Optimal Selection of Reactive Power For Single Tuned Passive Filter Based on Curve Fitting Technique
Keywords:
DC drives, Harmonic distortion, Optimal selection, Curve fitting technique, Passive filter, MATLAB/SimulationAbstract
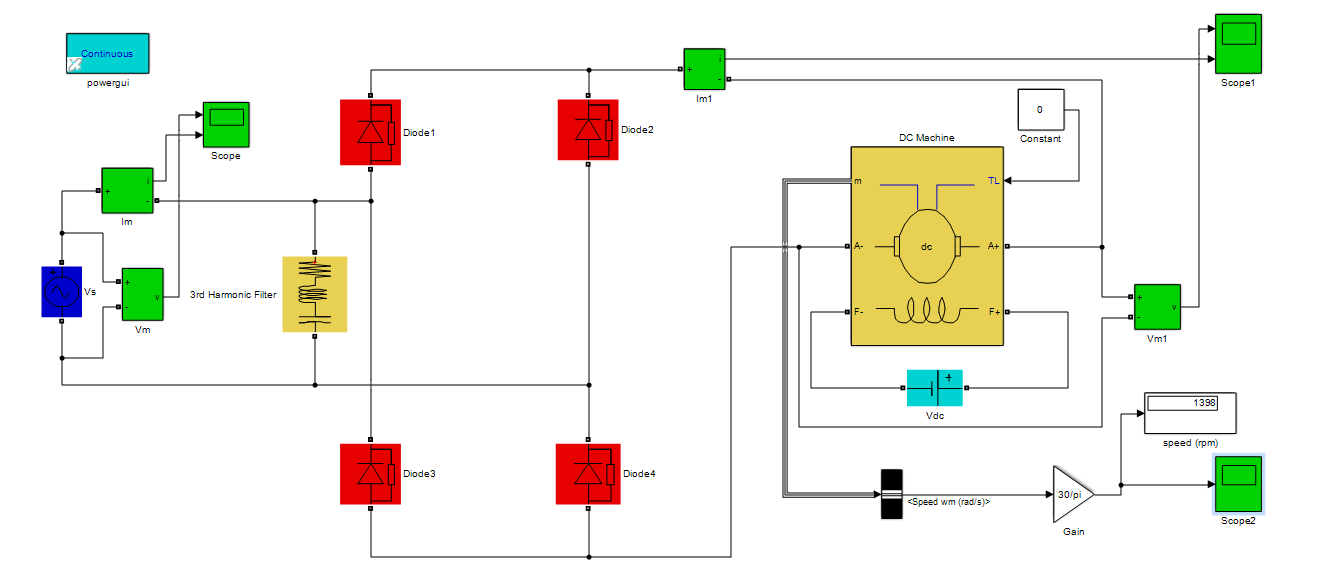
This research presents the Optimal Reactive Power (Qc) selection for a single-tuned passive filter. DC drives are very popular in the industrial zone due to their high performance, flexibility, easy control, and low cost. DC drives operate by giving supply from an AC utility and AC to DC can be converted using the AC-DC converter. But this conversion introduces harmonics in the input supply current that affect the performance of the DC drive and also cause serious problems for the overall power quality of the system. Many researchers are searching for the appropriate solutions to mitigate this cause. A passive filter is one solution to minimize or avoid harmonics from entering the electrical system. The key aspect of the passive filter design has been a difficult task. The parameters of the passive filter largely depends upon selecting the suitable value of reactive power (Qc). In this paper, the Simulink model of an AC-DC converter based on a separately excited dc motor is used as an industrial load, and a curve fitting technique has been used to select the optimal value of reactive power (Qc) for the passive filter. The simulation results and analysis show that optimal selection of reactive power for single tuned passive filter using the proposed technique is very effective by taking international standards limits for harmonic distortion.
References
N. Qasim, “DC Motor Drive with P, PI, and Particle Swarm Optimization Speed Controllers,” Int. J. Comput. Appl., vol. 166, no. 12, pp. 42–45, 2017, doi: 10.5120/ijca2017914032.
M. S. Bajwa, A. P. Memon, J. A. Ansari, and M. T. Bhatti, “An Experimental Investigation Based On Mathematical and Software Modeling Of Total Harmonic Distortion in Personal Computer,” no. June, 2016.
S. Saha, S. Das, and C. Nandi, “Harmonics Analysis of Power Electronics Loads,” Int. J. Comput. Appl., vol. 92, no. 10, pp. 32–36, 2014, doi: 10.5120/16046-5228.
K. Nikum and A. Wagh, “HARDWARE Implementation of Step-Switched SVCs to Correct Power factor and Mitigate Harmonics for Large DC Variable Loads,” J. Inst. Eng. Ser. B, vol. 101, no. 6, pp. 777–789, Dec. 2020, doi: 10.1007/S40031-020-00476-3/TABLES/5.
I. A. Channa, M. A. Koondhar, N. M. Mughal, M. S. Bajwa, S. A. A. S. Bukhari, and M. I. Jamali, “‘Simulation and Analysis of Active Power Filter for Mitigation of Power Quality Problems in a Wind Based Distributed Generation,’” J. Appl. Emerg. Sci., vol. 11, no. 1, p. 11, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.36785/2021111429.
K. K. Srivastava, S. Shakil, and A. V. Pandey, “Harmonics & Its Mitigation Technique by Passive Shunt Filter,” no. 2, pp. 325–332, 2013.
S. M. Khudher, I. bin Aris, M. Othman, and N. Mailah, “Output-Input Hybrid Passive Filter Design for Electric Vehicle Charging Station,” Coll. Eng. Univ. Mosul, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 132–142, Oct. 2021, doi: 10.33899/RENGJ.2021.129599.1084.
B. Park, J. Lee, H. Yoo, and G. Jang, “Harmonic Mitigation Using Passive Harmonic Filters: Case Study in a Steel Mill Power System,” Energies 2021, Vol. 14, Page 2278, vol. 14, no. 8, p. 2278, Apr. 2021, doi: 10.3390/EN14082278.
T. Adrikowski, D. Bula, and M. Pasko, “Selection of method for reactive power compensation and harmonic filtering in industrial plant,” 2017 Prog. Appl. Electr. Eng. PAEE 2017, no. August, 2017, doi: 10.1109/PAEE.2017.8009010.
Z. M. Ali, F. Q. Alenezi, S. S. Kandil, and S. H. E. Abdel Aleem, “Practical considerations for reactive power sharing approaches among multiple-arm passive filters in non-sinusoidal power systems,” Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst., vol. 103, pp. 660–675, Dec. 2018, doi: 10.1016/J.IJEPES.2018.06.044.
& F. V. P. R. H. M. Zubi, R.W. Dunn, “Comparison of different common passive filter topologies for harmonic mitigation,” in 45th International Universities Power Engineering Conference UPEC, 2010, pp. 1–6.
H. Azazi and E. EL-Kholy, “Review of passive and active circuits for power factor correction in single phase, low power AC-DC converters,” Int. Middle East Power Syst. Conf., no. 10, p. 154, 2010, [Online]. Available: http://www.sdaengineering.com/mepcon10/papers/154.pdf.
& A. P. V. S.P. Diwan, H.P. Inamdar, “Simulation Studies of Shunt Passive Harmonic Filters: Six Pulse Rectifier Load-Power Factor Improvement and Harmonic Control,” ACEEE Int. J. Electr. Power Eng., vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 1–6, 2011.
D. C. Bhonsle and R. B. Kelkar, “Harmonic pollution survey and simulation of passive filter using MATLAB,” 2011 Int. Conf. Recent Adv. Electr. Electron. Control Eng. IConRAEeCE’11 - Proc., pp. 230–236, 2011, doi: 10.1109/ICONRAEECE.2011.6129785.
Z. A. Memon, M. A. Uquaili, and M. A. Unar, “Harmonics Mitigation of Industrial Power System Using Passive Filters,” no. May, 2016, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1605.06684.
and M. M. S. Pyakuryal, “Filter design for AC to DC converter,” Int. Ref. J. Eng. Sci., vol. 2, no. 6, pp. 42–49, 2013.
C. L. Anooja and N. Leena, “Passive Filter For Harmonic Mitigation Of Power Diode Rectifier And SCR Rectifier Fed Loads,” Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res., vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 1615–1621, 2013, [Online]. Available: http://www.ijser.org.
and L. A. K. D. Maheswaran, N. Rajasekar, “Design of Passive Filters for Reducing Harmonics Distortion and Correcting power factor in Two Pulse Rectifier System Using Optimization,” J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol., vol. 62, no. 3, pp. 720–728, 2014.
A. Baitha and N. Gupta, “A comparative analysis of passive filters for power quality improvement,” Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Technol. Adv. Power Energy, TAP Energy 2015, pp. 327–332, Aug. 2015, doi: 10.1109/TAPENERGY.2015.7229640.
D. M. Soomro and M. M. Almelian, “Optimal design of a single tuned passive filter to mitigate harmonics in power frequency,” ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci., vol. 10, no. 19, pp. 9009–9014, 2015.
& P. F. R. B.P. de Campos, L.A. de Sousa, “Mitigation of harmonic distortion with passive filters,” in 17th International Conference on Harmonics and Quality of Power (ICHQP), 2016, pp. 646–651.
O. F. Kececioglu, H. Acikgoz, and M. Sekkeli, “Advanced configuration of hybrid passive filter for reactive power and harmonic compensation,” Springerplus, vol. 5, no. 1, 2016, doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-2917-7.
S. H. M. Almutairi, “Application of Single Tuned Passive Filters in Distribution Networks at the Point of Common Coupling,” Int. J. Electr. Comput. Energy. Electron. Commun. Eng., vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 176–182, 2017, [Online]. Available: internal-pdf://122.62.192.58/Application-of-Single-Tuned-Passive-Filters-in.pdf%0Ahttp://waset.org/publications/10006390.
M. I. Fahmi, U. Baafai, A. Hazmi, and T. H. Nasution, “Harmonic reduction by using single-tuned passive filter in plastic processing industry,” IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., vol. 308, no. 1, 2018, DOI: 10.1088/1757-899X/308/1/012035.
H. Mageed, A. S. Nada, S. Abu-Zaid, and R. S. Salah Eldeen, “Effects of Waveforms Distortion for Household Appliances on Power Quality,” Mapan - J. Metrol. Soc. India, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 559–572, 2019, doi: 10.1007/s12647-019-00352-6.
and W. J. R. Y.K. Haur, T.J. Son, L.K. Yun, “Design of Single-Tuned Passive Harmonic Filter to Meet Ieee-519 Standard By Means of Quality-Factor Manipulations,” Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol., vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 1364–1379, 2020.
C. S. Azebaze Mboving, “Investigation on the work efficiency of the lc passive harmonic filter chosen topologies,” Electron., vol. 10, no. 8, 2021, doi: 10.3390/electronics10080896.
M. J. H. Rawa, D. W. P. Thomas, and M. Sumner, “Mathematical Modeling of the Harmonic Distortion Caused by a Group of PCs Using Curve Fitting Technique,” Proc. - UKSim-AMSS 17th Int. Conf. Comput. Model. Simulation, UKSim 2015, pp. 386–390, Sep. 2016, doi: 10.1109/UKSIM.2015.41.
M. S. Bajwa and M. U. Keerio, “Modeling Of Factors Influencing Harmonic Distortion Based on Simulation Model of Personal Computer,” vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 173–180, 2020.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 50SEA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















