An Efficient Read and Mark Mechanism for Multiple-choice Questions Using Optical Character Recognition
Keywords:
Multiple Choice Questions, Optical Mark Recognition, Optical Character Recognition, International Business Machines, Computer Vision 2, Identification, Pakistani Rupee, Personal ComputersAbstract
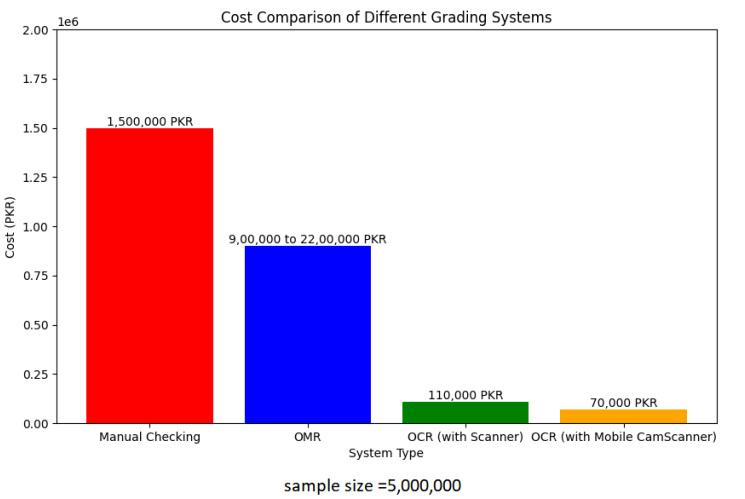
This research paper focuses on modifying the grading of multiple-choice questions (MCQs) to better the efficiency and incorrectness of educational tests. Conventional grading systems, such as optical mark recognition (OMR), have fundamental drawbacks, excluding the necessity for precise shading, time-wasting, and the use of special OMR sheets and OMR scanners. This conceptualization can be expensive and error-prone, especially if the MCQs papers are folded or unmarked. In comparison, the suggested OCR-based approach gives fundamental benefits in all necessary areas. It is less costly to use a simple scanner and software alternatively to costly OMR equipment. The method is motivated to be simple to set up and use. It importantly reduces error rates and marking time by employing precise OCR algorithms and processing greater amounts of answer sheets quickly. Moreover, the system is extremely accurate and scalable, allowing it to handle a rising amount of paper efficiently. It also has limited trust in external tools and is highly flexible and adaptable to different MCQ formats and grading settings. In General, the OCR-based approach outperforms existing methods by eliminating their shortcomings and delivering a trustworthy, time-saving alternative for automated MCQ grading.
References
G. K. W. Ramesh, S., S. Manjit Sidhu, “Exploring the potential of multiple choice questions in computer-based assessment of student learning,” Malaysian Online J. Instr. Technol., vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 1–15, 2005, [Online]. Available: https://www.academia.edu/17878894/Exploring_the_Potential_of_Multiple_Choice_Questions_in_Computer_Based_Assessment_of_Student_Learning
Stephen Merritt, “Mastering Multiple Choice: The Definitive Guide to Achieving Breakthrough Results on Multiple Choice Exams,” Canada: Brain Ranch, 2006, [Online]. Available: https://www.goodreads.com/book/show/21211821-mastering-multiple-choice
J. Noyes and K. Garland, “equivalent,” Ergonomics, vol. 51, no. 9, pp. 1352–1375, 2008.
J. A. Fisteus, A. Pardo, and N. F. García, “Grading Multiple Choice Exams with Low-Cost and Portable Computer-Vision Techniques,” J. Sci. Educ. Technol., vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 560–571, Aug. 2013, doi: 10.1007/S10956-012-9414-8/METRICS.
N. V. Patel and I. G. Prajapati, “Various techniques for assessment of MR sheets through ordinary 2D scanner: A survey,” Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol., vol. 4, no. 9, pp. 803–807, 2015, [Online]. Available: https://www.ijert.org/research/various-techniques-for-assessment-of-omr-sheets-through-ordinary-2d-scanner-a-survey-IJERTV4IS090675.pdf
S. G. P. S. Sandhu, G. Singla, “A generalized approach to optical mark recognition,” Int. Conf. Comput. Commun. Technol., pp. 1–3, 2012.
Y. R. Krisana Chinnasarn, “Image-processing-oriented optical mark reader,” Proc. Vol. 3808, Appl. Digit. Image Process. XXII, 1999, doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.365883.
T. D. Nguyen, Q. Hoang Manh, P. Bui Minh, L. Nguyen Thanh, and T. M. Hoang, “Efficient and reliable camera based multiple-choice test grading system,” Int. Conf. Adv. Technol. Commun., pp. 268–271, 2011, doi: 10.1109/ATC.2011.6027482.
M. Čupić, “A case study: Using multiple-choice tests at university level courses - Preparation and supporting infrastructure,” MIPRO 2009 - 32nd Int. Conv. Proc. Comput. Educ., vol. 4, pp. 163–168, 2009, doi: 10.1504/IJIDSS.2010.033679.
Z. K. M. Čupić, B. Karla, T. Hrkać, “Supporting automated grading of formative multiple choice exams by introducing student identifier matrices,” Proc. 34th Int. Conv., pp. 993–998, 2011.
G. M. I. Bonačić, T. Herman, T. Krznar, E. Mangić, “Optical character recognition of seven–segment display digits using neural networks,” Proc. MIPRO 2009 – 32nd Int. Conv. Inf. Commun. Technol. Electron. Microelectron., pp. 323–328, 2012.
M. Čupić, K. Brkić, T. Hrkać, Ž. Mihajlović, and Z. Kalafatić, “Automatic recognition of handwritten corrections for multiple-choice exam answer sheets,” 2014 37th Int. Conv. Inf. Commun. Technol. Electron. Microelectron. MIPRO 2014 - Proc., pp. 1136–1141, 2014, doi: 10.1109/MIPRO.2014.6859739.
Nutchanat Sattayakawee, “Test Scoring for Non-Optical Grid Answer Sheet Based on Projection Profile Method,” Int. J. Inf. Educ. Technol., vol. 3, no. 2, 2013, doi: 10.7763/IJIET.2013.V3.279.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 50Sea

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















