 2016, doi: 10.1002/DA.22466.
P. Vondráčková and R. Gabrhelík, “Prevention of Internet addiction: A systematic review,” J. Behav. Addict., vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 568–579, Dec. 2016, doi: 10.1556/2006.5.2016.085.
A. Shensa, J. E. Sidani, M. A. Dew, C. G. Escobar-Viera, and B. A. Primack, “Social Media Use and Depression and Anxiety Symptoms: A Cluster Analysis,” Am. J. Health Behav., vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 116–128, Mar. 2018, doi: 10.5993/AJHB.42.2.11.
T. Ding, F. Hasan, W. K. Bickel, and S. Pan, “Building High Performance Explainable Machine Learning Models for Social Media-based Substance Use Prediction,” https://doi.org/10.1142/S021821302060009X, vol. 29, no. 3–4, Jun. 2020, doi: 10.1142/S021821302060009X.
D. A. Alsaleh, M. T. Elliott, F. Q. Fu, and R. Thakur, “Cross-cultural differences in the adoption of social media,” J. Res. Interact. Mark., vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 119–140, Mar. 2019, doi: 10.1108/JRIM-10-2017-0092/FULL/XML.
H. AL Quraan, E. A. Shanab, S. Banitaan, and H. Al Tarawneh, “Motivations for using social media: comparative study based on cultural differences between American and Jordanian students,” Int. J. Soc. Media Interact. Learn. Environ., vol. 5, no. 1, p. 48, 2017, doi: 10.1504/IJSMILE.2017.086093.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 50sea

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















