A Demographic Fuzzy Similarity Computation Method for Recommender Systems
Keywords:
recommender systems, collaborative filtering, similarity measuresAbstract
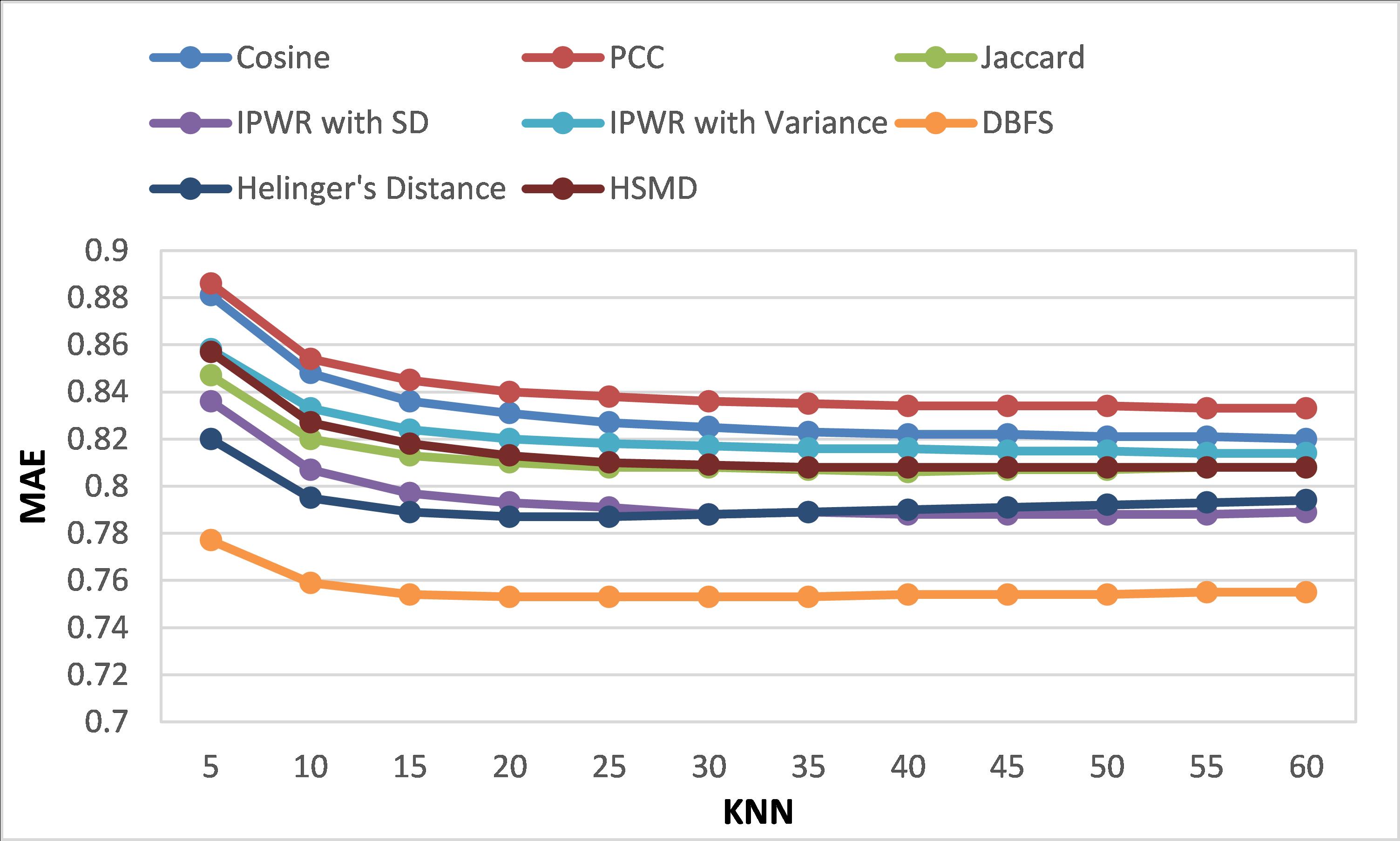
In this allegedly never-ending stream of e-commerce, it is crucial to offer high-quality suggestions so that consumers can choose wisely from a wide range of picks. Recommender Systems (RS) has proven to be an essential instrument for improving sales of online vendors and enabling consumers with personalized product recommendations. Collaborative Filtering (CF), an extensively preferred approach for Recommender Systems, provides suggestions based on the ratings of users with similar interests. The primary operating component in CF is to measure similarity among items or users. Recommender Systems use a user-item matrix, which is often highly sparse and suffers from cold start, ultimately leading to imprecise recommendations. Instead of relying merely on ratings that are uncertain and can be fake, we integrated the demographic information of users with CF to attain more precise predictions and recommendations in our work. To cope with the uncertainty factor in the recommendation process and to depict the physical world more realistically, we applied the Fuzzy set theory to users’ ratings and demographic features. ML-100K and ML-latest-small datasets are used to evaluate the accuracy of the proposed similarity measure. Compared to the most advanced methods, our proposed demographic fuzzy similarity computation method exhibits considerable achievements in terms of MAE, RMSE, and coverage metrics on standard recommendation datasets, which we used for experimentation.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 International Journal of Innovations in Science & Technology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















