Harnessing Language Intelligence: Innovative Approaches to Sustainable Mental Health Interventions in the Digital Age
Keywords:
Natural Language Processing, Mental Health Analysis, Digital Intelligence, Emotion Detection, Harnessing Language IntelligenceAbstract
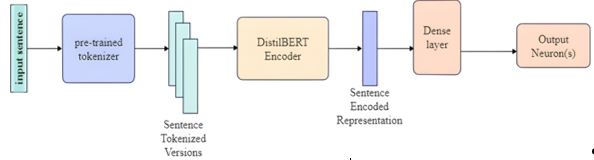
This study explores the advanced abilities of Natural Language Processing (NLP) methods to revolutionize mental health treatment by understanding how such interventions improve therapeutic outcomes. In doing so, the work of this study is demonstrated as an innovative approach to translating conversational data into actionable insights that bridge a large gap in the detection of subtle emotional cues in mental health assessments. The research used DistilBERT, an optimized version of the BERT framework, which has been fine-tuned on specially selected datasets to accurately identify emotional states such as sadness, joy, anger, and fear. Emotional and linguistic patterns were analyzed to identify often unarticulated signals to identify disorders such as depression, anxiety, and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) much earlier. In this regard, the model has been found to significantly enhance the understanding of patients' emotional states more accurately and subtly than through traditional means. The findings of this study highlight the potential of offering individualized therapeutic interventions within digital health applications, which enables immediate emotional well-being assessments. The study showcases the flexibility of AI-based systems, making them applicable to almost any environment, including a workplace setting, to promote both wellness and productivity. This study sets the ground for developing scalable, customized, and proactive mental health care strategies that are beyond conventional therapeutic frameworks.
References
F. Daniel Vigo, MD∙ Prof Graham Thornicroft, PhD∙ Prof Rifat Atun, “Estimating the true global burden of mental illness,” The Lancet Psychiatry, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 171–178, 2016, [Online]. Available: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanpsy/article/PIIS2215-0366(15)00505-2/fulltext
A. Caliskan, J. J. Bryson, and A. Narayanan, “Semantics derived automatically from language corpora contain human-like biases,” Science (80-. )., vol. 356, no. 6334, pp. 183–186, Apr. 2017, doi: 10.1126/SCIENCE.AAL4230/SUPPL_FILE/CALISKAN-SM.PDF.
M. V. Koroteev, “BERT: a review of applications in natural language processing and understanding,” arXiv Prepr. arXiv2103.11943, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2103.11943.
S. R. B. Yada Pruksachatkun, Jason Phang, Haokun Liu, Phu Mon Htut, Xiaoyi Zhang, Richard Yuanzhe Pang, Clara Vania, Katharina Kann, “Intermediate-task transfer learning with pretrained models for natural language understanding: When and why does it work?,” arXiv Prepr. arXiv2005.00628, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2005.00628.
M. U. Deepali Kulkarni, Abhijit Ghosh, Amey Girdhari, Shaomin Liu, L. Alexander Vance and J. Sarkar, “Enhancing pre-trained contextual embeddings with triplet loss as an effective fine-tuning method for extracting clinical features from electronic health record derived mental health clinical notes,” Nat. Lang. Process. J., vol. 6, p. 100045, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlp.2023.100045.
and J. L. Althoff, T., K. Clark, “Large-scale analysis of counseling conversations: An application of natural language processing to mental health,” Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist., vol. 4, pp. 463–476., 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1162/tacl_a_00111.
F. A. J. Md. Monirul Islam, Shahriar Hassan, Sharmin Akter and M. Sahidullah, “A comprehensive review of predictive analytics models for mental illness using machine learning algorithms,” Healthc. Anal., vol. 6, p. 100350, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.health.2024.100350.
D. G. Abdulqahar Mukhtar Abubakar and S. Parida, “A Reinforcement Learning Approach for Intelligent Conversational Chatbot For Enhancing Mental Health Therapy,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 235, pp. 916–925, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2024.04.087.
D. R. andKlinge O. V.-C. Rosa A. García-Hernández , Huizilopoztli Luna-García , , José M. Celaya-Padilla , Alejandra García-Hernández , Luis C. Reveles-Gómez , Luis Alberto Flores-Chaires , J. Ruben Delgado-Contreras, “A Systematic Literature Review of Modalities, Trends, and Limitations in Emotion Recognition, Affective Computing, and Sentiment Analysis,” Appl. Sci., vol. 14, no. 16, p. 7165, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167165.
C. Y. C. and R. M. Lin Sze Khoo ,Mei Kuan Lim, “Machine Learning for Multimodal Mental Health Detection: A Systematic Review of Passive Sensing Approaches,” Sensors, vol. 24, no. 2, p. 348, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s24020348.
Dp. Rohan Khera MD, MS, Evangelos K. Oikonomou MD, J. W. P. Girish N. Nadkarni MD, MPH, Jessica R. Morley PhD, P. Atul J. Butte MD, and E. J. T. MD, “Transforming Cardiovascular Care With Artificial Intelligence: From Discovery to Practice: JACC State-of-the-Art Review,” J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., vol. 84, no. 1, pp. 97–114, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2024.05.003.
J. T. A. Andrews, D. Zhao, W. Thong, and A. Modas, “Ethical considerations for responsible data curation,” Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst., 2023, doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2302.03629.
M. Deady et al., “Preventing depression using a smartphone app: a randomized controlled trial,” Psychol. Med., vol. 52, no. 3, pp. 457–466, Feb. 2022, doi: 10.1017/S0033291720002081.
S. D’Alfonso, “AI in mental health,” Curr. Opin. Psychol., vol. 36, pp. 112–117, Dec. 2020, doi: 10.1016/J.COPSYC.2020.04.005.
L. H. U. Tony Liu, Jonah Meyerhoff, Johannes C Eichstaedt, Chris J Karr, Susan M Kaiser, Konrad P Kording, David C Mohr, “The relationship between text message sentiment and self-reported depression.,” J. Affect. Disord., vol. 302, pp. 7–14, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.12.048.
Q. Lin, T. Li, P. M. Shakeel, and R. D. J. Samuel, “Advanced artificial intelligence in heart rate and blood pressure monitoring for stress management,” J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput., vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 3329–3340, Mar. 2021, doi: 10.1007/S12652-020-02650-3/METRICS.
M. M. Bennett Kleinberg,Isabelle van der Vegt, “Measuring emotions in the covid-19 real world worry dataset,” arXiv Prepr. arXiv2004.04225, 2020, [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2004.04225
R. Y. M. Cheung, H. S. Chung, and M. C. Y. Ng, “Expressive Writing and Well-Being in Chinese Emerging Adults: Is Emotion Regulation an Underlying Mechanism?,” https://doi.org/10.1177/2167696818824719, vol. 9, no. 6, pp. 679–689, Jan. 2019, doi: 10.1177/2167696818824719.
J. L. Chen, Yen-Chun Gan, Zhe Cheng, Yu Liu, Jingzhou, “Distilling knowledge learned in BERT for text generation,” arXiv Prepr. arXiv1911.03829, 2019, [Online]. Available: https://com-mendeley-prod-publicsharing-pdfstore.s3.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/18d1-CC-BY-2/10.18653/v1/2020.acl-main.705.pdf?X-Amz-Security-Token=IQoJb3JpZ2luX2VjEKT%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FwEaCWV1LXdlc3QtMSJHMEUCIQDEuYOI9e8oyolRd862kWVsJMEJ1I%2Fhljtgn
A. R. Thomas Wolf, Lysandre Debut, Victor Sanh, Julien Chaumond, Clement Delangue, Anthony Moi, Pierric Cistac, Tim Rault, Remi Louf, Morgan Funtowicz, Joe Davison, Sam Shleifer, Patrick von Platen, Clara Ma, Yacine Jernite, Julien Plu, Canwen Xu, Teven Le Scao, “Transformers: State-of-the-Art Natural Language Processing,” ACL Anthol., pp. 38–45, 2020, doi: 10.18653/v1/2020.emnlp-demos.6.
and A. A. A. Hadeer Adel, Abdelghani Dahou, Alhassan Mabrouk, Mohamed Abd Elaziz, Mohammed Kayed , Ibrahim Mahmoud El-Henawy, Samah Alshathri, “Improving Crisis Events Detection Using DistilBERT with Hunger Games Search Algorithm,” Mathematics, vol. 10, no. 3, p. 447, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/math10030447.
D. . Powers, “Evaluation: from precision, recall and F-measure to ROC, informedness, markedness and correlation,” arXiv Prepr. arXiv2010.16061, 2020, [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2010.16061
V. Sanh, L. Debut, J. Chaumond, and T. Wolf, “DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter,” arXiv Prepr. arXiv1910.01108, 2019, [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.01108
V. Kokane, A. Abhyankar, N. Shrirao, and P. Khadkikar, “Predicting Mental illness (Depression) with the help of NLP Transformers,” 2nd IEEE Int. Conf. Data Sci. Inf. Syst. ICDSIS 2024, 2024, doi: 10.1109/ICDSIS61070.2024.10594036.
L. and S. W. Liang, “Spanish Emotion Recognition Method Based on Cross-Cultural Perspective,” Front. Psychol., vol. 13, p. 849083, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.849083.
B. L. and N. G. Hamid Reza Saeidnia, Seyed Ghasem Hashemi Fotami, “Ethical Considerations in Artificial Intelligence Interventions for Mental Health and Well-Being: Ensuring Responsible Implementation and Impact,” Soc. Sci., vol. 13, no. 7, p. 381, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci13070381.
E. and G. O. Frank, “Privacy and data protection in AI-enabled healthcare systems,” Google Sch., 2024, [Online]. Available: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=VMeF1rTO1IMC&citation_for_view=VMeF1rTO1IMC:qjMakFHDy7sC
D. W. Wiechmann, Elma Kerz, Sourabh ZanwarSourabh Zanwar, Yu QiaoYu Qiao Daniel, “Toward explainable AI (XAI) for mental health detection based on language behavior,” Front. psychiatry, vol. 14, p. 1219479, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1219479.
M. M. and A. P. B. Subramanian, J. Kim, “Digital Twin Model: A Real-Time Emotion Recognition System for Personalized Healthcare,” IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 81155–81165, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3193941.
M. A.-J. Simon D’Alfonso, Olga Santesteban-Echarri, Simon Rice, Greg Wadley , Reeva Lederman , Christopher Miles, John Gleeson, “Artificial intelligence-assisted online social therapy for youth mental health,” Front. Psychol., vol. 2, no. 8, p. 796, 2017, doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00796.
J. M. Boucher, E.M., Nicole R. Harake, Haley E. Ward, Sarah Elizabeth Stoeckl, Junielly Vargas, “Artificially intelligent chatbots in digital mental health interventions: a review,” Expert Rev. Med. Devices, pp. 37–49, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/17434440.2021.2013200.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 50sea

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















