The Exploring Political Emotions Sentiment Analysis of Urdu Tweets
Keywords:
Political Emotions, Sentiment Analysis, Exploring, Urdu Tweets, Social Media, Political Discourse, Emotion Detection, Computational Linguistics, Urdu Language ProcessingAbstract
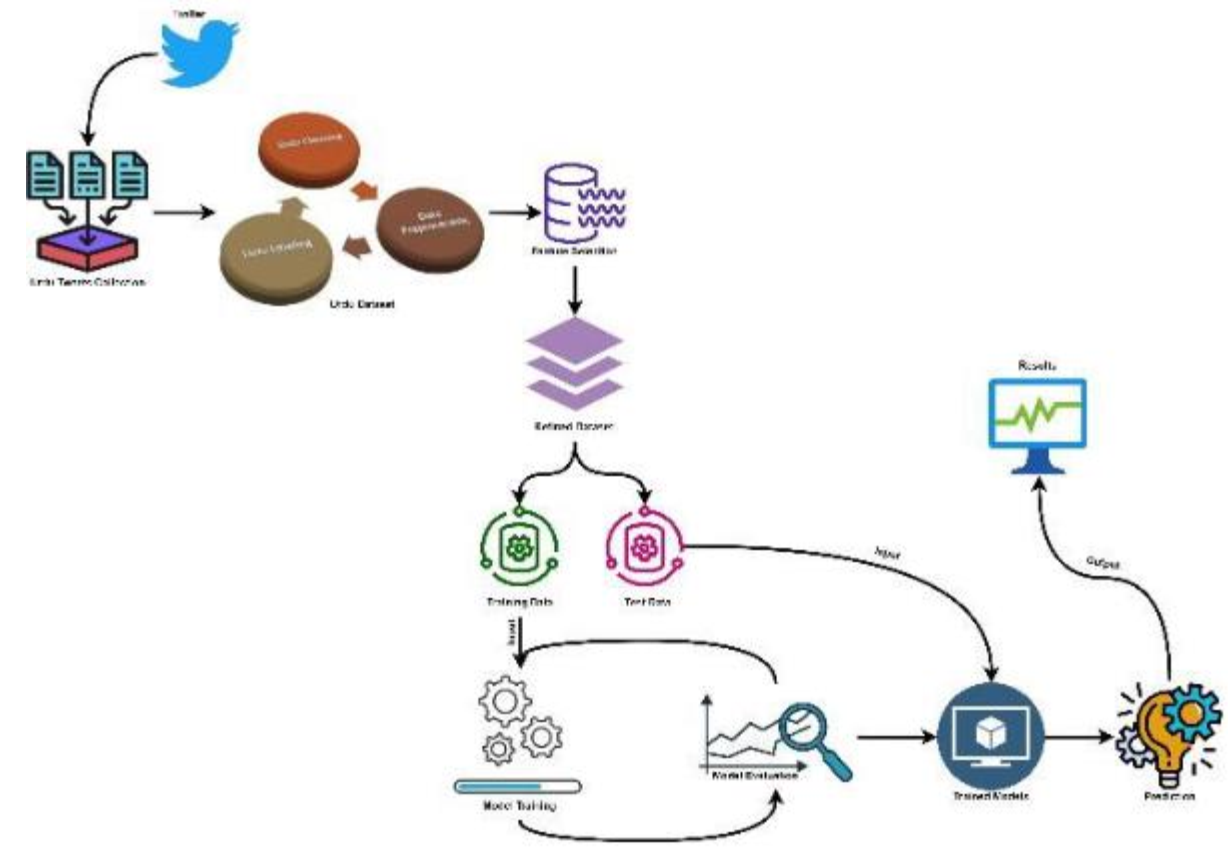
This research is a multi-text categorization based on a collection of Pakistani political texts. The major goal of this research is to use Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning classification models to categorize multi-text for Urdu. Political tweets from 13 different Pakistani famous leaders were collected for this research. These politicians make use of the platform to promote themselves and engage with their supporters. To analyze the model accuracy the desired dataset is divided into six categories which have been composed of their official Twitter account. We also collect top trends from Pakistan and around the world to examine current trends regularly. In the proposed research, the major political corpus data comprises 1300+ tweets in the Urdu language, encompassing political policies, campaigns, opinions, and so on. Sentiment analysis is an essential component of every deep learning approach. For that, we have used the deep learning approach i.e. sentiment analysis of the politician since it provides insight into their moods and views on a certain topic. Furthermore, text corpus pre-processing is conducted utilizing NLP techniques, such as data cleaning, data balancing, and stop word removal. TF-IDF is used as word filtering for feature extraction count vectors. Machine Learning classification algorithms such as SVM, Decision Tree, XGboost, and Random Forest, and for implementation of neural network we have used Word2vector.
References
G. L. Yovellia Londo, D. H. Kartawijaya, H. T. Ivariyani, P. W. P. Yohanes Sigit, A. P. Muhammad Rafi, and D. Ariyandi, “A Study of Text Classification for Indonesian News Article,” Proceeding - 2019 Int. Conf. Artif. Intell. Inf. Technol. ICAIIT 2019, pp. 205–208, Mar. 2019, doi: 10.1109/ICAIIT.2019.8834611.
Y. Zheng, “An exploration on text classification with classical machine learning algorithm,” Proc. - 2019 Int. Conf. Mach. Learn. Big Data Bus. Intell. MLBDBI 2019, pp. 81–85, Nov. 2019, doi: 10.1109/MLBDBI48998.2019.00023.
S. K. Dwivedi and C. Arya, “Automatic text classification in information retrieval: A Survey,” ACM Int. Conf. Proceeding Ser., vol. 04-05-March-2016, Mar. 2016, doi: 10.1145/2905055.2905191.
V. Korde, “Text Classification and Classifiers:A Survey,” Int. J. Artif. Intell. Appl., vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 85–99, Mar. 2012, doi: 10.5121/IJAIA.2012.3208.
“Analyzing political sentiment on twitter”, [Online]. Available: https://cdn.aaai.org/ocs/5702/5702-24478-1-PB.pdf
A. Tumasjan, T. O. Sprenger, P. G. Sandner, and I. M. Welpe, “Predicting Elections with Twitter: What 140 Characters Reveal about Political Sentiment,” Proc. Int. AAAI Conf. Web Soc. Media, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 178–185, May 2010, doi: 10.1609/ICWSM.V4I1.14009.
M. Choy, M. L. F. Cheong, M. N. Laik, and K. P. Shung, “A sentiment analysis of Singapore Presidential Election 2011 using Twitter data with census correction,” Aug. 2011, Accessed: Jun. 06, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1108.5520v1
S. N. Hao Wang, Dogan Can, Abe Kazemzadeh, François Bar, “A System for Real-time Twitter Sentiment Analysis of 2012 U.S. Presidential Election Cycle”, [Online]. Available: https://aclanthology.org/P12-3020/
T. Elghazaly, A. Mahmoud, and H. A. Hefny, “Political sentiment analysis using twitter data,” ACM Int. Conf. Proceeding Ser., vol. 22-23-March-2016, Mar. 2016, doi: 10.1145/2896387.2896396.
P. Sharma and T. S. Moh, “Prediction of Indian election using sentiment analysis on Hindi Twitter,” Proc. - 2016 IEEE Int. Conf. Big Data, Big Data 2016, pp. 1966–1971, 2016, doi: 10.1109/BIGDATA.2016.7840818.
A. Daud, W. Khan, and D. Che, “Urdu language processing: a survey,” Artif. Intell. Rev., vol. 47, no. 3, pp. 279–311, Mar. 2017, doi: 10.1007/S10462-016-9482-X/METRICS.
D. P. Rose and D. M. Greeley, “Education in fragile states: Capturing lessons and identifying good practice”, [Online]. Available: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=d0d3c719eced2e039700dc583919188d60773d34
S. W. Kazmi, “Role of education in globalization: A case for pakistan”, [Online]. Available: http://www.developyst.jellyfish.com.pk/files/article/39/Role of Education in Globalization.pdf
R. Lu and Q. Yang, “Trend Analysis of News Topics on Twitter,” Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput., pp. 327–332, 2012, doi: 10.7763/IJMLC.2012.V2.139.
J. R. Saffran, E. L. Newport, and R. N. Aslin, “Word Segmentation: The Role of Distributional Cues,” J. Mem. Lang., vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 606–621, Aug. 1996, doi: 10.1006/JMLA.1996.0032.
S. Zhang, C. Zhang, and Q. Yang, “Data preparation for data mining,” Appl. Artif. Intell., vol. 17, no. 5–6, pp. 375–381, May 2003, doi: 10.1080/713827180.
G. D. Salton, R. J. Ross, and J. D. Kelleher, “Idiom Token Classification using Sentential Distributed Semantics,” 54th Annu. Meet. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. ACL 2016 - Long Pap., vol. 1, pp. 194–204, 2016, doi: 10.18653/V1/P16-1019.
Y. Al Amrani, M. Lazaar, and K. E. El Kadirp, “Random Forest and Support Vector Machine based Hybrid Approach to Sentiment Analysis,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 127, pp. 511–520, Jan. 2018, doi: 10.1016/J.PROCS.2018.01.150.
“Kleinbaum, D.G., Dietz, K., Gail, M., et al. (2002) Logistic Regression. Springer-Verlag, New York, 43-53. - References - Scientific Research Publishing.” Accessed: Jun. 06, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=2959305
S. R. Safavian and D. Landgrebe, “A Survey of Decision Tree Classifier Methodology,” IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 660–674, 1991, doi: 10.1109/21.97458.
E. Podasca, “Predicting the Movement Direction of OMXS30 Stock Index Using XGBoost and Sentiment Analysis”, Accessed: Jun. 06, 2024. [Online]. Available: www.bth.se
J. Ali, R. Khan, N. Ahmad, and I. Maqsood, “Random Forests and Decision Trees,” 2012, Accessed: Jun. 06, 2024. [Online]. Available: www.IJCSI.org
W. Zhu, W. Zhang, G. Z. Li, C. He, and L. Zhang, “A study of damp-heat syndrome classification using Word2vec and TF-IDF,” Proc. - 2016 IEEE Int. Conf. Bioinforma. Biomed. BIBM 2016, pp. 1415–1420, Jan. 2017, doi: 10.1109/BIBM.2016.7822730.
O. B. Deho, W. A. Agangiba, F. L. Aryeh, and J. A. Ansah, “Sentiment analysis with word embedding,” IEEE Int. Conf. Adapt. Sci. Technol. ICAST, vol. 2018-August, Oct. 2018, doi: 10.1109/ICASTECH.2018.8506717.
C. Esteves, C. Allen-Blanchette, X. Zhou, and K. Daniilidis, “Polar Transformer Networks,” 6th Int. Conf. Learn. Represent. ICLR 2018 - Conf. Track Proc., Sep. 2017, Accessed: Jun. 06, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.01889v3
K. W. CHURCH, “Word2vec,” Nat. Lang. Eng., [Online]. Available: https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/natural-language-engineering/article/word2vec/B84AE4446BD47F48847B4904F0B36E0B
G. Grefenstette, “Tokenization,” pp. 117–133, 1999, doi: 10.1007/978-94-015-9273-4_9.
X. Rong, “word2vec Parameter Learning Explained,” Nov. 2014, Accessed: Jun. 06, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1411.2738v4
Y. Goldberg et al., “word2vec Explained: deriving Mikolov et al.’s negative-sampling word-embedding method,” Feb. 2014, Accessed: Jun. 06, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1402.3722v1
F. Morin and Y. Bengio, “Hierarchical Probabilistic Neural Network Language Model.” PMLR, pp. 246–252, Jan. 06, 2005. Accessed: Jun. 06, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://proceedings.mlr.press/r5/morin05a.html
A. Creswell, T. White, V. Dumoulin, K. Arulkumaran, B. Sengupta, and A. A. Bharath, “Generative Adversarial Networks: An Overview,” IEEE Signal Process. Mag., vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 53–65, Jan. 2018, doi: 10.1109/MSP.2017.2765202.
C. Steinruecken, “Compressing sets and multisets of sequences,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 61, no. 3, pp. 1485–1490, Mar. 2015, doi: 10.1109/TIT.2015.2392093.
P. F. Muhammad, R. Kusumaningrum, and A. Wibowo, “Sentiment Analysis Using Word2vec And Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) For Indonesian Hotel Reviews,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 179, pp. 728–735, Jan. 2021, doi: 10.1016/J.PROCS.2021.01.061.
R. Huang et al., “Well performance prediction based on Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural network,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 208, p. 109686, Jan. 2022, doi: 10.1016/J.PETROL.2021.109686.
M. Hossin and Sulaiman, “A REVIEW ON EVALUATION METRICS FOR DATA CLASSIFICATION EVALUATIONS,” Int. J. Data Min. Knowl. Manag. Process, vol. 5, no. 2, 2015, doi: 10.5121/ijdkp.2015.5201.
M. Kane, “The precision of measurements,” Appl. Meas. Educ., vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 355–379, 1996.
F. Buckland, M., and Gey, “‘The relationship between recall and precision.,’” J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci., vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 12–19, 1994.
O. M. Sulea, M. Zampieri, S. Malmasi, M. Vela, L. P. Dinu, and J. Van Genabith, “Exploring the Use of Text Classification in the Legal Domain,” CEUR Workshop Proc., vol. 2143, Oct. 2017, Accessed: Jun. 06, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.09306v1
F. Freese, “Testing Accuracy,” For. Sci., vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 139–145, Jun. 1960, doi: 10.1093/FORESTSCIENCE/6.2.139.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 50SEA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















