Lightweight Cryptography Algorithms for Internet of Things enabled Networks: A Comparative Study
Keywords:
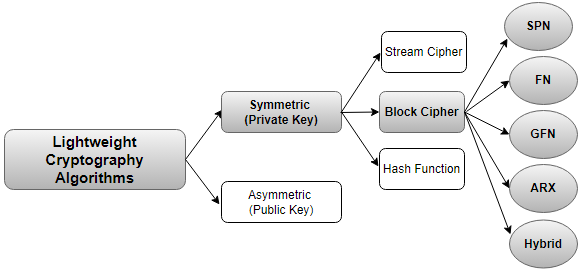
IoT, Lightweight, Lightweight Cryptography, Block Cipher, Cryptography FeatureAbstract
The rapid advancement of technology has facilitated the interconnection of numerous devices, enabling the collection of vast amounts of data. Consequently, ensuring security within Internet of Things networks has become a top priority. Cryptography is crucial in safeguarding network authentication, confidentiality, data integrity, and access control. In Internet of Things settings, conventional cryptographic protocols frequently prove impractical owing to the limitations confronting Internet of Things devices. Consequently, scholars have suggested multiple lightweight cryptographic algorithms and protocols customized for safeguarding data in Internet of Things networks, aiming to overcome this hurdle. This review article delves into the most recent lightweight cryptographic protocols designed for Internet of Things networks and furnishes a comparative evaluation of prevalent modern block ciphers. The comparative study discusses the most recent lightweight cryptographic algorithms in different evaluation parameters in terms of their performance metrics, cryptographic features and offering in-depth analysis of their efficiency. In the concluding section, the paper discusses necessary adaptations and suggests future research directions.
References
A. Hameed and A. Alomary, “Security issues in IoT: A survey,” 2019 Int. Conf. Innov. Intell. Informatics, Comput. Technol. 3ICT 2019, Sep. 2019, doi: 10.1109/3ICT.2019.8910320.
J. Lee, J. Kim, and J. Seo, “Cyber attack scenarios on smart city and their ripple effects,” 2019 Int. Conf. Platf. Technol. Serv. PlatCon 2019 - Proc., Mar. 2019, doi: 10.1109/PLATCON.2019.8669431.
and T. A. K. Demestichas, N. Peppes, “Survey on security threats in agricultural IoT and smart farmingSurvey on security threats in agricultural IoT and smart farming,” Sensors, vol. 20, no. 22, p. 6458, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226458.
M. K. and S. Moriai, “Lightweight cryptography for the internet of things,” Proc. Futur. Technol. Conf., vol. 3, pp. 780–795, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63092-8_52.
and Y. Y. L. Cui, G. Xie, Y. Qu, L. Gao, “Security and Privacy in Smart Cities: Challenges and Opportunities,” IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 46134–46145, 2018, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2853985.
M. Dr. Molly M. Jahn, William L. Oemichen, Dr. Gregory F. Treverton, Scott L. David, B. B. A. Rose, Max A. Brosig, Dr. Buddhika “Jay” Jayamaha, William K. Hutchison, and Rimestad, “Cyber Risk and Security Implications in Smart Agriculture and Food Systems,” White Pap. Jahn Res. Group, Univ. Wisconsin–Madison, Coll. Agric. Life Sci., pp. 1–20, 2019, [Online]. Available: https://jahnresearchgroup.webhosting.cals.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/223/2019/01/Agricultural-Cyber-Risk-and-Security.pdf
J. Laufs, H. Borrion, and B. Bradford, “Security and the smart city: A systematic review,” Sustain. Cities Soc., vol. 55, p. 102023, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102023.
and J. M. A. Gissinga, M. Timmsa, S. Browninga, R. Cromptona, “Compound natural disasters in Australia: a historical analysis,” Environ. Hazards, pp. 159–173, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/17477891.2021.1932405.
T. Bhattasali, “Licrypt: Lightweight cryptography technique for securing smart objects in internet of things environment,” CSI Commun., pp. 26–36, 2013.
S. K. and S. M. M. Gupta, M. Abdelsalam, “Security and Privacy in Smart Farming: Challenges and Opportunities,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 34564–34584, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2975142.
E. R. Naru, H. Saini, and M. Sharma, “A recent review on lightweight cryptography in IoT,” Proc. Int. Conf. IoT Soc. Mobile, Anal. Cloud, I-SMAC 2017, pp. 887–890, Oct. 2017, doi: 10.1109/I-SMAC.2017.8058307.
S. S. Dhanda, B. Singh, and P. Jindal, “Lightweight Cryptography: A Solution to Secure IoT,” Wirel. Pers. Commun., vol. 112, no. 3, pp. 1947–1980, Jun. 2020, doi: 10.1007/S11277-020-07134-3/METRICS.
V. Rao and K. V. Prema, “Comparative Study of Lightweight Hashing Functions for Resource Constrained Devices of IoT,” CSITSS 2019 - 2019 4th Int. Conf. Comput. Syst. Inf. Technol. Sustain. Solut. Proc., Dec. 2019, doi: 10.1109/CSITSS47250.2019.9031038.
and F. A. F. A. Alabaa, M. Othmana, I. A. T. Hashema, “Internet of Things security: A survey,” J. Netw. Comput. Appl., vol. 88, pp. 10–28, 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2017.04.002.
and K. K. V. Varadharajan, U. Tupakula, “Study of Security Attacks Against IoT Infrastructures,” Tech. Rep. TR1 ISIF ASIA Funded Proj., pp. 1–36, 2018, [Online]. Available: https://www.newcastle.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0020/552017/TR1-ISIF-ASIA.pdf
M. Mahbub, “Progressive researches on IoT security: An exhaustive analysis from the perspective of protocols, vulnerabilities, and preemptive architectonics,” J. Netw. Comput. Appl., vol. 168, p. 102761, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102761.
S. N. Swamy, D. Jadhav, and N. Kulkarni, “Security threats in the application layer in IOT applications,” Proc. Int. Conf. IoT Soc. Mobile, Anal. Cloud, I-SMAC 2017, pp. 477–480, Oct. 2017, doi: 10.1109/I-SMAC.2017.8058395.
A. Aggarwal, W. Asif, H. Azam, M. Markovic, M. Rajarajan, and P. Edwards, “User Privacy Risk Analysis for the Internet of Things,” 2019 6th Int. Conf. Internet Things Syst. Manag. Secur. IOTSMS 2019, pp. 259–264, Oct. 2019, doi: 10.1109/IOTSMS48152.2019.8939265.
M. A. Imran Makhdoom and W. N. Abbas, Haider, “Blockchain’s adoption in IoT: The challenges, and a way forward,” J. Netw. Comput. Appl., vol. 125, pp. 251–279, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2018.10.019.
B. C. Chifor, I. Bica, and V. V. Patriciu, “Mitigating DoS attacks in publish-subscribe IoT networks,” Proc. 9th Int. Conf. Electron. Comput. Artif. Intell. ECAI 2017, vol. 2017-January, pp. 1–6, Dec. 2017, doi: 10.1109/ECAI.2017.8166463.
M. Saadeh, A. Sleit, K. E. Sabri, and W. Almobaideen, “Hierarchical architecture and protocol for mobile object authentication in the context of IoT smart cities,” J. Netw. Comput. Appl., vol. 121, pp. 1–19, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2018.07.009.
H. P. Alahari and S. B. Yelavarthi, “Performance Analysis of Denial of Service DoS and Distributed DoS Attack of Application and Network Layer of IoT,” Proc. 3rd Int. Conf. Inven. Syst. Control. ICISC 2019, pp. 72–81, Jan. 2019, doi: 10.1109/ICISC44355.2019.9036403.
F. A. Bakhtiar, E. S. Pramukantoro, and H. Nihri, “A lightweight IDS based on j48 algorithm for detecting DoS attacks on IoT middleware,” 2019 IEEE 1st Glob. Conf. Life Sci. Technol. LifeTech 2019, pp. 41–42, Mar. 2019, doi: 10.1109/LIFETECH.2019.8884057.
I. G.-M. and J. L. M. M. Nasralla, “Defenses Against Perception-Layer Attacks on IoT Smart Furniture for Impaired People,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 119795–119805, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3004814.
Y. M. Tukur and Y. S. Ali, “Demonstrating the Effect of Insider Attacks on Perception Layer of Internet of Things (IoT) Systems,” 2019 15th Int. Conf. Electron. Comput. Comput. ICECCO 2019, Dec. 2019, doi: 10.1109/ICECCO48375.2019.9043248.
R. Kanagavelu and K. M. M. Aung, “A Survey on SDN Based Security in Internet of Things,” Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput., vol. 887, pp. 563–577, 2019, doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-03405-4_39.
A. K. Mishra, A. K. Tripathy, D. Puthal, and L. T. Yang, “Analytical Model for Sybil Attack Phases in Internet of Things,” IEEE Internet Things J., vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 379–387, Feb. 2019, doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2843769.
Y. Yang, L. Wu, G. Yin, L. Li, and H. Zhao, “A Survey on Security and Privacy Issues in Internet-of-Things,” IEEE Internet Things J., vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 1250–1258, Oct. 2017, doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2694844.
R. Yugha and S. Chithra, “A survey on technologies and security protocols: Reference for future generation IoT,” J. Netw. Comput. Appl., vol. 169, p. 102763, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102763.
Q. Jing, A. V. Vasilakos, J. Wan, J. Lu, and D. Qiu, “Security of the Internet of Things: perspectives and challenges,” Wirel. Networks, vol. 20, no. 8, pp. 2481–2501, Oct. 2014, doi: 10.1007/S11276-014-0761-7.
and N. M. K. McKay, L. Bassham, M. Snmez Turan, “Report on Lightweight Cryptography,” NISTIR, pp. 1–27, 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.6028/NIST.IR.8114.
M. A. R. and M. R. A. K. V. A. Thakor, “Lightweight Cryptography Algorithms for Resource-Constrained IoT Devices: A Review, Comparison and Research Opportunities,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 28177–28193, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3052867.
and M. I. H. A. Khattak, M. A. Shah, S. Khan, I. Ali, “Perception layer security in Internet of Things,” Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst., vol. 100, pp. 144–164, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.04.038.
and K. S. G. Leander, C. Paar, A. Poschmann, “New Lightweight DES Variants,” Springer, Berlin, Heidelb., pp. 196–210, 2007, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74619-5_13.
A. Shah and M. Engineer, “A Survey of Lightweight Cryptographic Algorithms for IoT-Based Applications,” Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput., vol. 851, pp. 283–293, 2019, doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-2414-7_27.
A. Bogdanov et al., “PRESENT: An ultra-lightweight block cipher,” Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. (including Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinformatics), vol. 4727 LNCS, pp. 450–466, 2007, doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-74735-2_31.
I. Bhardwaj, A. Kumar, and M. Bansal, “A review on lightweight cryptography algorithms for data security and authentication in IoTs,” 4th IEEE Int. Conf. Signal Process. Comput. Control. ISPCC 2017, vol. 2017-January, pp. 504–509, Sep. 2017, doi: 10.1109/ISPCC.2017.8269731.
W. Zhang, Z. Bao, D. Lin, V. Rijmen, B. Yang, and I. Verbauwhede, “RECTANGLE: A bit-slice lightweight block cipher suitable for multiple platforms,” Sci. China Inf. Sci., vol. 58, no. 12, pp. 1–15, Dec. 2015, doi: 10.1007/S11432-015-5459-7/METRICS.
T. A. and H. Hiwatari, “Very compact Hardware Implementations of the Block cipher CLEFIA,” Sel. Areas Cryptogr. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. Springer, pp. 278–292, 2012, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-28496-0_17.
D. Hong, “HIGHT: A New Block Cipher Suitable for Low Resource Device,” Cryptogr. Hardw. Embed. Syst. CHES 2006 Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. Springer, pp. 46–59, 2006, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/11894063_4.
A. S. and S. Morioka, “Hardware-Focused Performance Comparison for the Standard Block Ciphers AES, Camellia, and Triple-DES,” Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. Inf. Secur. Springer, pp. 252–266, 2003, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/10958513_20.
D. J. W. & R. M. Needham, “TEA, a tiny encryption algorithm,” Proceeding Int. Work. Fast Softw. Encryption”, Springer, Berlin, pp. 363–366, 1995, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-60590-8_29.
R. Beaulieu, S. Treatman-Clark, D. Shors, B. Weeks, J. Smith, and L. Wingers, “The SIMON and SPECK lightweight block cIPhers,” Proc. - Des. Autom. Conf., vol. 2015-July, Jul. 2015, doi: 10.1145/2744769.2747946.
A. V. Duka and B. Genge, “Implementation of SIMON and SPECK lightweight block ciphers on programmable logic controllers,” 2017 5th Int. Symp. Digit. Forensic Secur. ISDFS 2017, May 2017, doi: 10.1109/ISDFS.2017.7916501.
and E. K. T. Suzaki, K. Minematsu, S. Morioka, “TWINE: A Lightweight Block Cipher for Multiple Platforms,” Springer, pp. 339–354, 2012, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-35999-6_22.
L. Sleem and R. Couturier, “Speck-R: An ultra light-weight cryptographic scheme for Internet of Things,” Multimed. Tools Appl., vol. 80, no. 11, pp. 17067–17102, May 2021, doi: 10.1007/S11042-020-09625-8/METRICS.
P. Panahi, C. Bayılmış, U. Çavuşoğlu, and S. Kaçar, “Performance Evaluation of Lightweight Encryption Algorithms for IoT-Based Applications,” Arab. J. Sci. Eng., vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 4015–4037, Apr. 2021, doi: 10.1007/S13369-021-05358-4/METRICS.
and Ľ. C. I. Sokol, P. Hubinský, “Lightweight Cryptography for the Encryption of Data Communication of IoT Devices,” Electron., vol. 10, no. 21, p. 2567, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10212567.
Y. Guo, L. Li, and B. Liu, “Shadow: A Lightweight Block Cipher for IoT Nodes,” IEEE Internet Things J., vol. 8, no. 16, pp. 13014–13023, Aug. 2021, doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3064203.
and V. V. L. M. Shamala, G. Zayaraz, K. Vivekanandan, “Lightweight cryptography algorithms for internet of things enabled networks: An overview,” J. Phys. Conf. Ser., vol. 1717, no. 1, p. 012072, 2021, doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1717/1/012072.
and M. S. S. P. Prakasam, M. Madheswaran, K. P. Sujith, “An Enhanced Energy Efficient Lightweight Cryptography Method for various IoT devices,” ICT Express, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 487–492, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icte.2021.03.007.
A. Biswas, A. Majumdar, S. Nath, A. Dutta, and K. L. Baishnab, “LRBC: a lightweight block cipher design for resource constrained IoT devices,” J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput., vol. 14, no. 5, pp. 5773–5787, May 2023, doi: 10.1007/S12652-020-01694-9/METRICS.
and A. F. M. El-Hajj, H. Mousawi, “Analysis of lightweight cryptographic algorithms on iot hardware platform,” Futur. Internet, vol. 15, no. 2, p. 54, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15020054.
F. Thabit, O. Can, A. O. Aljahdali, G. H. Al-Gaphari, and H. A. Alkhzaimi, “Cryptography Algorithms for Enhancing IoT Security,” Internet of Things (Netherlands), vol. 22, Jul. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.iot.2023.100759.
K. B. Jithendra and T. Kassim Shahana, “ACT: An ultra-light weight block cipher for internet of things,” Int. J. Comput. Digit. Syst., vol. 9, no. 5, pp. 921–929, 2020.
P. Jha, H. Y. Zorkta, D. Allawi, and M. R. Al-Nakkar, “Improved lightweight encryption Algorithm (ILEA),” 2020 Int. Conf. Emerg. Technol. INCET 2020, Jun. 2020, doi: 10.1109/INCET49848.2020.9154170.
and A. A. H. P. C. Encarnacion, B. D. Gerardo, “Modified round function of SIMECK 32/64 block cipher,” Int. J. Adv. Trends Comput. Sci. Eng., vol. 9, no. 1–3, pp. 1–9, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.30534/ijatcse/2020/3991.32020.
and A. H. Z. S. Toprak, A. Akbulut, M. A. Aydın, “LWE: An energy-efficient lightweight encryption algorithm for medical sensors and IoT devices,” Istanbul Univ. - J. Electr. Electron. Eng., vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 71–80, 2020, doi: 10.5152/electrica.2020.19082.
and B. J. C. Thorat, V. Inamdar, “TED: A LIGHTWEIGHT BLOCK CIPHER FOR IoT DEVICES WITH SIDE-CHANNEL ATTACK RESISTANCE,” Int. J. Inf. Technol. Secur., vol. 12, no. 2, p. 83, 2020, [Online]. Available: https://openurl.ebsco.com/EPDB%3Agcd%3A9%3A1547961/detailv2?sid=ebsco%3Aplink%3Ascholar&id=ebsco%3Agcd%3A143815102&crl=c&link_origin=www.google.com
K. Sakamoto et al., “Tweakable TWINE: Building a Tweakable Block Cipher on Generalized Feistel Structure,” IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci., vol. E103.A, no. 12, pp. 1629–1639, Dec. 2020, doi: 10.1587/TRANSFUN.2019EAP1141.
D. Sehrawat and N. Gill, “Ultra BRIGHT: a tiny and fast ultra lightweight block cipher for IoT,” Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res., vol. 9, p. 1063, 2020.
N. H. Z. and M. D. A. A. Zakaria, A. H. Azni, F. Ridzuan, “Extended RECTANGLE Algorithm Using 3D Bit Rotation to Propose a New Lightweight Block Cipher for IoT,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 198646–198658, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3035375.
and M. E. R. A. Ramadan, B. W. Aboshosha, K. Yadav, I. M. Alseadoon, M. J. Kashout, “LBC-IoT: Lightweight Block Cipher for IoT Constraint Devices,” Comput. Mater. Contin., vol. 67, no. 3, pp. 3563–3579, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2021.015519.
and M. D. A. A. Zakaria, A. H. Ab Halim, F. Ridzuan, N. H. Zakaria, “LAO-3D: A Symmetric Lightweight Block Cipher Based on 3D Permutation for Mobile Encryption Application,” Symmetry (Basel)., vol. 14, no. 10, p. 2042, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14102042.
and J. Y. X. Huang, L. Li, “IVLBC: An involutive lightweight block cipher for Internet of Things,” IEEE Syst. J., vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 3192–3203, 2023, doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2022.3227951.
R. B. and N. Parvatham, “Light-Weight Present Block Cipher Model for IoT Security on FPGA,” Intell. Autom. Soft Comput., vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 13–34, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.32604/iasc.2022.020681.
J. Feng and L. Li, “SCENERY: a lightweight block cipher based on Feistel structure,” Front. Comput. Sci., vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 1–10, Jun. 2022, doi: 10.1007/S11704-020-0115-9/METRICS.
A. E.-S. and M. M. D. B. Aboushosha, R. A. Ramadan, A. D. Dwivedi, “SLIM: A Lightweight Block Cipher for Internet of Health Things,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 203747–203757, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3036589.
L. L. Juanli Kuang, Ying Guo, “IIoTBC: A Lightweight Block Cipher for Industrial IoT Security,” KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst., vol. 17, no. 1, 2023, doi: 10.3837/tiis.2023.01.006.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 50SEA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















