Enhancing Cardiovascular Disease Risk Prediction Using Resampling and Machine Learning
Keywords:
Machine Learning, Cardiovascular Disease, Risk Prediction, Resampling, Random Forest Model.Abstract
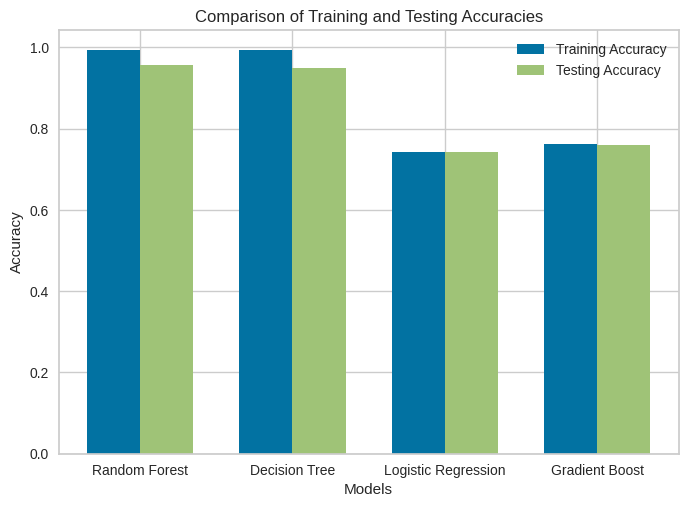
Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) remains a critical health concern around the globe, requiring precise risk prediction approaches for timely intervention. The primary motive of this study is to enhance CVD risk prediction through innovative techniques, just like resampling the imbalanced datasets using random oversampling and employing advanced Machine Learning (ML). In this study, different robust ML algorithms such as Random Forest Classifier, Decision Tree Classifier, XGBoost Classifier and Logistic Regression were trained on a diverse dataset encompassing demographic, clinical and lifestyle factors related to CVD. By addressing class imbalance through oversampling, the models showed significant performance improvements, showcasing the effectiveness of our ML algorithms in accurately forecasting CVD risks. Specifically, the Random Forest model with an accuracy score of 96% and AUC-ROC score of 99%. This study emphasizes the potential of modern approaches to improve CVD risk assessment by leveraging cutting-edge technologies for enhanced healthcare outcomes. Enfolding these approaches and tools, it becomes easy to pave the way for more personalized risk assessment and early intervention strategies, eventually aiming to alleviate the global burden of CVD.
References
M. Bakhtiyari et al., “Contribution of obesity and cardiometabolic risk factors in developing cardiovascular disease: a population-based cohort study,” Sci. Reports 2022 121, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 1–10, Jan. 2022, doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05536-w.
M. Y. Henein, S. Vancheri, G. Longo, and F. Vancheri, “The Role of Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease,” Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, Vol. 23, Page 12906, vol. 23, no. 21, p. 12906, Oct. 2022, doi: 10.3390/IJMS232112906.
S. Tiwari et al., “Lifestyle factors as mediators of area-level socio-economic differentials in cardiovascular disease risk factors. The Tromsø Study,” SSM - Popul. Heal., vol. 19, p. 101241, Sep. 2022, doi: 10.1016/J.SSMPH.2022.101241.
C. Y. Jurgens et al., “State of the Science: The Relevance of Symptoms in Cardiovascular Disease and Research: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association,” Circulation, vol. 146, no. 12, pp. E173–E184, Sep. 2022, doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001089.
S. Ghorashi et al., “Leveraging Regression Analysis to Predict Overlapping Symptoms of Cardiovascular Diseases,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 60254–60266, 2023, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3286311.
M. Jafari et al., “Automated diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases from cardiac magnetic resonance imaging using deep learning models: A review,” Comput. Biol. Med., vol. 160, p. 106998, Jun. 2023, doi: 10.1016/J.COMPBIOMED.2023.106998.
H. R. H. Al-Absi, M. T. Islam, M. A. Refaee, M. E. H. Chowdhury, and T. Alam, “Cardiovascular Disease Diagnosis from DXA Scan and Retinal Images Using Deep Learning,” Sensors, vol. 22, no. 12, p. 4310, Jun. 2022, doi: 10.3390/S22124310/S1.
G. Nicholson, S. R. Gandra, R. J. Halbert, A. Richhariya, and R. J. Nordyke, “Patient-level costs of major cardiovascular conditions: a review of the international literature,” Clin. Outcomes Res., vol. 8, pp. 495–506, Sep. 2016, doi: 10.2147/CEOR.S89331.
R. Luengo-Fernandez et al., “Cardiovascular disease burden due to productivity losses in European Society of Cardiology countries,” Eur. Hear. J. - Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 36–44, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.1093/EHJQCCO/QCAD031.
S. Mendis, I. Graham, and J. Narula, “Editorial: Reducing cardiovascular disease mortality and morbidity: implementing cost-effective and sustainable preventive interventions,” Front. Cardiovasc. Med., vol. 10, p. 1236210, Jun. 2023, doi: 10.3389/FCVM.2023.1236210/BIBTEX.
R. Bharti, A. Khamparia, M. Shabaz, G. Dhiman, S. Pande, and P. Singh, “Prediction of Heart Disease Using a Combination of Machine Learning and Deep Learning,” Comput. Intell. Neurosci., vol. 2021, 2021, doi: 10.1155/2021/8387680.
M. Pal, S. Parija, G. Panda, K. Dhama, and R. K. Mohapatra, “Risk prediction of cardiovascular disease using machine learning classifiers,” Open Med., vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 1100–1113, Jan. 2022, doi: 10.1515/MED-2022-0508/MACHINEREADABLECITATION/RIS.
S. Subramani et al., “Cardiovascular diseases prediction by machine learning incorporation with deep learning,” Front. Med., vol. 10, p. 1150933, Apr. 2023, doi: 10.3389/FMED.2023.1150933/BIBTEX.
A. Ogunpola, F. Saeed, S. Basurra, A. M. Albarrak, and S. N. Qasem, “Machine Learning-Based Predictive Models for Detection of Cardiovascular Diseases,” Diagnostics 2024, Vol. 14, Page 144, vol. 14, no. 2, p. 144, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.3390/DIAGNOSTICS14020144.
J. P. Li, A. U. Haq, S. U. Din, J. Khan, A. Khan, and A. Saboor, “Heart Disease Identification Method Using Machine Learning Classification in E-Healthcare,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 107562–107582, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3001149.
E. Dritsas, S. Alexiou, and K. Moustakas, “Cardiovascular Disease Risk Prediction with Supervised Machine Learning Techniques,” Int. Conf. Inf. Commun. Technol. Ageing Well e-Health, ICT4AWE - Proc., pp. 315–321, 2022, doi: 10.5220/0011088300003188.
K. Drożdż et al., “Risk factors for cardiovascular disease in patients with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: a machine learning approach,” Cardiovasc. Diabetol., vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 1–12, Dec. 2022, doi: 10.1186/S12933-022-01672-9/FIGURES/3.
E. Dritsas and M. Trigka, “Efficient Data-Driven Machine Learning Models for Cardiovascular Diseases Risk Prediction,” Sensors 2023, Vol. 23, Page 1161, vol. 23, no. 3, p. 1161, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.3390/S23031161.
N. Chandrasekhar and S. Peddakrishna, “Enhancing Heart Disease Prediction Accuracy through Machine Learning Techniques and Optimization,” Process. 2023, Vol. 11, Page 1210, vol. 11, no. 4, p. 1210, Apr. 2023, doi: 10.3390/PR11041210.
U. Kamdi, “Heart Disease Prediction Using Machine Learning,” vol. 4, no. 12, 2023.
M. P. Behera, A. Sarangi, D. Mishra, and S. K. Sarangi, “A Hybrid Machine Learning algorithm for Heart and Liver Disease Prediction Using Modified Particle Swarm Optimization with Support Vector Machine,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 218, pp. 818–827, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.1016/J.PROCS.2023.01.062.
P. S. Asih, Y. Azhar, G. W. Wicaksono, and D. R. Akbi, “Interpretable Machine Learning Model For Heart Disease Prediction,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 227, pp. 439–445, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.1016/J.PROCS.2023.10.544.
Z. K. D. Alkayyali, S. Anuar Bin Idris, and S. S. Abu-Naser, “A SYSTEMATIC LITERATURE REVIEW OF DEEP AND MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHMS IN CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES DIAGNOSIS,” J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol., vol. 28, no. 4, 2023, Accessed: May 20, 2024. [Online]. Available: www.jatit.org
M. Moshawrab, M. Adda, A. Bouzouane, H. Ibrahim, and A. Raad, “Smart Wearables for the Detection of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Literature Review,” Sensors 2023, Vol. 23, Page 828, vol. 23, no. 2, p. 828, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.3390/S23020828.
A. Khan, M. Qureshi, M. Daniyal, and K. Tawiah, “A Novel Study on Machine Learning Algorithm-Based Cardiovascular Disease Prediction,” Health Soc. Care Community, vol. 2023, pp. 1–10, Feb. 2023, doi: 10.1155/2023/1406060.
P. Rani, R. Kumar, N. M. O. S. Ahmed, and A. Jain, “A decision support system for heart disease prediction based upon machine learning,” J. Reliab. Intell. Environ., vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 263–275, Sep. 2021, doi: 10.1007/S40860-021-00133-6/METRICS.
C. Gupta, A. Saha, N. V. S. Reddy, and U. D. Acharya, “Cardiac Disease Prediction using Supervised Machine Learning Techniques.,” J. Phys. Conf. Ser., vol. 2161, no. 1, p. 012013, Jan. 2022, doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2161/1/012013.
M. M. Mijwil, A. K. Faieq, and M. Aljanabi, “Early Detection of Cardiovascular Disease Utilizing Machine Learning Techniques: Evaluating the Predictive Capabilities of Seven Algorithms,” Iraqi J. Comput. Sci. Math., vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 263–276, Feb. 2024, doi: 10.52866/IJCSM.2024.05.01.018.
“View of A Detailed Analysis of Detecting Heart Diseases Using Artificial Intelligence Methods.” Accessed: May 20, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://imiens.org/index.php/imiens/article/view/43/24
S. Mohan, C. Thirumalai, and G. Srivastava, “Effective heart disease prediction using hybrid machine learning techniques,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 81542–81554, 2019, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2923707.
S. Ahmed et al., “Prediction of Cardiovascular Disease on Self-Augmented Datasets of Heart Patients Using Multiple Machine Learning Models,” J. Sensors, vol. 2022, 2022, doi: 10.1155/2022/3730303.
K. Dissanayake and M. G. M. Johar, “Comparative study on heart disease prediction using feature selection techniques on classification algorithms,” Appl. Comput. Intell. Soft Comput., vol. 2021, 2021, doi: 10.1155/2021/5581806.
H. Arghandabi and P. Shams, “A Comparative Study of Machine Learning Algorithms for the Prediction of Heart Disease,” vol. 8, 2020, doi: 10.22214/ijraset.2020.32591.
A. O. Salau, T. A. Assegie, E. D. Markus, J. N. Eneh, and T. I. Ozue, “Prediction of the risk of developing heart disease using logistic regression,” Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng., vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 1809–1815, Apr. 2024, doi: 10.11591/IJECE.V14I2.PP1809-1815.
M. A. Naser, A. A. Majeed, M. Alsabah, T. R. Al-Shaikhli, and K. M. Kaky, “A Review of Machine Learning’s Role in Cardiovascular Disease Prediction: Recent Advances and Future Challenges,” Algorithms 2024, Vol. 17, Page 78, vol. 17, no. 2, p. 78, Feb. 2024, doi: 10.3390/A17020078.
N. Nissa, S. Jamwal, and M. Neshat, “A Technical Comparative Heart Disease Prediction Framework Using Boosting Ensemble Techniques,” Comput. 2024, Vol. 12, Page 15, vol. 12, no. 1, p. 15, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.3390/COMPUTATION12010015.
“Machine Learning-Based Cardiovascular Disease Detection Using Optimal Feature Selection”, [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=10416957
“Machine Learning for High Risk Cardiovascular Patient Identification”, [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Muhammad-Asad-Arshed/publication/363541183_Machine_Learning_for_High_Risk_Cardiovascular_Patient_Identification/links/63221052071ea12e36327f6e/Machine-Learning-for-High-Risk-Cardiovascular-Patient-Identification.pdf
M. Hussain, A. Shahzad, F. Liaquat, M. A. Arshed, S. Mansoor, and Z. Akram, “Performance Analysis of Machine Learning Algorithms for Early Prognosis of Cardiac Vascular Disease,” Tech. J., vol. 28, no. 02, pp. 31–41, Jun. 2023, Accessed: Dec. 26, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://tj.uettaxila.edu.pk/index.php/technical-journal/article/view/1778
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 50SEA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















