Appraisal the Impact of Urban Evolution and Change on Land Use and Land Cover: A Case Study of Abbottabad District
Keywords:
Urban Evolution, Land Surface Temperature, LULC, NDVIAbstract
Introduction/Importance of Study: Abbottabad district has gone through urban evolution drastically. The evident changes have observed in LULC of the district using RS/GIS techniques, which contributes to various environmental changes and put stress on the resources of the city. It is important to highlight areas at higher risk of urban expansion in the district to tackle the future growth of the city.
Novelty Statement: Our Research contributes to identify the increasing urban growth of the Abbottabad District from 1985-2023 using RS/GIS techniques that had not done previously. District’s LULC change and problems affiliated with it, has been addressed with solutions and recommendations, which will lead to the sustainable development of the city.
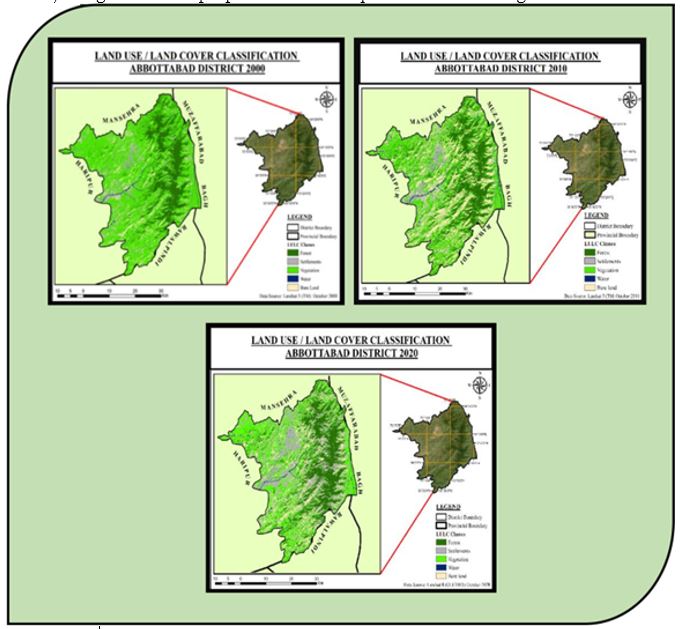
Material and Method: The study utilized the images of Landsat 5 (TM) and Landsat 8 (TIRS/OLI) collected from Earth Explorer of year 2000-2023. MLC classification has been carried on to identify the LULC classes in study area. The study employed the weighted overlay method, which provided the Urban Expansion Risk Model of the study area by analyzing parameters i.e. LULC, NDVI, LST, NDBI, Elevation and Population.
Result and Discussion: Our Findings represented the LULC changes of 2000-2020 through Maximum Likelihood Classification (MLC), which indicated the increase in built-up land that is 19.1% in last two decades and decrease in vegetation cover that has cleared for the construction and agricultural purposes. The LULC change brought problems in all spheres- housing, health, education, sanitation, transport, security, jobs etc. The NDVI values also showed the decrease in vegetation cover. To analyze Land Surface Temperature LST tool was used. LST calculations have represented the increase of 3o C in temperature. The study highlighted the consequences of NDVI and LST changes along with the environmental problems, such as pollution, Loss of biodiversity, land sliding, topographical changes and flooding. The field visit contributed towards understanding the ground realities.
Concluding Remarks: The study will help government to pay proper attention towards eradicating the problems of urban growth, pollution, urban flooding, land sliding and deforestation in the district. The better planning for the urban growth and LULC can prevent the further degradation of the district. It will also contribute towards sustainable growth of the city in future.
References
Archer, K. (2012). The city: The basics.
Satterthwaite, D. (2007). The transition to a predominantly urban world and its underpinnings (No. 4). Iied.
Jabeen, N., Farwa, U., & Jadoon, M. (2017). Urbanization in Pakistan: a governance perspective. Journal of the Research Society of Pakistan, 54(1), 127-136.
Raza, D., Karim, R. B., Nasir, A., Khan, S. U., Zubair, M. H., & Amir, R. (2019). Satellite based surveillance of LULC with deliberation on urban land surface temperature and precipitation pattern changes of Karachi. Pakistan. J. Geogr. Nat. Disast, 9(1037), 2167-0587
Anwar, Z., Alam, A., Elahi, N., & Shah, I. (2022). Assessing the trends and drivers of land use land cover change in district Abbottabad lower Himalayan Region Pakistan. Geocarto International, 37(25), 10855-10870.
Anwa, Z., Alam, A., & Khan, B. (2024). The Impact of Land Use Land Cover Changes on Livelihood Strategies of the Households in District Abbottabad, Pakistan. Remittances Review, 9(1), 1536-1561.
IUCN. (2004). Abbottabbad: State of the Environment and Development. Abbottabad: IUCN, Sarhad Programme. Retrieved from https://www.iucn.org/sites/default/ files/import/downloads/abbottabad_soed.pdf
Britannica, T. Editors of Encyclopaedia (2023, December 11). Abbottabad. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/place/Abbottabad
Poveda, G., & Salazar, L. F. (2004). Annual and interannual (ENSO) variability of spatial scaling properties of a vegetation index (NDVI) in Amazonia. Remote Sensing of Environment, 93(3), 391-401
Li, Z. L., Wu, H., Duan, S. B., Zhao, W., Ren, H., Liu, X., ... & Zhou, C. (2023). Satellite remote sensing of global land surface temperature: Definition, methods, products, and applications. Reviews of Geophysics, 61(1).
Mao, Q., Peng, J., & Wang, Y. (2021). Resolution enhancement of remotely sensed land surface temperature: Current status and perspectives. Remote Sensing, 13(7), 1306.
Bhandwal, M., & Tyagi, R. K. (2022). A new method to reduce the harmful gases and particulate matter emitted from the vehicles. Materials Today: Proceedings, 56, 3623-3626.
Pham, H. M., Yamaguchi, Y., & Bui, T. Q. (2011). A case study on the relation between city planning and urban growth using remote sensing and spatial metrics. Landscape and Urban Planning, 100(3), 223-230.
Afsar, S., Kazmi, S. J. H., & Bano, S. (2013). Quest of urban growth monitoring from myth to reality. Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences, 9, 222.
Abbas, S., Hussain, M. S., Im, S., Lee, S., & Shirazi, S. A. (2018). Urban growth and its effect on temperature trends of Lahore City, Pakistan. 기후연구, 13(3), 231-245.
Nisa, Z., Mir, K., Fatimah, H., & Batool, S. M. (2018). Application of satellite remote sensing in forest change detection and its environmental impacts in district Abbottabad, Pakistan. JPAA, 3(1).
Waseem, L. A., Khokhar, M. A. H., Naqvi, S. A. A., Hussain, D., Javed, Z. H., & Awan, H. B. H. (2021). Influence of urban sprawl on microclimate of abbottabad, Pakistan. Land, 10(2), 95.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 50SEA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















