EEG Based BCI for Intelligent Wheelchair Control System Using Deep Learning
Keywords:
EEG, BCI, Motor Imagery, Transformer Model, Wheelchair NavigationAbstract
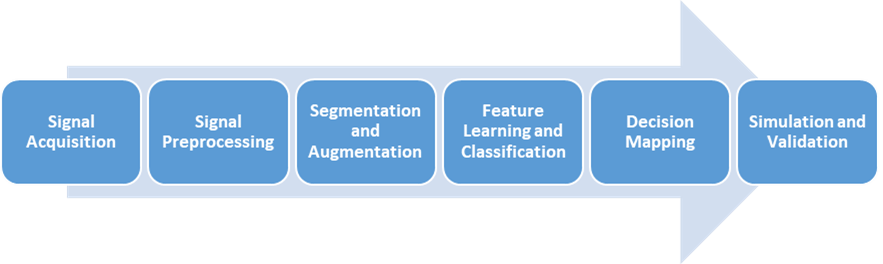
This research study presents the design of an Electroencephalography (EEG) based Brain Computer Interface (BCI) for intelligent wheelchair control to assist patients with mobility disorders. The concept of this research is to enable a direct communication link between the human brain and the machine without physical movement. This study used the BCI Competition IV 2a dataset, which contains EEG recordings of nine subjects performing four motor imagery (MI) tasks that were mapped to wheelchair navigation commands such as turning left, right, moving forward, and stopping. In this study, a deep learning architecture, TCFormer (Temporal Convolutional Transformer), was implemented to learn the spatial and temporal correlations between EEG channels. A lightweight Fusion Head module was added to enhance performance. It consisted of one-dimensional convolution and adaptive pooling operations for improved local temporal feature extraction. The proposed TCFormer-Fusion model achieved an overall classification accuracy of 75%, outperforming the baseline TCFormer model by 72%. Overall, this research study demonstrates that transformer-based models can learn complex EEG signal representations for motor imagery classification. The proposed model contributes toward developing an intelligent wheelchair control system that operates on brain signals, reducing external assistance. This work, with further optimization and real-time implementation, can contribute significantly to the assistive technology and human-computer interaction fields.
References
J. J. Vidal, “Toward direct brain-computer communication.,” Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng., vol. 2, no. Volume 2, 1973, pp. 157–180, Jun. 1973, doi: 10.1146/ANNUREV.BB.02.060173.001105/CITE/REFWORKS.
A. S. Widge, C. T. Moritz, and Y. Matsuoka, “Direct Neural Control of Anatomically Correct Robotic Hands,” pp. 105–119, 2010, doi: 10.1007/978-1-84996-272-8_7.
A. Nurmikko, “Challenges for Large-Scale Cortical Interfaces,” Neuron, vol. 108, no. 2, pp. 259–269, Oct. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.10.015.
E. C. Leuthardt, G. Schalk, J. R. Wolpaw, J. G. Ojemann, and D. W. Moran, “A brain–computer interface using electrocorticographic signals in humans*,” J. Neural Eng., vol. 1, no. 2, p. 63, Jun. 2004, doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/1/2/001.
G. Pfurtscheller and F. H. Lopes Da Silva, “Event-related EEG/MEG synchronization and desynchronization: basic principles,” Clin. Neurophysiol., vol. 110, no. 11, pp. 1842–1857, Nov. 1999, doi: 10.1016/S1388-2457(99)00141-8.
M. Y. M. Naser and S. Bhattacharya, “Towards Practical BCI-Driven Wheelchairs: A Systematic Review Study,” IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng., vol. 31, pp. 1030–1044, 2023, doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2023.3236251.
L. F. Nicolas-Alonso and J. Gomez-Gil, “Brain Computer Interfaces, a Review,” Sensors 2012, Vol. 12, Pages 1211-1279, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 1211–1279, Jan. 2012, doi: 10.3390/S120201211.
M. Orban, M. Elsamanty, K. Guo, S. Zhang, and H. Yang, “A Review of Brain Activity and EEG-Based Brain–Computer Interfaces for Rehabilitation Application,” Bioeng. 2022, Vol. 9, Page 768, vol. 9, no. 12, p. 768, Dec. 2022, doi: 10.3390/Bioengineering9120768.
X. Wan et al., “A Review on Electroencephalogram Based Brain Computer Interface for Elderly Disabled,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 36380–36387, 2019, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2903235.
B. Rebsamen et al., “A brain controlled wheelchair to navigate in familiar environments,” IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng., vol. 18, no. 6, pp. 590–598, Dec. 2010, doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2010.2049862.
M. Li, Y. Zhang, H. Zhang, and H. Hu, “An EEG Based Control System for Intelligent Wheelchair,” Appl. Mech. Mater., vol. 300–301, pp. 1540–1545, 2013, doi: 10.4028/WWW.SCIENTIFIC.NET/AMM.300-301.1540.
R. Bousseta, I. El Ouakouak, M. Gharbi, and F. Regragui, “EEG Based Brain Computer Interface for Controlling a Robot Arm Movement Through Thought,” IRBM, vol. 39, no. 2, pp. 129–135, Apr. 2018, doi: 10.1016/J.IRBM.2018.02.001.
F. A. Al-Nuaimi, R. J. Al-Nuaimi, S. S. Al-Dhaheri, S. Ouhbi, and A. N. Belkacem, “Mind Drone Chasing Using EEG-based Brain Computer Interface,” Proc. 2020 16th Int. Conf. Intell. Environ. IE 2020, pp. 74–79, Jul. 2020, doi: 10.1109/IE49459.2020.9154926.
M. M. Rafiq, S. K. Noon, A. Mannan, T. Awan, and N. Nisar, “Design and Implementation of Brain-Based Home Automation System,” VFAST Trans. Softw. Eng., vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 53–61, Sep. 2023, doi: 10.21015/VTSE.V11I3.1577.
J. S. Kumar and P. Bhuvaneswari, “Analysis of Electroencephalography (EEG) Signals and Its Categorization–A Study,” Procedia Eng., vol. 38, pp. 2525–2536, Jan. 2012, doi: 10.1016/J.PROENG.2012.06.298.
M. Grilo et al., “Limbs movement and motor imagery: An EEG study,” 2019 7th E-Health Bioeng. Conf. EHB 2019, Nov. 2019, doi: 10.1109/EHB47216.2019.8969891.
A. Delorme, S. Makeig, and T. Sejnowski, “Automatic Artifact Rejection For Eeg Data Using High-Order Statistics And Independent Component Analysis”, Accessed: Nov. 21, 2025. [Online]. Available: www.salk.edu/~scott/ica.html
N. Padfield, J. Zabalza, H. Zhao, V. Masero, and J. Ren, “EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces Using Motor-Imagery: Techniques and Challenges,” Sensors 2019, Vol. 19, Page 1423, vol. 19, no. 6, p. 1423, Mar. 2019, doi: 10.3390/S19061423.
T. Barbera et al., “On Using AI for EEG-Based BCI Applications: Problems, Current Challenges and Future Trends,” Int. J. Human–Computer Interact., pp. 1–20, Sep. 2025, doi: 10.1080/10447318.2025.2561185;WGROUP:STRING:PUBLICATION.
G. Bao et al., “Data Augmentation for EEG-Based Emotion Recognition Using Generative Adversarial Networks,” Front. Comput. Neurosci., vol. 15, p. 723843, Dec. 2021, doi: 10.3389/FNCOM.2021.723843/BIBTEX.
F. Lotte and C. Guan, “Regularizing common spatial patterns to improve BCI designs: Unified theory and new algorithms,” IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., vol. 58, no. 2, pp. 355–362, Feb. 2011, doi: 10.1109/TBME.2010.2082539.
F. Lotte, M. Congedo, A. Lécuyer, F. Lamarche, and B. Arnaldi, “A review of classification algorithms for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces,” J. Neural Eng., vol. 4, no. 2, p. R1, Jan. 2007, doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/4/2/R01.
F. J. Ramírez-Arias et al., “Evaluation of Machine Learning Algorithms for Classification of EEG Signals,” Technologies, vol. 10, no. 4, p. 79, Aug. 2022, doi: 10.3390/TECHNOLOGIES10040079/S1.
M. Mohammadpour, M. K. Ghorbanian, and S. Mozaffari, “Comparison of EEG signal features and ensemble learning methods for motor imagery classification,” 2016 8th Int. Conf. Inf. Knowl. Technol. IKT 2016, pp. 288–292, Dec. 2016, doi: 10.1109/IKT.2016.7777767.
A. Echtioui, W. Zouch, M. Ghorbel, C. Mhiri, and H. Hamam, “A Novel Ensemble Learning Approach for Classification of EEG Motor Imagery Signals,” 2021 Int. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. IWCMC 2021, pp. 1648–1653, 2021, doi: 10.1109/IWCMC51323.2021.9498833.
A. M. Hamed, A. F. Attia, and H. El-Behery, “Optimization of EEG-based wheelchair control: machine learning, feature selection, outlier management, and explainable AI,” J. Big Data 2025 121, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 175-, Jul. 2025, doi: 10.1186/S40537-025-01238-Y.
B. Paneru, B. Paneru, B. Thapa, and K. N. Poudyal, “EEG-based AI-BCI Wheelchair Advancement: A Brain-Computer Interfacing Wheelchair System Using Deep Learning Approach,” Oct. 2024, Accessed: Nov. 22, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.09763v4
Seyed-Ali Sadegh-Zadeh, Nasrin Sadeghzadeh, S. Ommolbanin Soleimani,Saeed Shiry Ghidary, and S.-Y. M. Movahedi, “Comparative analysis of dimensionality reduction techniques for EEG-based emotional state classification,” Am J Neurodegener Dis, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 23–33, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.62347/ZWRY8401.
X. Gu et al., “EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs): A Survey of Recent Studies on Signal Sensing Technologies and Computational Intelligence Approaches and Their Applications,” IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinforma., vol. 18, no. 5, pp. 1645–1666, 2021, doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2021.3052811.
P. Wang, J. Lu, B. Zhang, and Z. Tang, “A review on transfer learning for brain-computer interface classification,” 2015 5th Int. Conf. Inf. Sci. Technol. ICIST 2015, pp. 315–322, Oct. 2015, doi: 10.1109/ICIST.2015.7288989.
D. Wu, J. T. King, C. H. Chuang, C. T. Lin, and T. P. Jung, “Spatial Filtering for EEG-Based Regression Problems in Brain-Computer Interface (BCI),” IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 771–781, Apr. 2018, doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2017.2688423.
G. E. Fabiani, D. J. McFarland, J. R. Wolpaw, and G. Pfurtscheller, “Conversion of EEG activity into cursor movement by a brain-computer interface (BCI),” IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng., vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 331–338, Sep. 2004, doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2004.834627.
A. Subasi and E. Erçelebi, “Classification of EEG signals using neural network and logistic regression,” Comput. Methods Programs Biomed., vol. 78, no. 2, pp. 87–99, May 2005, doi: 10.1016/J.CMPB.2004.10.009.
V. J. Lawhern, A. J. Solon, N. R. Waytowich, S. M. Gordon, C. P. Hung, and B. J. Lance, “EEGNet: a compact convolutional neural network for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces,” J. Neural Eng., vol. 15, no. 5, p. 056013, Jul. 2018, doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/AACE8C.
R. T. Schirrmeister et al., “Deep learning with convolutional neural networks for EEG decoding and visualization,” Hum. Brain Mapp., vol. 38, no. 11, pp. 5391–5420, Nov. 2017, doi: 10.1002/HBM.23730; Journal:10970193;Wgroup:String:Publication.
Y. Roy, H. Banville, I. Albuquerque, A. Gramfort, T. H. Falk, and J. Faubert, “Deep learning-based electroencephalography analysis: a systematic review,” J. Neural Eng., vol. 16, no. 5, p. 051001, Aug. 2019, doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/AB260C.
H. Li, M. Ding, R. Zhang, and C. Xiu, “Motor imagery EEG classification algorithm based on CNN-LSTM feature fusion network,” Biomed. Signal Process. Control, vol. 72, p. 103342, Feb. 2022, doi: 10.1016/J.BSPC.2021.103342.
Z. Khademi, F. Ebrahimi, and H. M. Kordy, “A transfer learning-based CNN and LSTM hybrid deep learning model to classify motor imagery EEG signals,” Comput. Biol. Med., vol. 143, p. 105288, Apr. 2022, doi: 10.1016/J.COMPBIOMED.2022.105288.
Y. E. Lee and S. H. Lee, “EEG-Transformer: Self-attention from Transformer Architecture for Decoding EEG of Imagined Speech,” Int. Winter Conf. Brain-Computer Interface, BCI, vol. 2022-February, 2022, doi: 10.1109/BCI53720.2022.9735124.
B. Abibullaev, A. Keutayeva, and A. Zollanvari, “Deep Learning in EEG-Based BCIs: A Comprehensive Review of Transformer Models, Advantages, Challenges, and Applications,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 127271–127301, 2023, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3329678.
Z. Wan, R. Yang, M. Huang, N. Zeng, and X. Liu, “A review on transfer learning in EEG signal analysis,” Neurocomputing, vol. 421, pp. 1–14, Jan. 2021, doi: 10.1016/J.NEUCOM.2020.09.017.
L. Hu, W. Hong, and L. Liu, “MSATNet: multi-scale adaptive transformer network for motor imagery classification,” Front. Neurosci., vol. 17, p. 1173778, Jun. 2023, doi: 10.3389/FNINS.2023.1173778/BIBTEX.
H. Gu, T. Chen, X. Ma, M. Zhang, Y. Sun, and J. Zhao, “CLTNet: A Hybrid Deep Learning Model for Motor Imagery Classification,” Brain Sci. 2025, Vol. 15, Page 124, vol. 15, no. 2, p. 124, Jan. 2025, doi: 10.3390/BRAINSCI15020124.
W. Zgallai et al., “Deep Learning AI Application to an EEG driven BCI Smart Wheelchair,” 2019 Adv. Sci. Eng. Technol. Int. Conf. ASET 2019, May 2019, doi: 10.1109/ICASET.2019.8714373.
T. M. Ingolfsson, M. Hersche, X. Wang, N. Kobayashi, L. Cavigelli, and L. Benini, “EEG-TCNet: An Accurate Temporal Convolutional Network for Embedded Motor-Imagery Brain-Machine Interfaces,” Conf. Proc. - IEEE Int. Conf. Syst. Man Cybern., vol. 2020-October, pp. 2958–2965, Oct. 2020, doi: 10.1109/SMC42975.2020.9283028.
R. Yang and E. Modesitt, “ViT2EEG: Leveraging Hybrid Pretrained Vision Transformers for EEG Data,” Proc. KDD Undergrad. Consort. (KDD-UC ’23), vol. 1, Aug. 2023,
H. Altaheri, F. Karray, and A. H. Karimi, “Temporal convolutional transformer for EEG based motor imagery decoding,” Sci. Reports 2025 151, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 32959-, Sep. 2025, doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-16219-7.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 50sea

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















