Analyzing the Impact of Smog on Human Health in District Lahore, Pakistan
Keywords:
Impact, Smog, Human, Health, Air Pollution, Public HealthAbstract
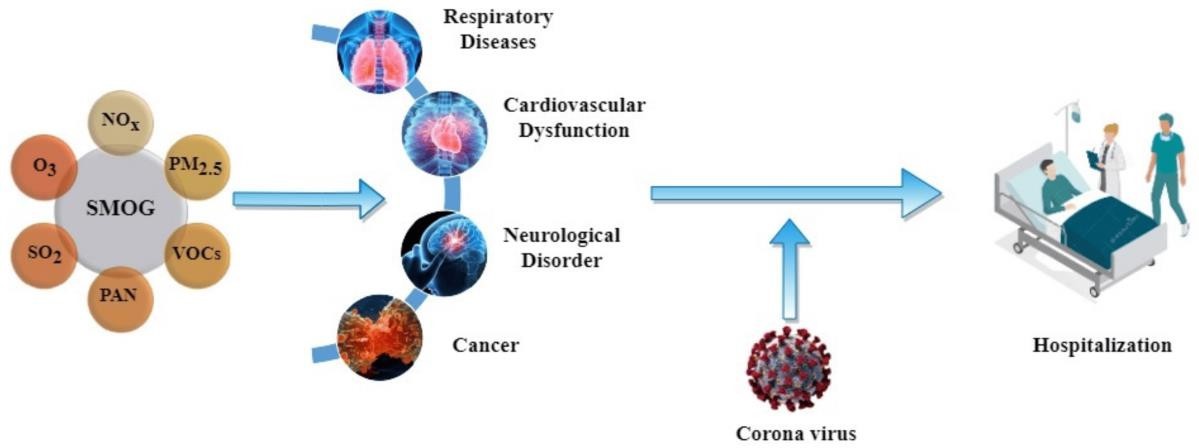
Smog is a term used to describe pollution suspended in humid air, consisting of dust particles of various sizes, non-metal oxides, organic compounds, and heavy metals. Exposure to these toxic compounds, in addition to cigarette smoking, is a significant factor in the development of respiratory diseases. Smog is a visible form of air pollution that results from excessive emissions of primary pollutants such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), hydrocarbons, sulfur dioxide (SO₂), nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), and nitrogen dioxide (NO₂). These pollutants react in the atmosphere to form harmful and carcinogenic secondary smog components. Airborne chemicals that adversely impact public health include ozone and particulate matter (PM) of various sizes—PM2.5, PM2.5–10, and PM10—as well as nitrogen oxides. Special attention is given to lead, carbon dioxide (CO₂), sulfur dioxide (SO₂), and carbon monoxide (CO), with a focus on smaller dust particles (PM10 and PM2.5) because they can penetrate the lower respiratory tract. This page explores the effects of atmospheric pollutants on the onset and exacerbation of respiratory diseases, including asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and lung cancer. It also discusses legislative measures implemented in various countries to mitigate exposure to harmful air pollution. Based on the survey responses, it appears that the individual may be experiencing symptoms related to respiratory, skin, and cardiac conditions, such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. They have been diagnosed with several health issues, including asthma, chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, and ischemic heart disease. Diagnostic tests such as chest X-rays and arterial blood gas (ABG) tests are likely to have been performed during their hospital stay. The individual has reported experiencing symptoms and health effects associated with air pollution or smog during their hospitalization.
References
Naureen I, Saleem A, Aslam S, Zakir L, Mukhtar A, Nazir R, Zulqarnain S. Potential Impact of Smog on Human Health. Haya Saudi J Life Sci. 2022;7(3):78-84.
Gaffney JS, Marley NA, Frederick JE. Formation and effects of smog. Environmental and Ecological Chemistry; Sabljic, A., Ed.; Eolss Publishers Co., Ltd.: Oxford, UK. 2009 Feb 4;2:25-51.
Ali Y, Razi M, De Felice F, Sabir M, Petrillo A. A VIKOR based approach for assessing the social, environmental and economic effects of “smog” on human health. Science of the Total Environment. 2019 Feb 10;650:2897-905.
Grzywa-Celińska A, Krusiński A, Milanowski J. ‘Smoging kills’-effects of air pollution on human respiratory system. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine. 2020;27(1):1-5.
Moelling K, Broecker F. Air microbiome and pollution: composition and potential effects on human health, including SARS coronavirus infection. Journal of environmental and public health. 2020 May 28;2020.
S. Geravandi, P. Sicard, Y. O. Khaniabadi et al., “A comparative study of hospital admissions for respiratory diseases during normal and dusty days in Iran,” Environmental Science and Pollution Research, vol. 24, no. 22, pp. 18152–18159, 2017.
R. B. Hayes, C. Lim, Y. Zhang et al., “PM2.5 air pollution and cause-specific cardiovascular disease mortality,” International Journal of Epidemiology, vol. 49, no. 1, pp. 25–35, 2020.
P. J. Landrigan, R. Fuller, N. J. R. Acosta et al., “The Lancet Commission on pollution and health,” Lancet (London, England), vol. 391, no. 391, pp. 462–512, 2018.
International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA), 2011, http://www.unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/env/documents/2011/eb/wg5/WGSR48/Informal%20docs
/Info.doc.8_CIAM_report_on_Cost_effective_emission_reductions_to_improve_air_quality_in_ Europe_in_2010.pdf.
Javed A, Aamir F, Gohar UF, Mukhtar H, Zia-Ui-Haq M, Alotaibi MO, Bin-Jumah MN, Marc RA, Pop OL. The potential impact of smog spell on humans’ health amid COVID-19 rages. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021 Oct 29;18(21):11408.
Ali Y, Razi M, De Felice F, Sabir M, Petrillo A. A VIKOR based approach for assessing the social, environmental and economic effects of “smog” on human health. Science of the Total Environment. 2019 Feb 10;650:2897-905.
Raza W, Saeed S, Saulat H, Gul H, Sarfraz M, Sonne C, Sohn ZH, Brown RJ, Kim KH. A review on the deteriorating situation of smog and its preventive measures in Pakistan. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2021 Jan 10;279:123676.
Javed A, Aamir F, Gohar UF, Mukhtar H, Zia-Ui-Haq M, Alotaibi MO, Bin-Jumah MN, Marc RA, Pop OL. The potential impact of smog spell on humans’ health amid COVID-19 rages. International journal of environmental research and public health. 2021 Oct 29;18(21):11408.
Usman M, Amjad S, Khan A. Clearing the Air: Legal Strategies for Combating Smog and Pollution. Journal of Strategic Policy and Global Affairs. 2023 Dec 3;4(01).
Ghorani-Azam A, Riahi-Zanjani B, Balali-Mood M. Effects of air pollution on human health and practical measures for prevention in Iran. Journal of research in medical sciences: the official journal of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences. 2016;21.
Naureen I, Saleem A, Aslam S, Zakir L, Mukhtar A, Nazir R, Zulqarnain S. Potential Impact of Smog on Human Health. Haya Saudi J Life Sci. 2022 Mar;7(3):78-84.
Grzywa-Celińska A, Krusiński A, Milanowski J. ‘Smoging kills’-effects of air pollution on human respiratory system. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine. 2020;27(1):1-5
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 50SEA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















