A Conceptual Framework for Reducing Requirement Engineering Challenges in Industrial-Scale Software Projects
Keywords:
Software Development, Malicious Software Factors, Requirements, challengesAbstract
Introduction/Importance of Study: Industrial-scale software development tends to create more business value and effective strategic capabilities in software industries. IT organizations are spending about 50% of the budget on software development to build faster software programs at minimal cost to achieve success in industrial-scale projects. The crucial part of developing industrial-scale software is deciding ‘what is intended to be built’. If the problem is not tackled properly, this can result in serious errors that impact the entire Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) and make it difficult and costly to repair in later stages. Similarly, challenges in industrial-scale development related to Requirements are complex including Requirement scope, elicitation, specification, validation, and management. The Requirement engineering challenges become bigger and harder to overcome in industrial-scale projects due to time and cost factors. The money spent on Requirement change may affect the overall development time of the project. The complexity of industrial-scale projects does not increase linearly, thus, impacting the development process.
Novelty Statement: Therefore, the need to address challenges in large IT projects comes with the reason of their economic value in local and international markets. Researchers have come up with the identification of challenges, but their studies lack the overall Requirement engineering process. There is a need to design a comprehensive solution to overcome the Requirement engineering challenges that contribute to project failure.
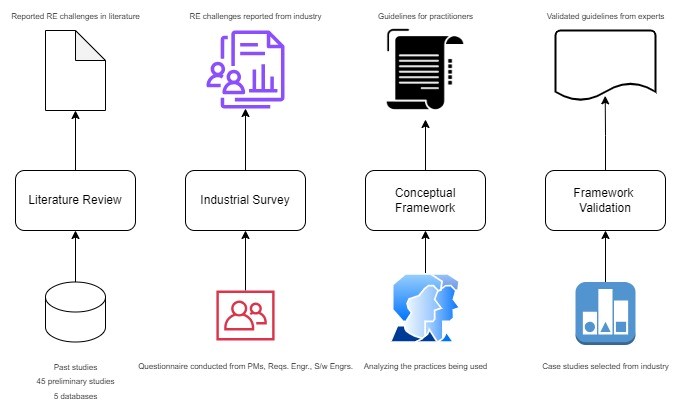
Material and Method: Therefore, the research is divided into three phases: “The Identification Phase”, where the project challenges would be identified; “The Implementation Phase”, where these factors would be shortlisted to design a framework; and “The Validation Phase”, in which validation of the framework would be done using triangulation technique.
Result and Discussion: The outcomes will focus on facilitating the software development industry for addressing the Requirement of engineering challenges in industrial-scale projects to reduce the chances of failure.
References
K. Dikert, M. Paasivaara, and C. Lassenius, “Challenges and success factors for large-scale agile transformations: A systematic literature review,” J. Syst. Softw., vol. 119, pp. 87–108, Sep. 2016, doi: 10.1016/J.JSS.2016.06.013.
S. Group, “The Standish Group report - Chaos,” 2015, [Online]. Available: https://www.standishgroup.com/sample_research_files/CHAOSReport2015-Final.pdf
G. Fridgen, J. Klier, M. Beer, and T. Wolf, “Improving Business Value Assurance in Large-Scale IT Projects—A Quantitative Method Based on Founded Requirement Assessment,” ACM Trans. Manag. Inf. Syst., vol. 5, no. 3, Aug. 2014, doi: 10.1145/2638544.
A. R. Asghar, A. Tabassum, S. N. Bhatti, and A. M. Jadi, “Impact and challenges of Requirement elicitation & prioritization in quality to agile process: Scrum as a case scenario,” Int. Conf. Commun. Technol. ComTech 2017, pp. 50–55, Oct. 2017, doi: 10.1109/COMTECH.2017.8065749.
H. Dar, M. I. Lali, H. Ashraf, M. Ramzan, T. Amjad, and B. Shahzad, “A systematic study on software Requirement elicitation techniques and its challenges in mobile application development,” IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 63859–63867, 2018, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2874981.
M. A. Akbar, Nasrullah, M. Shameem, J. Ahmad, A. Maqbool, and K. Abbas, “Investigation of project administration related challenging factors of Requirement change management in global software development: A systematic literature review,” 2018 Int. Conf. Comput. Electron. Electr. Eng. ICE Cube 2018, Jan. 2019, doi: 10.1109/ICECUBE.2018.8610966.
P. Lombriser, F. Dalpiaz, G. Lucassen, and S. Brinkkemper, “Gamified Requirement Engineering: Model and Experimentation,” Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. (including Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinformatics), vol. 9619, pp. 171–187, 2016, doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-30282-9_12.
“An Insight into Requirement Engineering Processes”, [Online]. Available: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-35615-5_48#:~:text=Requirement Engineering (RE) determines the,%26 validation%2C and Requirement management.
S. Ouhbi, A. Idri, J. L. Fernández-Alemán, and A. Toval, “Requirement engineering education: a systematic mapping study,” Requir. Eng., vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 119–138, Mar. 2015, doi: 10.1007/S00766-013-0192-5/METRICS.
A. Bennaceur, T. T. Tun, Y. Yu, and B. Nuseibeh, “Requirement Engineering,” Handb. Softw. Eng., pp. 51–92, Feb. 2019, doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-00262-6_2.
S. A. Fricker, R. Grau, and A. Zwingli, “Requirement Engineering: Best Practice,” Requir. Eng. Digit. Heal., pp. 25–46, Jan. 2015, doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-09798-5_2.
T. E. Fægri and N. B. Moe, “Re-conceptualizing Requirement engineering: Findings from a large-scale, agile project,” ACM Int. Conf. Proceeding Ser., vol. 25-29-May-2015, May 2015, doi: 10.1145/2764979.2764983.
D. Fucci et al., “Needs and Challenges for a Platform to Support Large-scale Requirement Engineering. A Multiple Case Study,” Int. Symp. Empir. Softw. Eng. Meas., Aug. 2018, doi: 10.1145/3239235.3240498.
H. Shareef Dar, S. Imtiaz, and M. I. Lali, “A Proactive Approach to Reduce Requirement Ambiguity via Gamify4Req,” vol. 19, Accessed: Jun. 03, 2024. [Online]. Available: http://xisdxjxsu.asia
“Understanding and supporting large-scale Requirement management.” Accessed: Jun. 03, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://lucris.lub.lu.se/ws/portalfiles/portal/3588635/1566591.pdf
A. M. H. Al-Said Ahmad, “Agile Large-Scale Software Development: Success Factors, Challenges and Solutions,” i-manager’s J. Softw. Eng., vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 1–12, Mar. 2014, doi: 10.26634/JSE.8.3.2807.
K. Wnuk, B. Regnell, and B. Berenbach, “Scaling Up Requirement Engineering – Exploring the Challenges of Increasing Size and Complexity in Market-Driven Software Development,” Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. (including Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinformatics), vol. 6606 LNCS, pp. 54–59, 2011, doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-19858-8_6.
“A Historical Perspective on Requirement Engineering.” Accessed: Jun. 03, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.scenarioplus.org.uk/papers/historical/historical.htm
P. Zave, “Classification of research efforts in Requirement engineering,” ACM Comput. Surv., vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 315–321, 1997, doi: 10.1145/267580.267581.
N. Sekitoleko, F. Evbota, E. Knauss, A. Sandberg, M. Chaudron, and H. H. Olsson, “Technical Dependency Challenges in Large-Scale Agile Software Development,” Lect. Notes Bus. Inf. Process., vol. 179, pp. 46–61, 2014, doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-06862-6_4.
H. Taherdoost and A. Keshavarzsaleh, “A Theoretical Review on IT Project Success / Failure Factors and Evaluating the Associated Risks,” 2015.
“Experiences from Measuring Learning and Performance in Large-Scale Distributed Software Development”, [Online]. Available: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2%3A1143810&dswid=-4702
S. Madhavan, “Delays and Failures in Projects Final.pdf,” Proc. 22nd World Multi-Conference Syst. Cybern. Informatics (WMSCI 2018), Jan. 2018, Accessed: Jun. 03, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.academia.edu/38369185/Delays_and_Failures_in_Projects_Final_pdf
K. H. Rolland, “‘Desperately’ seeking research on agile Requirement in the context of large-scale agile projects,” ACM Int. Conf. Proceeding Ser., vol. 25-29-May-2015, May 2015, doi: 10.1145/2764979.2764984.
“Identifying the Reasons for Software Project Failure and Some of their Proposed Remedial through BRIDGE Process Models 8 . 1,” 2017.
D. Pimchangthong and V. Boonjing, “Effects of Risk Management Practice on the Success of IT Project,” Procedia Eng., vol. 182, pp. 579–586, Jan. 2017, doi: 10.1016/J.PROENG.2017.03.158.
S. N. Kumari and A. S. Pillai, “Requirement elicitation issues and project performance: A test of a contingency model,” Proc. 2015 Sci. Inf. Conf. SAI 2015, pp. 889–896, Sep. 2015, doi: 10.1109/SAI.2015.7237247.
I. Inayat, L. Moraes, M. Daneva, and S. S. Salim, “A reflection on agile Requirement engineering: Solutions brought and challenges posed,” ACM Int. Conf. Proceeding Ser., vol. 25-29-May-2015, May 2015, doi: 10.1145/2764979.2764985.
K. M. Whitney and C. B. Daniels, “The Root Cause of Failure in Complex IT Projects: Complexity Itself,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 20, pp. 325–330, Jan. 2013, doi: 10.1016/J.PROCS.2013.09.280.
W. Alsaqaf, M. Daneva, and R. Wieringa, “Quality Requirement challenges in the context of large-scale distributed agile: An empirical study,” Inf. Softw. Technol., vol. 110, pp. 39–55, Jun. 2019, doi: 10.1016/J.INFSOF.2019.01.009.
K. Conboy and N. Carroll, “Implementing Large-Scale Agile Frameworks: Challenges and Recommendations,” IEEE Softw., vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 44–50, Mar. 2019, doi: 10.1109/MS.2018.2884865.
V. N. Vithana and S. Lanka, “Scrum Requirement Engineering Practices and Challenges in Offshore Software Development,” Int. J. Comput. Appl., vol. 116, no. 22, pp. 975–8887, 2015.
“A Reflection on Why Large Public Projects Fail”, [Online]. Available: https://www.jbs.cam.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/a-reflection-on-why-large-public-it-projects-fail---kjetil--mark-thompson-s-chapter.pdf
A. Alami, “Why Do Information Technology Projects Fail?,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 100, pp. 62–71, Jan. 2016, doi: 10.1016/J.PROCS.2016.09.124.
R. Kasauli, G. Liebel, E. Knauss, S. Gopakumar, and B. Kanagwa, “Requirement Engineering Challenges in Large-Scale Agile System Development,” Proc. - 2017 IEEE 25th Int. Requir. Eng. Conf. RE 2017, pp. 352–361, Sep. 2017, doi: 10.1109/RE.2017.60.
T. Dyba and T. Dingsoyr, “Agile Project Management: From Self-Managing Teams to Large-Scale Development,” Proc. - Int. Conf. Softw. Eng., vol. 2, pp. 945–946, Aug. 2015, doi: 10.1109/ICSE.2015.299.
“Influencing Factors for IT Software Project Failures in Developing Countries — A Critical Literature Survey - Volume 11 Number 11 (Nov. 2016) - Journal of Software.” Accessed: Jun. 03, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.jsoftware.us/index.php?m=content&c=index&a=show&catid=174&id=2702
“Scope management complexity in software projects.” Accessed: Jun. 03, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265015432_Scope_management_complexity_in_software_projects
S. C. P. Ardhendu M., “Identifying the Reasons for Software Project Failure and Some of their Proposed Remedial through BRIDGE Process Models,” Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng., vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 118–126, 2015.
E. Sońta-Drączkowska and A. Krogulec, “Challenges of scaling agile in large enterprises and implications for project management,” Int. J. Manag. Proj. Bus., vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 360–384, Apr. 2024, doi: 10.1108/IJMPB-11-2023-0244/FULL/XML.
T. Dingsøyr, N. B. Moe, T. E. Fægri, and E. A. Seim, “Exploring software development at the very large-scale: a revelatory case study and research agenda for agile method adaptation,” Empir. Softw. Eng., vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 490–520, Feb. 2018, doi: 10.1007/S10664-017-9524-2/TABLES/6.
W. Scacchi, “Winning and losing in large-scale software development: A multi-decade perspective,” Computer (Long. Beach. Calif)., vol. 51, no. 10, pp. 58–65, Oct. 2018, doi: 10.1109/MC.2018.3971348.
A. Sadovykh, B. Said, D. Truscan, and H. Bruneliere, “An iterative approach for model-based Requirement engineering in large collaborative projects: A detailed experience report,” Sci. Comput. Program., vol. 232, p. 103047, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.1016/J.SCICO.2023.103047.
D. Zowghi, F. Da Rimini, and M. Bano, “Problems and challenges of user involvement in software development: An empirical study,” ACM Int. Conf. Proceeding Ser., vol. 27-29-April-2015, Apr. 2015, doi: 10.1145/2745802.2745810.
S. L. Lim and A. Finkelstein, “StakeRare: Using social networks and collaborative filtering for large-scale Requirement elicitation,” IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng., vol. 38, no. 3, pp. 707–735, 2012, doi: 10.1109/TSE.2011.36.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 50SEA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















