Performance Analysis of Task Distribution Mechanism in Multi-User’ Collaborative Assembly Task' In 3d Virtual Environment
Keywords:
3D Interaction, Virtual Reality, Collaborative Virtual Environment, Awareness, User PerformanceAbstract
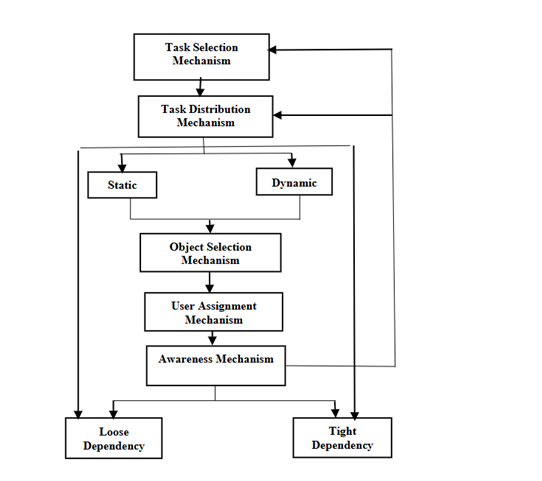
CVEs are real-time, computer-simulated environments where two or more actors can mutually complete a task using synthetic objects. User performance is one of the major problems that arise due to coordination problems, a good mechanism to divide tasks, or less understanding or interaction among users collaborating. The impact of multi-user collaboration on using the task distribution mechanism remains unexplored. In this study, the impact of TDM on multi-users’ collaborative virtual environment is investigated. The TDM model assigns the task to collaborating users in CVEs on a static or dynamic manner. In static distribution, there exists weak coupling, and the amount of communication during the actual execution of a task is low, while in dynamic distribution, users are tightly coupled and hence need to communicate more. To study the effect of static and dynamic task distribution strategies on user’s performance in CVEs on multi users, a CVE prototype was developed using C++ and OpenGL, simulating an assembly task with distinct roles for multiple users, where twenty (20) group (each consists of two users) perform a task in collaboration under both strategies (static and dynamic) on two users and three users using arrow-casting and audio aids. The result shows that static with arrows-casting for two users takes an average time of 331.15 sec, and for three users, 321.45sec, and for audio (342.73sec and 326.34sec, respectively. Similarly, the dynamic with arrow casting for two users takes 347.76 sec, and for three users, 333.24 sec, and for audio, 350.12 sec and 344.4 sec, respectively. The findings provide valuable insights into how multi-user collaboration, task distribution methods, and cognitive aids can influence task efficiency and teamwork. However, when the number of users increased to three users, there is a chance that the performance will be degraded because, from the experimental data, a lower improvement was observed for three users than for two users. This research contributes to improving task management and collaboration in CVEs, with potential applications in training, education, and remote teamwork.
References
G. Burdea, “Virtual Reality Technology,” John Wiley Sons, 2003, [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/computer-science/virtual-reality-technology
L. H. P. M. Renata Maria Abrantes Baracho, Mozart Joaquim Magalhães Vidigal, Luiz Gustavo da Silva Santiago, Marcelo Franco Porto, “Virtual Reality and Building Information Modeling in Architecture,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 256, pp. 673–680, 2025, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2025.02.166.
O. Bamodu and X. M. Ye, “Virtual Reality and Virtual Reality System Components,” Adv. Mater. Res., vol. 765–767, pp. 1169–1172, 2013, doi: 10.4028/WWW.SCIENTIFIC.NET/AMR.765-767.1169.
M. W. Krueger, “Chapter 7 - An Easy Entry Artificial Reality,” Virtual Real., pp. 147–161, 1993, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-745045-2.50017-9.
I. D. Bishop and C. Stock, “Using collaborative virtual environments to plan wind energy installations,” Renew. Energy, vol. 35, no. 10, pp. 2348–2355, 2010, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2010.04.003.
N. G. Sam Redfern, “Collaborative Virtual Environments to Support Communication and Community in Internet-Based Distance Education,” J. Inf. Technol. Educ. Res., vol. 1, no. 3, 2002, doi: 10.28945/356.
R. . Adams, “Virtual Training for a Manual Assembly Task,” Electron. J. haptics Res., vol. 2, 2001, [Online]. Available: https://digital.lib.washington.edu/researchworks/items/e2636bb7-20ad-437a-b1c7-60b06666261a
E. G. C. Sotiris Avgousti, “Medical telerobotic systems: current status and future trends,” Biomed. Eng. Online, vol. 15, no. 1, p. 96, 2016, doi: 10.1186/s12938-016-0217-7.
A. M. T. Tycho T. De Back, “Learning in immersed collaborative virtual environments: design and implementation,” Interact. Learn. Environ., vol. 31, no. 8, pp. 5364–5382, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2021.2006238.
S. Nistor and Cezar Oniciuc, “Complete biconservative surfaces in the hyperbolic space,” Nonlinear Anal., vol. 198, p. 111860, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.na.2020.111860.
C. Gunn, “Collaborative virtual sculpting with haptic feedback,” Virtual Real., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 73–83, Oct. 2006, doi: 10.1007/S10055-006-0044-4/METRICS.
S. Khalid, S. Ullah, and A. Alam, “Task Distribution Mechanism for Effective Collaboration in Virtual Environments: Task Distribution Mechanism for Effective Collaboration in Virtual Environments,” Proc. Pakistan Acad. Sci. A. Phys. Comput. Sci., vol. 53, no. 1, pp. 49–59, Jun. 2021, Accessed: Oct. 19, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.ppaspk.org/index.php/PPAS-A/article/view/356
A. E. J. Jason Leigh, “Issues in the design of a flexible distributed architecture for supporting persistence and interoperability in collaborative virtual environments,” Proc. Int. Conf. Supercomput., 1997, [Online]. Available: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/509593.509614
C. Greenhalgh, “Large Scale Collaborative Virtual Environments,” Large Scale Collab. Virtual Environ., 1999, doi: 10.1007/978-1-4471-0867-2.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 50sea

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















