Combatting Illegal Logging with AI-powered IoT Devices for Forest Monitoring
Keywords:
Forest Monitoring, AI Against Illegal Logging, Real-time Alerts, Environmental Conservation, IoT for Anti- LoggingAbstract
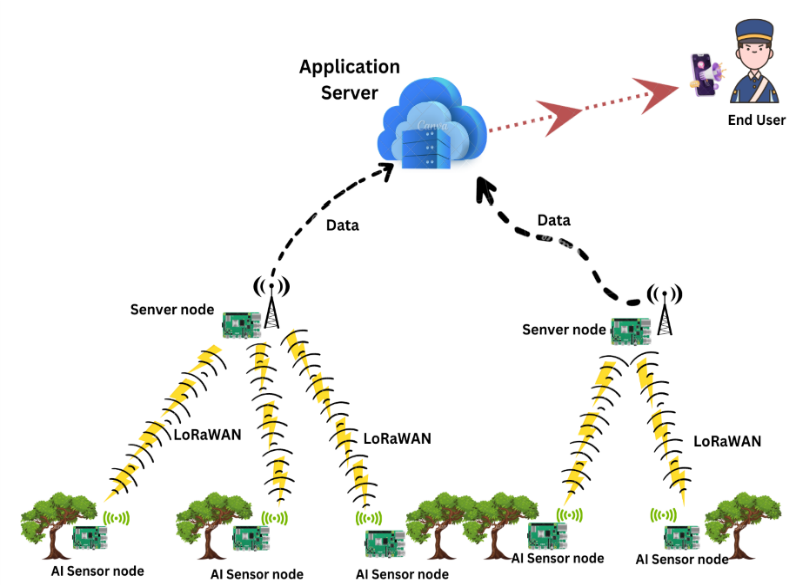
This research presents a comprehensive strategy for tackling illegal logging by leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies. In high-risk forestry areas, sensors-equipped Internet of Things devices are used to continuously monitor and detect the sound of the surroundings. The AI component uses machine learning methods to identify potential unlawful logging activities by accurately detecting and distinguishing sound patterns associated with chainsaw and logging operations such as tree cutting and also detecting natural disasters like wildfires. When such activities are detected by these smart AI-powered IoT devices installed in the forest, real-time notifications are generated after such activity which allows surrounding enforcement agencies, such as the forest department, to intervene promptly. By providing a targeted and prompt solution to the issue of illicit logging, this strategy supports biodiversity preservation and sustainable forest management.
References
C. Anjanappa, S. Parameshwara, M. K. Vishwanath, M. Shrimali, and C. Ashwini, “AI and IoT based Garbage classification for the smart city using ESP32 cam,” Int. J. Health Sci. (Qassim)., vol. 6, no. S3, pp. 4575–4585, May 2022, doi: 10.53730/IJHS.V6NS3.6905.
“ESP32 Wi-Fi & Bluetooth SoC | Espressif Systems.” Accessed: May 06, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.espressif.com/en/products/socs/esp32
S. B. Calo, M. Touna, D. C. Verma, and A. Cullen, “Edge computing architecture for applying AI to IoT,” Proc. - 2017 IEEE Int. Conf. Big Data, Big Data 2017, vol. 2018-January, pp. 3012–3016, Jul. 2017, doi: 10.1109/BIGDATA.2017.8258272.
M. Ali, Y. S. Kwon, C.-H. Lee, J. Kim, and Y. Kim, Eds., “Current Approaches in Applied Artificial Intelligence,” vol. 9101, 2015, doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-19066-2.
M. Merenda, C. Porcaro, and D. Iero, “Edge Machine Learning for AI-Enabled IoT Devices: A Review,” Sensors 2020, Vol. 20, Page 2533, vol. 20, no. 9, p. 2533, Apr. 2020, doi: 10.3390/S20092533.
X. Yang, H. Xing, and X. Su, “AI-based sound source localization system with higher accuracy,” Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst., vol. 141, pp. 1–15, Apr. 2023, doi: 10.1016/J.FUTURE.2022.10.023.
D. Roggen, R. Cobden, A. Pouryazdan, and M. Zeeshan, “Wearable FPGA Platform for Accelerated DSP and AI Applications,” 2022 IEEE Int. Conf. Pervasive Comput. Commun. Work. other Affil. Events, PerCom Work. 2022, pp. 66–69, 2022, doi: 10.1109/PERCOMWORKSHOPS53856.2022.9767398.
I. Ahmad, S. E. Shariffudin, A. F. Ramli, S. M. M. Maharum, Z. Mansor, and K. A. Kadir, “Intelligent Plant Monitoring System Via IoT and Fuzzy System,” 2021 IEEE 7th Int. Conf. Smart Instrumentation, Meas. Appl. ICSIMA 2021, pp. 123–127, Aug. 2021, doi: 10.1109/ICSIMA50015.2021.9526312.
“Edge Impulse - The Leading edge AI platform.” Accessed: May 06, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://edgeimpulse.com/
S. R. Madikeri and H. A. Murthy, “Mel filter bank energy-based slope feature and its application to speaker recognition,” 2011 Natl. Conf. Commun. NCC 2011, 2011, doi: 10.1109/NCC.2011.5734713.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 50sea

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















