LectureBuddy: Towards Anonymous, Continuous, Real-time, and Automated Course Evaluation System
Keywords:
improving classroom teaching, evaluation methodologies, interactive learning environments, computer-mediated communication, student feedback systemAbstract
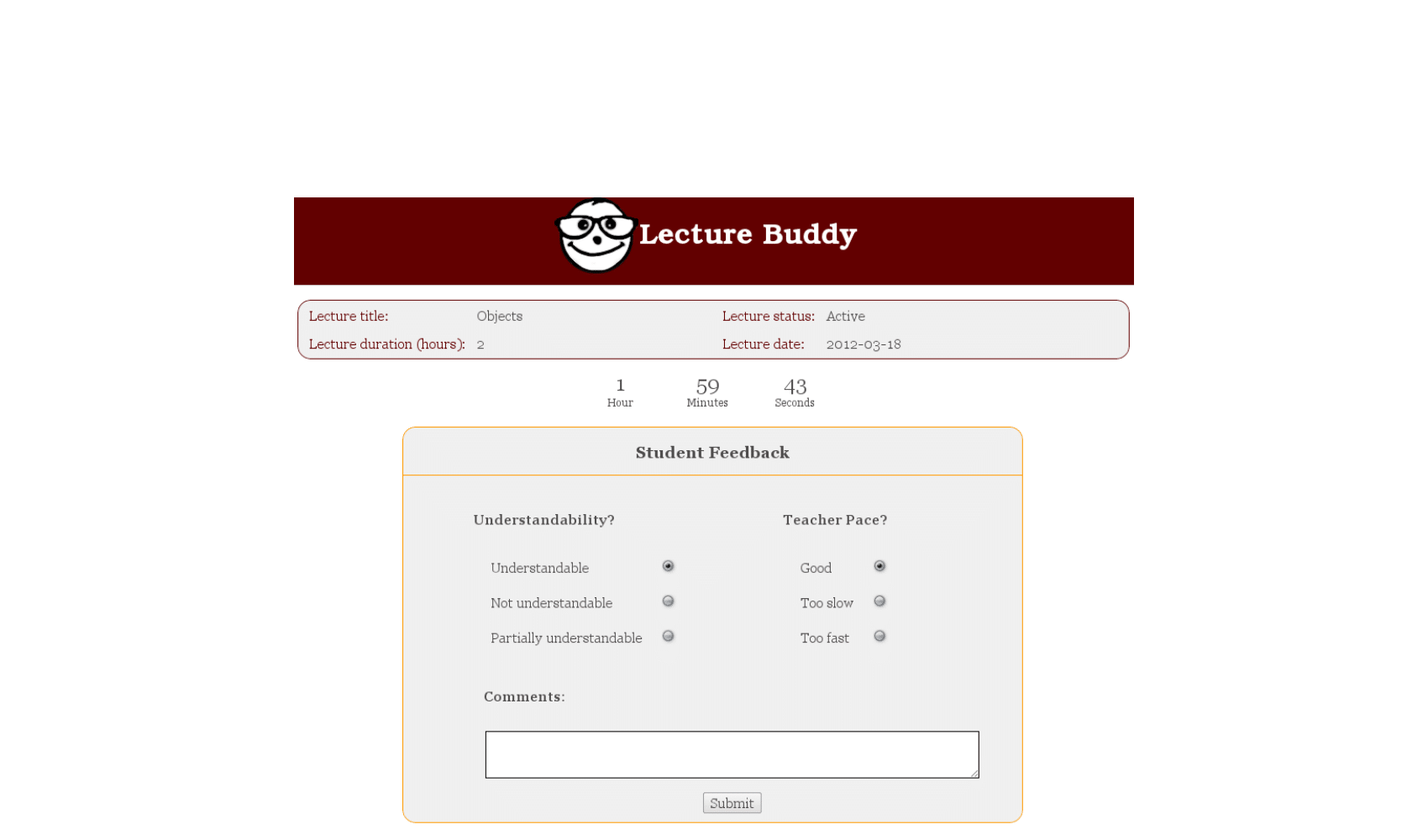
Student’s course evaluations are a primary tool for measuring teaching effectiveness. The traditional practice in course evaluation at most institutes is carried out once, at the end of each semester. The effectiveness of this system requires candid participation from the students, followed up by the administration, and the faculty. While corrective action took place behind the scenes over a long period, students never observed any immediate change(s) based on the feedback they were provided through the existing course evaluation systems. This discourages students from considering the evaluation seriously. In this paper, we investigate the need for an innovative system to replace the existing course evaluation systems. We conducted two separate surveys from 210 students and 67 teachers to gain insight into the existing course evaluation systems. The survey participants answered questions based on the tendency of feedback provided by students, method of teacher’s evaluations, frequency of evaluations conducted by institutes, and steps to make classrooms more interactive. We also conducted a comprehensive statistical analysis of the data collected from the surveys, both qualitative and quantitative. Our study showed a need for an innovative course evaluation system to continuously gather student feedback throughout the semester anonymously. These findings led us to develop the prototype of an innovative course evaluation system, “Lecture Buddy”, which is anonymous, continuous, real-time, and automated and which alleviates the shortcomings of the traditional course evaluation systems.
References
C. Steyn, C. Davies, and A. Sambo, “Eliciting student feedback for course development: the application of a qualitative course evaluation tool among business research students,” Assess. Eval. High. Educ., vol. 44, no. 1, pp. 11–24, Jan. 2019, doi: 10.1080/02602938.2018.1466266.
H. W. Marsh and D. Hocevar, “Student’s evaluations of teaching effectiveness: The stability of mean ratings of the same teachers over a 13-year period,” Teach. Teach. Educ., vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 303–314, Jan. 1991, doi: 10.1016/0742-051X(91)90001-6.
O. Mitchell and M. Morales, “The effect of switching to mandatory online course assessments on response rates and course ratings,” Assess. Eval. High. Educ., vol. 43, no. 4, pp. 629–639, May 2018, doi: 10.1080/02602938.2017.1390062.
A. S. Rosen, “Correlations, trends and potential biases among publicly accessible web-based student evaluations of teaching: a large-scale study of RateMyProfessors.com data,” Assess. Eval. High. Educ., vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 31–44, Jan. 2018, doi: 10.1080/02602938.2016.1276155.
J. V. Adams, “Student evaluations: The ratings game.” 1997. Accessed: Sep. 18, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://philpapers.org/rec/ADASET
D. E. Clayson, “Student evaluation of teaching and matters of reliability,” Assess. Eval. High. Educ., vol. 43, no. 4, pp. 666–681, May 2018, doi: 10.1080/02602938.2017.1393495.
A. VANACORE and M. S. Pellegrino, “An agreement-based approach for reliability assessment of Student’s Evaluations of Teaching,” Third Int. Conf. High. Educ. Adv., p. 2017, Jun. 2017, doi: 10.4995/HEAd17.2017.5583.
H. W. Marsh, “Student’s Evaluations of University Teaching: Dimensionality, Reliability, Validity, Potential Biases and Usefulness,” Scholarsh. Teach. Learn. High. Educ. An Evidence-Based Perspect., pp. 319–383, Jun. 2007, doi: 10.1007/1-4020-5742-3_9.
B. Uttl, C. A. White, and D. W. Gonzalez, “Meta-analysis of faculty’s teaching effectiveness: Student evaluation of teaching ratings and student learning are not related,” Stud. Educ. Eval., vol. 54, pp. 22–42, Sep. 2017, doi: 10.1016/J.STUEDUC.2016.08.007.
P. B. Stark and R. Freishtat, “An Evaluation of Course Evaluations,” Sci. Res., vol. 0, no. 0, Sep. 2014, doi: 10.14293/S2199-1006.1.SOR-EDU.AOFRQA.V1.
L. McClain, A. Gulbis, and D. Hays, “Honesty on student evaluations of teaching: effectiveness, purpose, and timing matter!,” Assess. Eval. High. Educ., vol. 43, no. 3, pp. 369–385, Jul. 2018, doi: 10.1080/02602938.2017.1350828.
K. Young, J. Joines, T. Standish, and V. Gallagher, “Student evaluations of teaching: the impact of faculty procedures on response rates,” Assess. Eval. High. Educ., vol. 44, no. 1, pp. 37–49, Jan. 2019, doi: 10.1080/02602938.2018.1467878.
M. A. Bush, S. Rushton, J. L. Conklin, and M. H. Oermann, “Considerations for Developing a Student Evaluation of Teaching Form,” Teach. Learn. Nurs., vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 125–128, Apr. 2018, doi: 10.1016/J.TELN.2017.10.002.
K. Sedova, M. Sedlacek, and R. Svaricek, “Teacher professional development as a means of transforming student classroom talk,” Teach. Teach. Educ., vol. 57, pp. 14–25, Jul. 2016, doi: 10.1016/J.TATE.2016.03.005.
N. Denson, T. Loveday, and H. Dalton, “Student evaluation of courses: what predicts satisfaction?,” High. Educ. Res. Dev., vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 339–356, Aug. 2010, doi: 10.1080/07294360903394466.
“What Can We Learn from End-of-Course Evaluations?” https://www.facultyfocus.com/articles/faculty-development/can-learn-end-course-evaluations/ (accessed Sep. 18, 2023).
P. Brickman, C. Gormally, and A. M. Martella, “Making the grade: Using instructional feedback and evaluation to inspire evidence-based teaching,” CBE Life Sci. Educ., vol. 15, no. 4, Dec. 2016, doi: 10.1187/CBE.15-12-0249/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/AR75FIG5.JPEG.
A. Boring, K. Ottoboni, P. B. Stark, and G. Steinem, “Student Evaluations of Teaching (Mostly) Do Not Measure Teaching Effectiveness,” Sci. Res., vol. 0, no. 0, Jan. 2016, doi: 10.14293/S2199-1006.1.SOR-EDU.AETBZC.V1.
W. Stroebe, “Why Good Teaching Evaluations May Reward Bad Teaching,” https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691616650284, vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 800–816, Nov. 2016, doi: 10.1177/1745691616650284.
L. Mandouit, “Using student feedback to improve teaching,” Educ. Action Res., vol. 26, no. 5, pp. 755–769, Oct. 2018, doi: 10.1080/09650792.2018.1426470.
R. J. Avery, W. K. Bryant, A. Mathios, H. Kang, and D. Bell, “Electronic Course Evaluations: Does an Online Delivery System Influence Student Evaluations?,” J. Econ. Educ., vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 21–37, Dec. 2006, doi: 10.3200/JECE.37.1.21-37.
A. Hoon, E. Oliver, K. Szpakowska, and P. Newton, “Use of the ‘Stop, Start, Continue’ method is associated with the production of constructive qualitative feedback by students in higher education,” Assess. Eval. High. Educ., vol. 40, no. 5, pp. 755–767, Jul. 2015, doi: 10.1080/02602938.2014.956282.
T. H. Reisenwitz, “Student evaluation of teaching: An investigation of nonresponse bias in an online context,” J. Mark. Educ., vol. 38, no. 1, pp. 7–17, 2016.
T. Standish, J. A. Joines, K. R. Young, and V. J. Gallagher, “Improving SET Response Rates: Synchronous Online Administration as a Tool to Improve Evaluation Quality,” Res. High. Educ., vol. 59, no. 6, pp. 812–823, Sep. 2018, doi: 10.1007/S11162-017-9488-5/METRICS.
F. Yang and F. W. B. Li, “Study on student performance estimation, student progress analysis, and student potential prediction based on data mining,” Comput. Educ., vol. 123, pp. 97–108, Aug. 2018, doi: 10.1016/J.COMPEDU.2018.04.006.
M. Chassignol, A. Khoroshavin, A. Klimova, and A. Bilyatdinova, “Artificial Intelligence trends in education: a narrative overview,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 136, pp. 16–24, Jan. 2018, doi: 10.1016/J.PROCS.2018.08.233.
M. Amjad and N. Jahan Linda, “A Web Based Automated Tool for Course Teacher Evaluation System (TTE),” Int. J. Educ. Manag. Eng., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 11–19, Apr. 2020, doi: 10.5815/IJEME.2020.02.02.
R. Lalit, K. Handa, and N. Sharma, “FUZZY BASED AUTOMATED FEEDBACK COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS SYSTEM REEMA LALIT, KARUN HANDA and NITIN SHARMA,” Adv. Appl. Math. Sci., vol. 18, no. 8, 2019.
A. P. Cavalcanti et al., “Automatic feedback in online learning environments: A systematic literature review,” Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell., vol. 2, p. 100027, Jan. 2021, doi: 10.1016/J.CAEAI.2021.100027.
L. Tian and Y. Zhou, “Learner engagement with automated feedback, peer feedback and teacher feedback in an online EFL writing context,” System, vol. 91, p. 102247, Jul. 2020, doi: 10.1016/J.SYSTEM.2020.102247.
E. Jensen et al., “Toward Automated Feedback on Teacher Discourse to Enhance Teacher Learning,” Conf. Hum. Factors Comput. Syst. - Proc., Apr. 2020, doi: 10.1145/3313831.3376418.
I. G. Ndukwe and B. K. Daniel, “Teaching analytics, value and tools for teacher data literacy: a systematic and tripartite approach,” Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ., vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 1–31, Dec. 2020, doi: 10.1186/S41239-020-00201-6/FIGURES/6.
I. Sindhu, S. Muhammad Daudpota, K. Badar, M. Bakhtyar, J. Baber, and M. Nurunnabi, “Aspect-Based Opinion Mining on Student’s Feedback for Faculty Teaching Performance Evaluation,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 108729–108741, 2019, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2928872.
Q. Lin, Y. Zhu, S. Zhang, P. Shi, Q. Guo, and Z. Niu, “Lexical based automated teaching evaluation via student’s short reviews,” Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ., vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 194–205, Jan. 2019, doi: 10.1002/CAE.22068.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 50SEA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















