Computer-Aided System for the Detection of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Keywords:
Rheumatoid arthritis, Deep learning, Disease detection, Medical ImagingAbstract
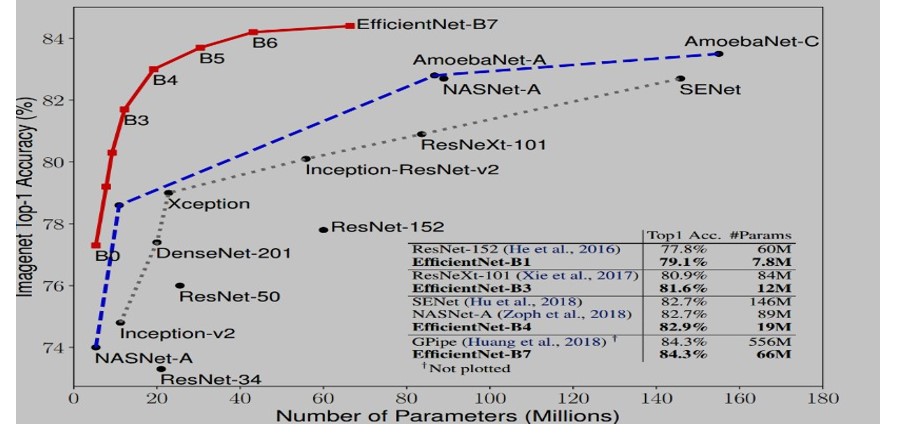
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic disease that causes disability in movement. RA classification is critical for effective diagnosis and treatment planning. This work explores the application of the EfficientNetB6 architecture using transfer learning to classify RA severity into three categories: Healthy, Moderate and Severe. Medical imaging dataset containing X-Ray images, enhanced with contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE), data augmentation techniques and fine-tuning of hyper-parameters were applied in this work. We compared EfficientNetB6 with all the models of EfficientNet family and all other state of the art models. When we combined EfficientNetB6 with CLAHE, we achieved the highest accuracy of 96.06%. Without using CLAHE accuracy dropped by 4% to 5% for all the models. For healthy class model, we achieved precision, recall and F1-score of 99.36%,97.81%,98.58% respectively, showing robustness in identifying healthy cases. Moderate class yielded precision, recall and F1-score of 89.45%,95.07%,92.17% respectively, demonstrating the model’s effectiveness in identifying moderate cases with minimal false negatives. The Severe class presented more challenges with a precision, recall and F1-score of 85.11%,78.43%, 81.63% highlighting the need for improved recall value. To further improve results we suggest enhancements such as advanced data augmentation and synthetic data generation, particularly for the Severe class consequently aiding clinicians for identification of RA.
References
B. Heidari, “Rheumatoid Arthritis: Early diagnosis and treatment outcomes,” Casp. J. Intern. Med., vol. 2, no. 1, p. 161, Dec. 2011, Accessed: Jul. 09, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3766928/
D. A. F. J Michelle Kahlenberg, “Advances in the Medical Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis,” Hand Clin, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 11–20, 2011, [Online]. Available: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3135413/
G. S. Firestein, “Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis,” Nature, vol. 423, no. 6937, pp. 356–361, May 2003, doi: 10.1038/NATURE01661,.
J. Gao, Q. Jiang, B. Zhou, and D. Chen, “Convolutional neural networks for computer-aided detection or diagnosis in medical image analysis: An overview,” Math. Biosci. Eng., vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 6536–6561, 2019, doi: 10.3934/MBE.2019326,.
T. B. Hongming Chen, Ola Engkvist, Yinhai Wang, Marcus Olivecrona, “The rise of deep learning in drug discovery,” Drug Discov. Today, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 1241–1250, 2018, [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1359644617303598
I. B. M. Josef S Smolen, Daniel Aletaha, “Rheumatoid arthritis,” Lancet, vol. 388, no. 10055, pp. 2023–2038, 2016, [Online]. Available: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27156434/
G. Litjens et al., “A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis,” Med. Image Anal., vol. 42, pp. 60–88, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2017.07.005.
D. L. Orange DE, Agius P, DiCarlo EF, Robine N, Geiger H, Szymonifka J, McNamara M, Cummings R, Andersen KM, Mirza S, Figgie M, Ivashkiv LB, Pernis AB, Jiang CS, Frank MO, Darnell RB, Lingampali N, Robinson WH, Gravallese E; Accelerating Medicines Partnership i, “Identification of Three Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Subtypes by Machine Learning Integration of Synovial Histologic Features and RNA Sequencing Data,” Arthritis Rheumatol, vol. 70, no. 5, pp. 690–701, 2018, doi: 10.1002/art.40428.
L. Shamir et al., “Knee X-ray image analysis method for automated detection of osteoarthritis,” IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., vol. 56, no. 2, pp. 407–415, Feb. 2009, doi: 10.1109/TBME.2008.2006025,.
D. S. Teoh YX, Lai KW, Usman J, Goh SL, Mohafez H, Hasikin K, Qian P, Jiang Y, Zhang Y, “Discovering Knee Osteoarthritis Imaging Features for Diagnosis and Prognosis: Review of Manual Imaging Grading and Machine Learning Approaches,” J Heal. Eng, 2022, doi: 10.1155/2022/4138666.
N. T. A. Alexopoulos, J. Hirvasniemi, S. Klein, C Donkervoort, E.H.G. Oei, “Early detection of knee osteoarthritis using deep learning on knee magnetic resonance images,” Osteoarthr. Imaging, vol. 3, no. 1, p. 100112, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ostima.2023.100112.
J. Antony, K. McGuinness, N. E. O’Connor, and K. Moran, “Quantifying radiographic knee osteoarthritis severity using deep convolutional neural networks,” Proc. - Int. Conf. Pattern Recognit., vol. 0, pp. 1195–1200, Jan. 2016, doi: 10.1109/ICPR.2016.7899799.
S. Murakami, K. Hatano, J. Tan, H. Kim, and T. Aoki, “Automatic identification of bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis from hand radiographs based on deep convolutional neural network,” Multimed. Tools Appl., vol. 77, no. 9, pp. 10921–10937, May 2018, doi: 10.1007/S11042-017-5449-4/METRICS.
L. C. Wang HJ, Su CP, Lai CC, Chen WR, Chen C, Ho LY, Chu WC, “Deep Learning-Based Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis with Hand X-ray Images Conforming to Modified Total Sharp/van der Heijde Score,” Biomedicines, vol. 10, no. 6, p. 1355, 2022, doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061355.
A. S. Jose L. Salmeron, Samira Abbasgholizadeh Rahimi, Amir Mohammad Navali, “Medical diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis using data driven PSO–FCM with scarce datasets,” Neurocomputing, vol. 232, pp. 104–112, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.09.113.
O. I. Dziekan T, Weissbach C, Voigt J, Ebert B, Macdonald R, Bahner ML, Mahler M, Schirner M, Berliner M, Berliner B, Osel J, “Detection of rheumatoid arthritis by evaluation of normalized variances of fluorescence time correlation functions,” J Biomed Opt, vol. 16, no. 7, p. 076015, 2011, doi: 10.1117/1.3599958.
R. M. Bernd Ebert, Thomas Dziekan, Carmen Weissbach, Marianne Mahler, Michael Schirner, Birgitt Berliner, Daniel Bauer, Jan Voigt, Michael Berliner, Malte L. Bahner, “Detection of rheumatoid arthritis in humans by fluorescence imaging,” Proc. SPIE, vol. 7555, 2010, doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.840913.
A. Frize, Monique ; Adéa, Cynthia ; Payeur, Pierre ; Di Primio, Gina ; Karsh, Jacob ; Ogungbemile, “Detection of rheumatoid arthritis using infrared imaging,” Proc. SPIE, vol. 7962, 2011, doi: 10.1117/12.874552.
A. Das M, Ganesh Kumar; Goswami, “Automatic Classification of the Severity of Knee Osteoarthritis Using Enhanced Image Sharpening and CNN,” Appl. Sci., vol. 13, no. 3, p. 1658, 2023, doi: 10.3390/app13031658.
Y. H. and F. W. T. Yang, H. Zhu, X. Gao, Y. Zhang, “Grading of Metacarpophalangeal Rheumatoid Arthritis on Ultrasound Images Using Machine Learning Algorithms,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2982027.
R. T. Wahyuningrum, L. Anifah, I. K. Eddy Purnama, and M. Hery Purnomo, “A New Approach to Classify Knee Osteoarthritis Severity from Radiographic Images based on CNN-LSTM Method,” 2019 IEEE 10th Int. Conf. Aware. Sci. Technol. iCAST 2019 - Proc., Oct. 2019, doi: 10.1109/ICAWST.2019.8923284.
M.-P. J. Bonakdari H, Jamshidi A, Pelletier JP, Abram F, Tardif G, “A warning machine learning algorithm for early knee osteoarthritis structural progressor patient screening,” Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis, 2021, doi: 10.1177/1759720X21993254.
Abdullah, S.S.; Rajasekaran, M.P. Automatic detection and classification of knee osteoarthritis using deep learning approach. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 398–406.
Y. LeCun, Y. Bengio, and G. Hinton, "Deep learning," Nature, vol. 521, no. 7553, pp. 436-444, May 2022. doi 10.1038/nature14539
Samek, W., Montavon, G., Vedaldi, A., Hansen, L. K., & Müller, K. R. (2019). Explainable AI: interpreting, explaining, and visualizing deep learning. Springer.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 50sea

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















