Enhancing Management Strategies: Machine Learning and Creative Performance Insights in Employee Attrition Analysis and Prediction
Keywords:
Attrition, Prediction, Machine Learning, SMOTEAbstract
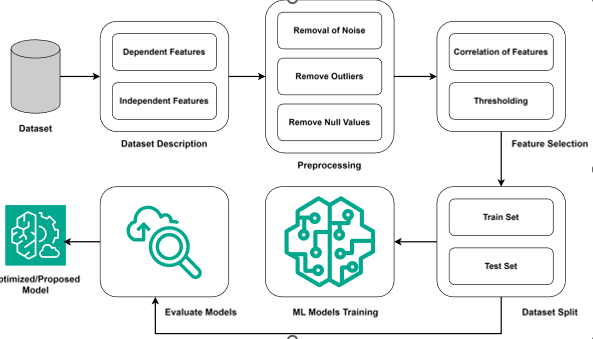
Employee attrition and excessive turnover are major difficulties in today's competitive employment market, affecting many industries. To overcome these difficulties, firms are increasingly relying on artificial intelligence (AI) to forecast staff loss and devise effective retention strategies. This study investigates famous machine learning (ML) models to forecast employee turnover and deliver data-driven solutions. The first section of the study compares various ML models on an imbalanced dataset. The second section introduces the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) for data oversampling and applies ML models to the enlarged dataset. ML can predict employee turnover by examining historical data, employee behavior, and external factors. This early detection enables organizations to respond proactively with targeted retention strategies. The study concludes that the Random Forest model is the best model when combined with SMOTE, achieving performance scores of 0.96 out of 1.
References
S. Rughoobur-Seetah, “The Unprecedented Lockdown: The consequences of job loss,” Zagreb Int. Rev. Econ. Bus., vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 1–23, 2021, doi: 10.2478/zireb-2021-0008.
A. Serenko, “The Great Resignation: the great knowledge exodus or the onset of the Great Knowledge Revolution?,” J. Knowl. Manag., vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 1042–1055, Mar. 2023, doi: 10.1108/JKM-12-2021-0920/FULL/XML.
“19 Employee Retention Statistics That Will Surprise you (2024 ).” Accessed: Aug. 27, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.apollotechnical.com/employee-retention-statistics/
Peng and Baoyi, “Statistical analysis of employee retention,” SPIE, vol. 12163, p. 1216303, Apr. 2022, doi: 10.1117/12.2628107.
“JOLTS Home : U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.” Accessed: Aug. 27, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.bls.gov/jlt/
“U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics : U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.” Accessed: Aug. 27, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.bls.gov/
“SHRM Survey: Average cost per hire is $4,129.” Accessed: Aug. 27, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.businessmanagementdaily.com/46997/shrm-survey-average-cost-per-hire-is-4129/
N. Thomas Rincy and R. Gupta, “A Survey on Machine Learning Approaches and Its Techniques:,” 2020 IEEE Int. Students’ Conf. Electr. Electron. Comput. Sci. SCEECS 2020, Feb. 2020, doi: 10.1109/SCEECS48394.2020.190.
M. E. Korkmaz, M. K. Gupta, E. Çelik, N. S. Ross, and M. Günay, “Tool wear and its mechanism in turning aluminum alloys with image processing and machine learning methods,” Tribol. Int., vol. 191, p. 109207, Mar. 2024, doi: 10.1016/J.TRIBOINT.2023.109207.
M. P. Ngoc, T. N. Duy, H. H. Duc, and K. T. Anh, “A Proposed CNN Model for Audio Recognition on Embedded Device,” Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol., vol. 18, no. 08, pp. 116–126, Apr. 2024, doi: 10.3991/IJIM.V18I08.45917.
Y. Rashid and J. I. Bhat, “Topological to deep learning era for identifying influencers in online social networks :a systematic review,” Multimed. Tools Appl., vol. 83, no. 5, pp. 14671–14714, Feb. 2024, doi: 10.1007/S11042-023-16002-8/METRICS.
Nisha Gurung, MD Rokibul Hasan, Md Sumon Gazi, and Md Zahidul Islam, “Algorithmic Trading Strategies: Leveraging Machine Learning Models for Enhanced Performance in the US Stock Market,” J. Bus. Manag. Stud., vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 132–143, Apr. 2024, doi: 10.32996/JBMS.2024.6.2.13.
T. S. De, P. Singh, and A. Patel, “A Machine learning and Empirical Bayesian Approach for Predictive Buying in B2B E-commerce,” ACM Int. Conf. Proceeding Ser., pp. 17–24, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.1145/3647750.3647754.
I. Attri, L. K. Awasthi, and T. P. Sharma, “Machine learning in agriculture: a review of crop management applications,” Multimed. Tools Appl., vol. 83, no. 5, pp. 12875–12915, Feb. 2024, doi: 10.1007/S11042-023-16105-2/METRICS.
F. Fallucchi, M. Coladangelo, R. Giuliano, and E. W. De Luca, “Predicting Employee Attrition Using Machine Learning Techniques,” Comput. 2020, Vol. 9, Page 86, vol. 9, no. 4, p. 86, Nov. 2020, doi: 10.3390/COMPUTERS9040086.
“Why an employee leaves: Predicting using data mining techniques - Google Search.” Accessed: Aug. 27, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.google.com/search?q=Why+an+employee+leaves%3A+Predicting+using+data+mining+techniques&oq=Why+an+employee+leaves%3A+Predicting+using+data+mining+techniques&gs_lcrp=EgZjaHJvbWUyBggAEEUYOdIBBzc1NmowajeoAgCwAgA&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8
“(PDF) Employee attrition prediction using neural network cross validation method.” Accessed: Aug. 27, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341878934_Employee_attrition_prediction_using_neural_network_cross_validation_method
“(PDF) Employee Attrition Prediction.” Accessed: Aug. 27, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326029536_Employee_Attrition_Prediction
A. Nurhindarto, E. W. Andriansyah, F. Alzami, P. Purwanto, M. A. Soeleman, and D. P. Prabowo, “Employee Attrition and Performance Prediction using Univariate ROC feature selection and Random Forest,” Kinet. Game Technol. Inf. Syst. Comput. Network, Comput. Electron. Control, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 345–350, Nov. 2021, doi: 10.22219/KINETIK.V6I4.1345.
F. Ozdemir, M. Coskun, C. Gezer, and V. Cagri Gungor, “Assessing Employee Attrition Using Classifications Algorithms,” ACM Int. Conf. Proceeding Ser., pp. 118–122, May 2020, doi: 10.1145/3404663.3404681.
P. R. Srivastava and P. Eachempati, “Intelligent Employee Retention System for Attrition Rate Analysis and Churn Prediction: An Ensemble Machine Learning and Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Approach,” https://services.igi-global.com/resolvedoi/resolve.aspx?doi=10.4018/JGIM.20211101.oa23, vol. 29, no. 6, pp. 1–29, Jan. 1AD, doi: 10.4018/JGIM.20211101.OA23.
R. Maharjan, “Employee Churn Prediction using Logistic Regression and Support Vector Machine,” Master’s Proj., Dec. 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.31979/etd.3t5h-excq.
K. Sekaran and S. Shanmugam, “Interpreting the Factors of Employee Attrition using Explainable AI,” 2022 Int. Conf. Decis. Aid Sci. Appl. DASA 2022, pp. 932–936, 2022, doi: 10.1109/DASA54658.2022.9765067.
F. K. Alsheref, I. E. Fattoh, and W. Mead, “Automated Prediction of Employee Attrition Using Ensemble Model Based on Machine Learning Algorithms,” Comput. Intell. Neurosci., vol. 2022, no. 1, p. 7728668, Jan. 2022, doi: 10.1155/2022/7728668.
R. Joseph, S. Udupa, S. Jangale, K. Kotkar, and P. Pawar, “Employee attrition using machine learning and depression analysis,” Proc. - 5th Int. Conf. Intell. Comput. Control Syst. ICICCS 2021, pp. 1000–1005, May 2021, doi: 10.1109/ICICCS51141.2021.9432259.
A. Raza, K. Munir, M. Almutairi, F. Younas, and M. M. S. Fareed, “Predicting Employee Attrition Using Machine Learning Approaches,” Appl. Sci. 2022, Vol. 12, Page 6424, vol. 12, no. 13, p. 6424, Jun. 2022, doi: 10.3390/APP12136424.
P. Kumar, S. B. Gaikwad, S. T. Ramya, T. Tiwari, M. Tiwari, and B. Kumar, “Predicting Employee Turnover: A Systematic Machine Learning Approach for Resource Conservation and Workforce Stability,” Eng. Proc. 2023, Vol. 59, Page 117, vol. 59, no. 1, p. 117, Dec. 2023, doi: 10.3390/ENGPROC2023059117.
Md Sumon Gazi, Md Nasiruddin, Shuvo Dutta, Rajesh Sikder, Chowdhury Badrul Huda, and Md Zahidul Islam, “Employee Attrition Prediction in the USA: A Machine Learning Approach for HR Analytics and Talent Retention Strategies,” J. Bus. Manag. Stud., vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 47–59, May 2024, doi: 10.32996/JBMS.2024.6.3.6.
“IBM HR Analytics Employee Attrition & Performance.” Accessed: Aug. 27, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/pavansubhasht/ibm-hr-analytics-attrition-dataset
“Altair AI Studio - Altair RapidMiner Documentation.” Accessed: Aug. 27, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://docs.rapidminer.com/latest/studio/
“Data Analytics and AI Platform | Altair RapidMiner.” Accessed: Aug. 27, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://altair.com/altair-rapidminer
E. Fix and J. L. Hodges, “Discriminatory Analysis. Nonparametric Discrimination: Consistency Properties,” Int. Stat. Rev. / Rev. Int. Stat., vol. 57, no. 3, p. 238, Dec. 1989, doi: 10.2307/1403797.
“The Regression Analysis of Binary Sequences on JSTOR.” Accessed: Aug. 27, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.jstor.org/stable/2983890
T. Han, “Research on Chinese Patent Text Classification Based on SVM,” Jul. 2023, doi: 10.4108/EAI.26-5-2023.2334244.
T. K. Ho, “Random decision forests,” Proc. Int. Conf. Doc. Anal. Recognition, ICDAR, vol. 1, pp. 278–282, 1995, doi: 10.1109/ICDAR.1995.598994.
A. P. Bradley, “The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms,” Pattern Recognit., vol. 30, no. 7, pp. 1145–1159, Jul. 1997, doi: 10.1016/S0031-3203(96)00142-2.
H. Younis, M. Asad Arshed, F. ul Hassan, M. Khurshid, H. Ghassan, and M. Haseeb-, “Tomato Disease Classification using Fine-Tuned Convolutional Neural Network,” Int. J. Innov. Sci. Technol., vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 123–134, Feb. 2022, doi: 10.33411/IJIST/2022040109.
M. A. Arshed, W. Qureshi, M. Rumaan, M. T. Ubaid, A. Qudoos, and M. U. G. Khan, “Comparison of Machine Learning Classifiers for Breast Cancer Diagnosis,” 4th Int. Conf. Innov. Comput. ICIC 2021, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ICIC53490.2021.9692926.
M. A. Arshed, Z. Akram, H. Z. Bajwa, M. H. Azeem, M. A. Dawood, and F. Riaz, “Enhancing Pakistan Rice Plant Disease Detection: A Highly Effective Pre-Trained CNN Model,” 2023 25th Int. Multi Top. Conf. INMIC 2023 - Proc., 2023, doi: 10.1109/INMIC60434.2023.10465842.
M. A. Arshed, H. Ghassan, M. Hussain, M. Hassan, A. Kanwal, and R. Fayyaz, “A Light Weight Deep Learning Model for Real World Plant Identification,” 2022 2nd Int. Conf. Distrib. Comput. High Perform. Comput. DCHPC 2022, pp. 40–45, 2022, doi: 10.1109/DCHPC55044.2022.9731841.
M. Mubeen, M. A. Arshed, and H. A. Rehman, “DeepFireNet - A Light-Weight Neural Network for Fire-Smoke Detection,” Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci., vol. 1616 CCIS, pp. 171–181, 2022, doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-10525-8_14/COVER.
R. A. A. Shahzad, M. A. Arshed, F. Liaquat, M. Tanveer, M. Hussain, “Pneumonia Classification from Chest X-ray Images Using Pre-Trained Network Architectures,” VAWKUM trans. Comput. sci., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 34–44, 2022.
N. V. Chawla, K. W. Bowyer, L. O. Hall, and W. P. Kegelmeyer, “SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique,” J. Artif. Intell. Res., vol. 16, pp. 321–357, Jun. 2002, doi: 10.1613/JAIR.953.
Copyright © by authors and 50Sea. This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 50SEA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















