Comprehensive Assessment of Air Quality Dynamics Around Yosemite National Park Using Remote Sensing, GIS, and Computational Analysis During Wildfire Events
Keywords:
Air pollution, Wildfire, AODV, Yosemite National ParkAbstract
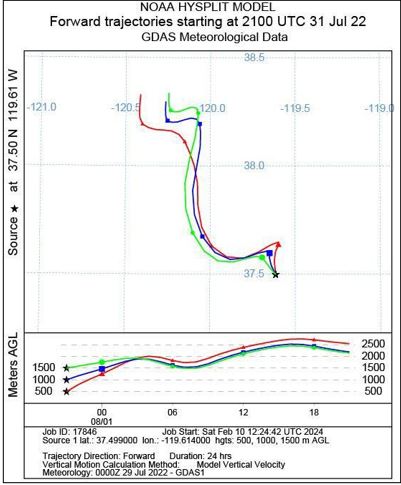
In recent years, Mariposa County has experienced several significant wildfires, including the catastrophic Rim Fire of 2013. On July 22, 2022, Yosemite National Park faced one of its most devastating wildfires, profoundly affecting Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) and overall air quality. This study employs an integrated approach using remote sensing, GIS, and advanced computational tools to investigate the impact of these wildfires on air quality, focusing specifically on aerosol pollution dynamics and key atmospheric pollutants. The research leverages satellite data from TROPOMI, MODIS AQUA, and Suomi NPP/VIIRS, along with meteorological inputs from GDAS. Data processing and analysis were performed using Python, MATLAB, and R, with spatial mapping and visualization achieved through ArcMap and Google Earth Engine. The study utilized the MODIS MAIAC algorithm to conduct a detailed examination of AOD fluctuations in the Yosemite region, spanning from July 21 to August 1, 2022. Our comprehensive analysis reveals significant temporal and spatial variations in aerosol pollution during the wildfire. Initial findings indicate a marked increase in AOD with the onset of the wildfire, reflecting severe impacts on atmospheric composition. Pre-fire AOD levels were relatively low at 0.12, but surged to 0.20 at the wildfire's peak, demonstrating a substantial rise in atmospheric aerosol loading. The average AOD throughout the study period was recorded at 0.16, highlighting the wildfire's prolonged effect on air quality. Furthermore, the study identifies elevated concentrations of key pollutants, including NO₂, SO₂, CO, HCHO, and O₃, during the wildfire event. The integration of data from various satellite sources and the application of machine learning models provided a more nuanced understanding of pollution patterns. The HYSPLIT model was also employed to track the distribution of air masses and contaminants, revealing significant northwestward transport. This research advances our understanding of the intricate relationships between wildfires, aerosol pollution, and air quality in Yosemite National Park. The findings offer critical insights for public health preparedness, the development of resilience strategies against wildfires, and the formulation of effective mitigation measures in fire-prone regions like Yosemite.
References
A. Ahmad Jabatan Sains et al., “The Use of Remote Sensing and GIS to Estimate Air Quality Index (AQI) Over Peninsular Malaysia”.
P. Roy, “FOREST FIRE AND DEGRADATION ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING AND GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM,” 2005, Accessed: Jan. 03, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/FOREST-FIRE-AND-DEGRADATION-ASSESSMENT-USING-REMOTE-Roy/a3ce1dff2fe6e1a5eb81eb5473b5e1114b9cd655
H. Adab, K. D. Kanniah, and K. Solaimani, “Modeling forest fire risk in the northeast of Iran using remote sensing and GIS techniques,” Nat. Hazards, vol. 65, no. 3, pp. 1723–1743, Jan. 2013, doi: 10.1007/S11069-012-0450-8/METRICS.
R. H. Narashid and W. M. N. Wan Mohd, “Air quality monitoring using remote sensing and GIS technologies,” CSSR 2010 - 2010 Int. Conf. Sci. Soc. Res., pp. 1186–1191, 2010, doi: 10.1109/CSSR.2010.5773713.
Y. Korchenko, Oleksandr; Pohrebennyk, Volodymyr; Kreta, Dmytro; Klymenko, Viktoriia; Anpilova, “GIS AND REMOTE SENSING AS IMPORTANT TOOLS FOR ASSESSMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION”, [Online]. Available: https://www.proquest.com/openview/78c64aca18e8abcd693d18a050a766a8/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=1536338#:~:text=The creation of an environmental,provision for decision making on
Y. Liu, R. A. Kahn, A. Chaloulakou, and P. Koutrakis, “Analysis of the impact of the forest fires in August 2007 on air quality of Athens using multi-sensor aerosol remote sensing data, meteorology and surface observations,” Atmos. Environ., vol. 43, no. 21, pp. 3310–3318, Jul. 2009, doi: 10.1016/J.ATMOSENV.2009.04.010.
D. M. J. S. Bowman, C. A. Kolden, J. T. Abatzoglou, F. H. Johnston, G. R. van der Werf, and M. Flannigan, “Vegetation fires in the Anthropocene,” Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020 110, vol. 1, no. 10, pp. 500–515, Aug. 2020, doi: 10.1038/s43017-020-0085-3.
E. Chuvieco et al., “Development of a framework for fire risk assessment using remote sensing and geographic information system technologies,” Ecol. Modell., vol. 221, no. 1, pp. 46–58, Jan. 2010, doi: 10.1016/J.ECOLMODEL.2008.11.017.
H. Adab, K. D. Kanniah, and K. Solaimani, “Modeling forest fire risk in the northeast of Iran using remote sensing and GIS techniques,” Nat. Hazards, vol. 65, no. 3, pp. 1723–1743, Jan. 2013, doi: 10.1007/S11069-012-0450-8/METRICS.
D. A. Jaffe et al., “Scientific assessment of background ozone over the U.S.: Implications for air quality management,” Elem. (Washington, D.C.), vol. 6, no. 1, 2018, doi: 10.1525/ELEMENTA.309.
S. Tariq, ul H. Zia, and M. Ali, “Satellite and ground-based remote sensing of aerosols during intense haze event of October 2013 over lahore, Pakistan,” Asia-Pacific J. Atmos. Sci., vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 25–33, Feb. 2016, doi: 10.1007/S13143-015-0084-3/METRICS.
“The applications of GISystems to wilderness search and rescue, an overview within a GIScience context and examples from Yosemite National Park.” Accessed: Aug. 03, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/0hq8z72c
L. Mei et al., “Integration of remote sensing data and surface observations to estimate the impact of the Russian wildfires over Europe and Asia during August 2010,” Biogeosciences, vol. 8, no. 12, pp. 3771–3791, 2011, doi: 10.5194/BG-8-3771-2011.
J. C. A. Baker and D. V. Spracklen, “Climate Benefits of Intact Amazon Forests and the Biophysical Consequences of Disturbance,” Front. For. Glob. Chang., vol. 2, p. 443097, Aug. 2019, doi: 10.3389/FFGC.2019.00047/BIBTEX.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 50SEA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















