Impact of Internal Forces on Employee Behaviors: Role of Situational Factors
Keywords:
Motivation, Ability, Role Perception, Situational Factors, Organizational Citizenship Behaviour, Counter Productive Work Behaviours, Turnover IntentionAbstract
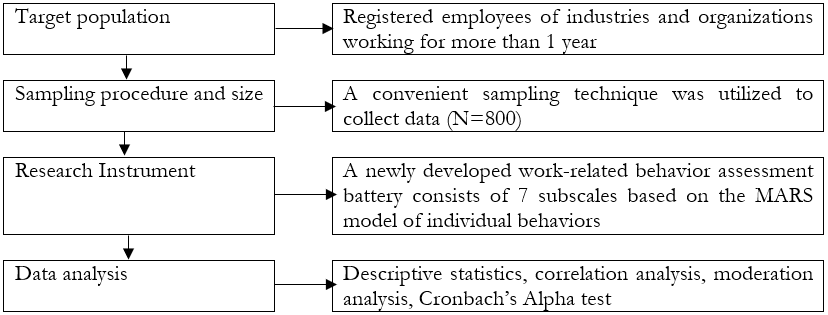
The current research investigated the effects of motivation, ability, and role perception (internal forces), also known as drivers on employee behaviors as well as to find out the moderating role of situational factors between drivers and employee behaviors. Data were collected from 800 in-service employees across various organizations and industries in Gujranwala using a convenience sampling technique. Work-related behaviors assessment battery was used to collect data from individuals which consists of 7 scales. Each scale consists of 10 items and the response rate varies from 1= strongly disagree to 5= strongly agree. Analysis indicates that motivation, ability, and role perception have a significant effect on employee behaviors. Moderation analysis results indicate that situational factors significantly moderate the relationship between drivers and behaviors. The current research sheds light on the significance of behaviors depending upon the four driving forces that need to be changed, or modified in regards to an increase in organizational performance.
References
S. L. McShane and M. A. Y. Von Glinow, “Organizational behavior : emerging knowledge, global reality,” p. 44, 2024.
X. Zhang and K. M. Bartol, “Linking empowering leadership and employee creativity: the influence of psychological empowerment, intrinsic motivation, and creative process engagement,” Acad. Manag. J., vol. 53, no. 1, pp. 107–128, Feb. 2010, doi: 10.5465/AMJ.2010.48037118.
C. P. Cerasoli, J. M. Nicklin, and M. T. Ford, “Intrinsic motivation and extrinsic incentives jointly predict performance: a 40-year meta-analysis,” Psychol. Bull., vol. 140, no. 4, pp. 980–1008, 2014, doi: 10.1037/A0035661.
“Entrepreneurial motivation and business Performance of SMEs in the SUCI Clothing Center, Bandung, Indonesia | Request PDF.” Accessed: Aug. 28, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311670444_Entrepreneurial_motivation_and_business_Performance_of_SMEs_in_the_SUCI_Clothing_Center_Bandung_Indonesia
“Organizational Behavior, 12th Edition: Stephen P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge: 9780132431569: Amazon.com: Books.” Accessed: Aug. 28, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.amazon.com/Organizational-Behavior-12th-Stephen-Robbins/dp/0132431564
S. Robbins, T. Judge, R. Saraswati, and F. Sirait, “Perilaku Organisasi (Organizational Behavior),” 2008.
“Kinerja dan Pengembangan Kompetensi SDM Teori Dimensi Pengukuran dan Implementasi dalam Organisasi - 2009.” Accessed: Aug. 28, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://elibrary.bsi.ac.id/readbook/202941/kinerja-dan-pengembangan-kompetensi-sdm-teori-dimensi-pengukuran-dan-implementasi-dalam-organisasi
S. K. Parker, “‘That is my job’: How employees’ role orientation affects their job performance,” Hum. Relations, vol. 60, no. 3, pp. 403–434, Mar. 2007, doi: 10.1177/0018726707076684.
P. J. Burke and J. E. Stets, “Identity Theory,” Identity Theory, pp. 1–272, May 2009, doi: 10.1093/ACPROF:OSO/9780195388275.001.0001.
S. Abdelnour, H. Hasselbladh, and J. Kallinikos, “Agency and Institutions in Organization Studies,” https://doi.org/10.1177/0170840617708007, vol. 38, no. 12, pp. 1775–1792, Jun. 2017, doi: 10.1177/0170840617708007.
K. Lee and N. J. Allen, “Organizational citizenship behavior and workplace deviance: the role of affect and cognitions.,” J. Appl. Psychol., vol. 87, no. 1, pp. 131–142, 2002, doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.87.1.131.
L. Alfonso, F. Zenasni, S. Hodzic, and P. Ripoll, “Understanding the mediating role of quality of work life on the relationship between emotional intelligence and organizational citizenship behaviors,” Psychol. Rep., vol. 118, no. 1, pp. 107–127, Feb. 2016, doi: 10.1177/0033294115625262.
S. Dastgir, A. Abror, D. Patrisia, ; Syahrizal Syahrizal, and R. Sarianti, “Self-Efficacy, Employee Engagement, Remuneration and Employee Loyalty in Higher Education: The Role of Satisfaction and Ocb,” Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol., vol. 29, no. 03, pp. 5456–5470, 2020, Accessed: Aug. 28, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/340081855
R. P. Steel and J. W. Lounsbury, “Turnover process models: Review and synthesis of a conceptual literature,” Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev., vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 271–282, Dec. 2009, doi: 10.1016/J.HRMR.2009.04.002.
B. Gerhart and M. Fang, “Pay for (individual) performance: Issues, claims, evidence and the role of sorting effects,” Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev., vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 41–52, 2014, doi: 10.1016/J.HRMR.2013.08.010.
X. Liu, W. Lu, S. Liu, and C. Qin, “Hatred out of love or love can be all-inclusive? Moderating effects of employee status and organizational affective commitment on the relationship between turnover intention and CWB,” Front. Psychol., vol. 13, p. 993169, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.3389/FPSYG.2022.993169/BIBTEX.
M. Mert, “The Mediator Role of Burnout in The Effect of Personality on Counterproductive Work Behaviors / Kişiliğin Üretkenlik Karşıtı İş Davranışına Olan Etkisinde Tükenmişliğin Aracı Rolü,” Uluslararası Ekon. İşletme ve Polit. Derg., vol. Cilt: 7 Sayı: 1, no. Cilt: 7 Sayı: 1, p. 1, Apr. 2023, doi: 10.29216/UEIP.1250774.
J. M. Kraak, Y. Griep, R. Lunardo, and Y. Altman, “The effects of host country language proficiency on the relationship between psychological contract breach, violation, and work behaviors: A moderated mediation model,” Eur. Manag. J., vol. 42, no. 4, pp. 611–622, Aug. 2024, doi: 10.1016/J.EMJ.2023.04.001.
D. Lestari and M. Margaretha, “Work life balance, job engagement and turnover intention: Experience from Y generation employees,” Manag. Sci. Lett., pp. 165–170, 2021, doi: 10.5267/J.MSL.2020.8.019.
“Organisational behaviour during the pandemic - Google Search.” Accessed: Aug. 28, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.google.com/search?q=Organisational+behaviour+during+the+pandemic&oq=Organisational+behaviour+during+the+pandemic&gs_lcrp=EgZjaHJvbWUyBggAEEUYOTIHCAEQIRigATIHCAIQIRigATIHCAMQIRigAdIBBzg3NGowajeoAgCwAgA&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8
E. Manik and I. Sidharta, “The Impact of Motivation, Ability, Role Perception on Employee Performance and Situational Factor as Moderating Variable of Public Agency in Bandung, Indonesia,” Int. J. Manag. Sci. Bus. Adm., vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 65–73, 2017, doi: 10.18775/IJMSBA.1849-5664-5419.2014.34.1008.
B. Sohana Wadud Ahmed, T. Khan, S. Wadud Ahmad α, and T. Khan σ, “Does Motivation Lead to Organizational Citizenship Behavior?– A Theoritical Review,” Type Double Blind Peer Rev. Int. Res. J. Publ. Glob. Journals Inc, vol. 16, 2016.
K. R. Mehta and K. R. Mehta, “Examining the relationships between motivational traits and Examining the relationships between motivational traits and counterproductive work behaviors counterproductive work behaviors EXAMINING THE RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN MOTIVATIONAL TRAITS AND COUNTERPRODUCTIVE WORK BEHAVIORS,” 2004, Accessed: Aug. 28, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://repository.lsu.edu/gradschool_theses
A. Khan, I. Khan, and Z. Zakir, “Relationship between Employees Motivation and Turnover Intention: Empirical Study of Traffic Police of District Charsadda,” Sarhad J. Manag. Sci., vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 113–127, Dec. 2016, doi: 10.31529/SJMS.2016.2.2.2.
S. Sumarsi and A. Rizal, “The Effect of Competence and Quality of Work Life on Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) with Organizational Commitment Mediation,” Jan. 05, 2022. Accessed: Aug. 28, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=4001395
H. Hamsani, E. T. Sule, H. Hilmiana, and U. Kaltum, “Islamic Perspective on Work Ethic and Competence to Increasing Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) to Sharia Bank Employees in The Bangka Belitung Islands Province,” 2018.
B. Wörtler, N. W. Van Yperen, and D. P. H. Barelds, “Do individual differences in need strength moderate the relations between basic psychological need satisfaction and organizational citizenship behavior?,” Motiv. Emot., vol. 44, no. 2, pp. 315–328, Apr. 2020, doi: 10.1007/S11031-019-09775-9/TABLES/4.
hardin h, A. M. Azizu, and W. O. D. P. Sari, “The Influence of Competence, Organizational Culture, Spiritual Leadership on Organizational Behavior and Its Impact on Lecturer Performance at Higher Education in Baubau City,” Int. J. Manag. Prog., vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 50–72, Feb. 2020, doi: 10.35326/IJMP.V1I2.784.
P. Chand and P. Chand, “Emotional Competencies towards Counterproductive Work Behaviour in Banking Sector,” 2014.
P. P. Choi, W. M. Lee, S. S. Wong, and M. H. Tiu, “Competencies of Nurse Managers as Predictors of Staff Nurses’ Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention,” Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, vol. 19, no. 18, Sep. 2022, doi: 10.3390/IJERPH191811461.
Y. O. Choong, L. P. Ng, S. Ai Na, and C. E. Tan, “The role of teachers’ self-efficacy between trust and organisational citizenship behaviour among secondary school teachers,” Pers. Rev., vol. 49, no. 3, pp. 864–886, Mar. 2020, doi: 10.1108/PR-10-2018-0434.
A. R. Terzi and R. Derin, “Primary School Teachersâ Views on the Relation between Organizational Commitment and Organizational Citizenship Behavior,” Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci., vol. 5, no. 10, 2015, Accessed: Aug. 28, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.academia.edu/21331610/Primary_School_Teachers_Views_on_the_Relation_between_Organizational_Commitment_and_Organizational_Citizenship_Behavior
E. W. MORRISON, “ROLE DEFINITIONS AND ORGANIZATIONAL CITIZENSHIP BEHAVIOR: THE IMPORTANCE OF THE EMPLOYEE’S PERSPECTIVE.,” Acad. Manag. J., vol. 37, no. 6, pp. 1543–1567, Dec. 1994, doi: 10.2307/256798.
A. Deslatte and W. L. Swann, “Elucidating the Linkages Between Entrepreneurial Orientation and Local Government Sustainability Performance,” https://doi.org/10.1177/0275074019869376, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 92–109, Aug. 2019, doi: 10.1177/0275074019869376.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 50SEA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















