Synthesis of Picric Acid at Domestic Scales.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33411/ijist/20190102022Keywords:
Picric acid, Synthetic dye, Picramic acid, Sodium picramate and IR Spectra.Abstract
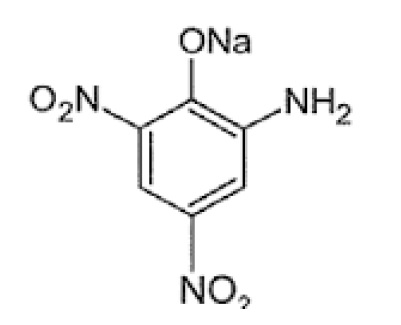
Picric acid and its derivatives are widely used in various applications/industries. The first synthetic dye was prepared in 1771 using picric acid. It was used to dye silk fabric into greenish-yellow color. In this study, Picric acid and their derivatives were synthesized and characterized by their physical and chemical properties. The derivatives of Picric acid which are considered in this research include Picramic acid and Sodium Picramate. The physical properties like melting point, colors, physical state and solubility of Picric acid and its derivatives were determined and confirmed using IR Spectra. IR spectra proved efficient in scanning and mapping.
References
Kadiyala, V. and Spain, J. C. A two-component monooxygenase catalyzes both the hydroxylation of p-nitrophenol and the oxidative release of nitrite from 4-nitrocatechol in Bacillus sphaericus, J.Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 2479-2484 (1998).
Lenke, H. and Knack, H. J. M. Initial hydrogenation and extensive reduction of substituted 2, 4-dinitrophenols,J. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62: 784-790 (1996).
Furniss, B. S., Hannaford, A. J., Smith, P. W. G. and Tatchell, A. R. " Vogel’s Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry," 4th ed. Longman, London and New York, (1986).
Gaensslen, R., Mertens, J., Lee, H. and Stolotow, M. “Staining and Extraction Techniques”, Proceeding of a Forensic Science Symposium on the Analysis of Sexual Assault Evidence, FBI Academy. (1983).
Becker, L. C., Bergfeld,W. F., Belsito, D. V., Klaassen, C. D., Marks, J. G.,Shank, R.C., Slaga, T. J.,Snyder, P. W. AndAndersen, A. F. Amended safety assessment of sodium picramate and picramic acid, J.Int. Toxicol.
(2): (2009).6.Kadiyala, V. and Spain. J. C. A two-component monooxygenase catalyzes both the hydroxylation of p-nitrophenol and the oxidative release of nitrite from 4-nitrocatechol in Bacillus sphaericus, J. Appl. Environ. Microbial. 64: 2479-2484 (1998).
Oxford, G. S. and Pooler, J. P. Selective modification of sodium channel gating in lobster axons by 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol: Evidence for two inactivation mechanisms,J. Gen. Physiol. 66(6): 765-779 (1975).
Wyman, J. F., Guard, H. E., Won, W. D. and Quay, J. H. Conversion of 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol to a mutagen by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, J. Appl. and Environ. Microbiol. 37(2): 222-226 (1979).
Coombes, R. G. and Diggle, A. W. The Mechanism of nitration of phenol and 4-methylphenol by nitrogen dioxide in solution, 35,(34): 6373-6376, (1994).
Rieger, P. G. and Knackmuss, H. J. Basic Knowledge and Perspectives on Biodegradation of 2, 4, 6-Trinitrotoluene and Related Nitroaromatic Compounds in Contaminated Soil, Environ. Sci. Res. 49: 1-18 (1995).
Rieger, P. G., Sinnwell, V., Preu, A., Francke, W. And Knackmus, H. J. Hydride-Meisenheimer Complex Formation and Protonation as Key Reactions of 2, 4, 6-Trinitrophenol Biodegradation by Rhodococcuserythropolis, J. Becteriol. 181 (4): 1189-1195 (1999).
Behrend, C. and Wagner, K. H. Formation of Hydride-MeisenheimerComplexes of Picric acid (2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol) and 2, 4-dinitrophenol during Mineralization of picric acid by Nocardioides sp. Strain CB 22-2, J. Appl. and Environ. Microbiol. 65(4): 1372-1377 (1999).
Ebert, S., Rieger, P. G. and Knackmuss, H. J. Function of Coenzyme F420 in Aerobic Catabolism of 2, 4, 6-Trinitrophenol and 2,4-Dinitrophenol by Nocardioides simplex FJ2-1A, J.Bicteriol. 181 (9): 2669-2674 (1999).
Gupta, V. K., Srivastava1, S. K. and Tyagi, R. Design parameters for the treatment of phenolic wastes by carbon columns (obtained from fertilizer waste material), 34(5): 1543-1550 (2000).
Ahmed, S. A., Patil, R. C., Nakayama, M. and Ogura, K. Characterization of picric-acid-doped poly (o-toluidine) and the picric-acid-doped poly (o-toluidine)-induced conductive composite of acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene, Synth. Met. 114(2): 155-160 (2000).
Zolfigol, M. A., Ghaemi, E. and Madrakian, E. Nitration of Phenol under Mild and Heterogeneous Conditions, Mol.6: 614-620 (2001).
Dagade, S. P., Kadam, V. S. and Dongare, M. K. Regioselective nitration of phenol over solid acid catalysts, Catal. Commun.3: 67-70 (2002).
Ksibia, M., Zemzemia, A. and Boukchinab, R. Photocatalytic degradability of substituted phenols over UV irradiated TiO2,J. Photochem. And Photobiol. A: Chem. 159 (1): 61-70 (2003).
Noguchi, M., Onuki, T. and Mitamura, J. Hair dye composition. 2003. US. Pat. Appl. 10/148,408.
Shankaran, D. R., Gobi, K. V., Matsumoto, K., Imato, T., Toko, K. and Miura, N. Highly sensitive surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for parts-per-trillion level detection of 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol, Sens. Actuators, B. Chem.100(3): 450-454 (2004).
Nipper, M., Carr, R. S., Biedenbach, J. M., Hooten, D. L. and Miller, k. Fate and effects of picric acid and 2,6-DNT in marine environments: Toxicity of degradation products. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 55 (11): 1205-1217 (2005).
Srinivasan, P., Gunasekaran, M., Kanagasekaran, T., Gopalakrishnan, R. and Ramasamy, P. 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol (TNP): An organic material for nonlinear optical(NLO) applications,J. Cryst. Growth. 289 (2):639-649 (2006).
Greenberg, N. A. and Shipe, W. F. Comparison of the abilities of tricbloroacetic, picric, sulfosalicylic, and tungstic acids to precipitate protein hydrolysate and proteins, J. Food Sci. 44(3): 735-737 (2006).
Weidhaas, J. L., Schroeder, E. D. and Chang, D. P. Y. An aerobic sequencing batch reactor for 2, 4,6 -trinitrophenol (picric acid) biodegradation, Biotechnol. And Bioeng. 97 (6): 1408-1414 (2007).
Goodfellow, W. L., Burton, D. T., Graves, W. C., Hall, L. W. and Cooper, K. R. Acute toxicity of picric acid and picramic acid to rainbow trout, salmogairdneri and American oyster, Crassostrea virginica,J. Am. water Resour. Assoc. 16 (4): 641-648 (2007).
Shen, J., He, R., Yu, H., Wang, L., Zhang, J., Sun, X., Li, J., Han, W. and Xu, L. Biodegradation of 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol (picric acid) in a biological aerated filter (BAF), Bioresour. Technol. 100 (6): 1922-1930 (2009).
Becker, L. C., Bergfeld, W. F., Belsito, D. V., Klaassen, C. D., Marks,J. G., Shank, R. C., Slaga, T. J., Synder, P. W. and Anderson, A. F. Amended safety assessment of sodium picramate and picramic acid, J. Int. Toxicol. 28(6): (2009).
Sheth, A., Doshi, N., Sen, D. J., Badmanaban, R. and Patel, C. N. Synthesis and biological screening of picric acid and amino phenols derivatives for anti-microbial activity,J. Chem. Pharm.2 (2): 1-12 (2010).
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2019 50Sea

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















