Assessing Drought Conditions using SPEI in Bahawalpur Division, Punjab, Pakistan
Keywords:
Climate Change, Drought, Rainfall, Variability, SPEIAbstract
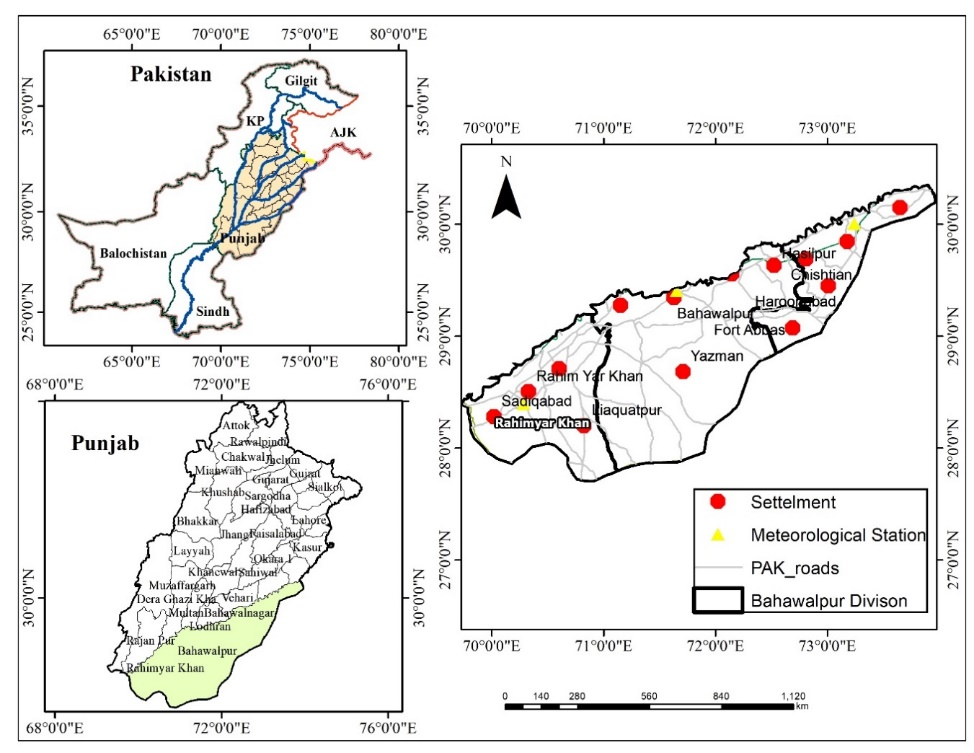
This research study analyzes drought conditions using the Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI) in Bahawalpur Division, South Punjab, Pakistan. Drought is one of the most complex natural disasters and is difficult to predict due to several involved factors. Among all natural hazards, drought causes significant damage to human lives and other living communities. Nearly 85% of all disasters are related to weather events, and drought is one of the most damaging among them. In Pakistan, drought causes damage in many areas, and Bahawalpur Division is one of those facing severe drought conditions. Temporal data on temperature and rainfall were collected from the Pakistan Meteorological Department for the period 1992 to 2020. The data were analyzed spatially using GIS technology. Precipitation and temperature data were analyzed using SPEI to monitor drought in three selected districts in Bahawalpur Division: Bahawalnagar, Bahawalpur, and Rahim Yar Khan. The study revealed that less rainfall was recorded in all three districts, leading to drought conditions. Moreover, this reduced rainfall severely affected the concerned districts.
References
A. K. Mishra and V. P. Singh, “A review of drought concepts,” J. Hydrol., vol. 391, no. 1–2, pp. 202–216, Sep. 2010, doi: 10.1016/J.JHYDROL.2010.07.012.
D. W. S. Edward R. Cook, Richard Seager, Mark A. Cane, “North American drought: Reconstructions, causes, and consequences,” Earth-Science Rev., vol. 81, no. 1–2, pp. 93–134, 2007, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2006.12.002.
N. W. Hege Hisdal, Lena M. Tallaksen, Tobias Gauster, John P. Bloomfield, Simon Parry, Christel Prudhomme, “Hydrological drought characteristics,” Hydrol. Drought (Second Ed., pp. 157–231, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819082-1.00006-0.
X. Liu, X. Zhu, Y. Pan, S. Li, Y. Liu, and Y. Ma, “Agricultural drought monitoring: Progress, challenges, and prospects,” J. Geogr. Sci., vol. 26, no. 6, pp. 750–767, Jun. 2016, doi: 10.1007/S11442-016-1297-9/METRICS.
Peter Folger, “Drought in the United States: Causes and Current Understanding,” Congr. Res. Serv., 2017, [Online]. Available: https://sgp.fas.org/crs/misc/R43407.pdf
K. R. B. & J. S. Kevin E. Trenberth, Aiguo Dai, Gerard van der Schrier, Philip D. Jones, Jonathan Barichivich, “Global warming and changes in drought,” Nat. Clim. Chang., vol. 4, pp. 17–22, 2014, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2067.
C. C. Aderita Sena, Christovam Barcellos, Carlos Freitas, “Managing the Health Impacts of Drought in Brazil,” Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal., vol. 11, no. 10, pp. 10737–10751, 2014, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph111010737.
N. Y. K. Shoaib Jamro, Falak Naz Channa, Ghulam Hussain Dars, Kamran Ansari, “Exploring the Evolution of Drought Characteristics in Balochistan, Pakistan,” Appl. Sci., vol. 10, no. 3, p. 913, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030913.
H. A. J. van L. &P. J. J. F. T. G. Wong, “Probabilistic analysis of hydrological drought characteristics using meteorological drought,” Hydrol. Sci. J., vol. 58, no. 2, 2013, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2012.753147.
M. A. Muhammad Shahzaman, Weijun Zhu, Muhammad Bilal, Birhanu Asmerom Habtemicheal, Farhan Mustafa, “Remote Sensing Indices for Spatial Monitoring of Agricultural Drought in South Asian Countries,” Remote Sens, vol. 13, no. 11, p. 2059, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13112059.
W. P. Jahangir Khan, “Mapping MODIS LST NDVI imagery for drought monitoring in Punjab Pakistan,” IEEE Access, 2018, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2821717.
M. A. Irfan Ullah, Xieyao Ma, Jun Yin, Farhan Saleem, Sidra Syed, Abubaker Omer, Birhanu Asmerom Habtemicheal, Mengyang Liu, “Observed changes in seasonal drought characteristics and their possible potential drivers over Pakistan,” Int. J. Climatol., vol. 42, no. 3, p. 3, 2022, [Online]. Available: https://rmets.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/joc.7321
A. Dai, T. Zhao, and J. Chen, “Climate Change and Drought: a Precipitation and Evaporation Perspective,” Curr. Clim. Chang. Reports, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 301–312, Sep. 2018, doi: 10.1007/S40641-018-0101-6/METRICS.
N. W. and M. F. P. B. Yoshihide Wada, Ludovicus P H van Beek, “Human water consumption intensifies hydrological drought worldwide,” Environ. Res. Lett, 2013, [Online]. Available: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1748-9326/8/3/034036
S. Adnan, K. Ullah, and S. Gao, “Characterization of drought and its assessment over Sindh, Pakistan during 1951-2010,” J. Meteorol. Res., vol. 29, no. 5, pp. 837–857, Oct. 2015, doi: 10.1007/S13351-015-4113-Z/METRICS.
Atta-ur-Rahman and M. Dawood, “Spatio-statistical analysis of temperature fluctuation using Mann–Kendall and Sen’s slope approach,” Clim. Dyn., vol. 48, no. 3–4, pp. 783–797, Feb. 2017, doi: 10.1007/S00382-016-3110-Y/METRICS.
B. Önöz and M. Bayazit, “Block bootstrap for Mann-Kendall trend test of serially dependent data,” Hydrol. Process., vol. 26, no. 23, pp. 3552–3560, Nov. 2012, doi: 10.1002/HYP.8438;REQUESTEDJOURNAL:JOURNAL:10991085;WGROUP:STRING:PUBLICATION.
S. A. S. Muhammad Dawood, “Geo-spatial analysis of rainfall variability in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, Pakistan,” Ecol. Quest., vol. 34, no. 1, 2022, [Online]. Available: https://apcz.umk.pl/EQ/article/view/39285
Atta-ur-Rahman and A. N. Khan, “Analysis of flood causes and associated socio-economic damages in the Hindukush region,” Nat. Hazards, vol. 59, no. 3, pp. 1239–1260, Dec. 2011, doi: 10.1007/S11069-011-9830-8/METRICS.
M. Dawood, A. ur Rahman, S. Mahmood, G. Rahman, and S. Nazir, “Assessing the impact of climatic change on discharge in Swat river basin using fuzzy logic model,” Arab. J. Geosci., vol. 14, no. 18, pp. 1–16, Sep. 2021, doi: 10.1007/S12517-021-08219-4/METRICS.
M. Dawood, A. ur Rahman, S. Ullah, S. Mahmood, G. Rahman, and K. Azam, “Spatio-statistical analysis of rainfall fluctuation, anomaly and trend in the Hindu Kush region using ARIMA approach,” Nat. Hazards, vol. 101, no. 2, pp. 449–464, Mar. 2020, doi: 10.1007/S11069-020-03881-5/METRICS.
Y. Jiang, C. Liu, H. Zheng, X. Li, and X. Wu, “Responses of river runoff to climate change based on nonlinear mixed regression model in chaohe river basin of hebei province, China,” Chinese Geogr. Sci., vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 152–158, May 2010, doi: 10.1007/S11769-010-0152-7/METRICS.
G. Rahman, A. U. Rahman, S. Ullah, M. Dawood, M. F. U. Moazzam, and B. G. Lee, “Spatio-temporal characteristics of meteorological drought in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan,” PLoS One, vol. 16, no. 4, p. e0249718, Apr. 2021, doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0249718.
Atta-ur-Rahman and A. N. Khan, “Analysis of 2010-flood causes, nature and magnitude in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan,” Nat. Hazards, vol. 66, no. 2, pp. 887–904, Mar. 2013, doi: 10.1007/S11069-012-0528-3/METRICS.
and J. I. L.-M. Vicente-Serrano, Sergio M. Beguería, Santiago, “A Multiscalar Drought Index Sensitive to Global Warming: The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index,” J. Clim., vol. 23, no. 7, p. 4, 2010, [Online]. Available: https://journals.ametsoc.org/view/journals/clim/23/7/2009jcli2909.1.xml
M. Ahmed, N., Hussain, T., & Akhtar, “Meteorological drought assessment in Punjab using SPI and SPEI,” Arab. J. Geosci., vol. 12, no. 15, pp. 1–12, 2019.
S. Latif, M., Abbas, F., & Saeed, “Assessment of meteorological drought in Pakistan using multiple drought indices,” Nat. Hazards, vol. 103, no. 2, pp. 1941–1962, 2020.
M. Dawood, A. ur Rahman, S. Ullah, G. Rahman, and K. Azam, “Spatio-temporal analysis of temperature variability, trend, and magnitude in the Hindu Kush region using Monte Carlo and Sen’s slope approaches,” Arab. J. Geosci., vol. 11, no. 16, pp. 1–15, Aug. 2018, doi: 10.1007/S12517-018-3823-9/METRICS.
I. Ullah et al., “Evaluating the meteorological drought characteristics over Pakistan using in situ observations and reanalysis products,” Int. J. Climatol., vol. 41, no. 9, pp. 4437–4459, Jul. 2021, doi: 10.1002/JOC.7063;PAGE:STRING:ARTICLE/CHAPTER.
G. Rahman, Atta-ur-Rahman, Samiullah, and M. Dawood, “Spatial and temporal variation of rainfall and drought in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province of Pakistan during 1971–2015,” Arab. J. Geosci., vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 1–13, Feb. 2018, doi: 10.1007/S12517-018-3396-7/METRICS.
A. Q. Aslam, S. R. Ahmad, I. Ahmad, Y. Hussain, and M. S. Hussain, “Vulnerability and impact assessment of extreme climatic event: A case study of southern Punjab, Pakistan,” Sci. Total Environ., vol. 580, pp. 468–481, Feb. 2017, doi: 10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2016.11.155.
A. U. R. Ghani Rahman, “Spatio-temporal characteristics of meteorological drought in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan,” Plosone, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0249718.
G. R. A. R. S. M. M. F. U. M. M. D. M. M. S. Panezai, “Trend analysis of historical and future precipitation projections over a diverse topographic region of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa using SDSM Open Access,” J. Water Clim. Chang., vol. 13, no. 11, pp. 3792–3811, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2022.160.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2025 50sea

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















