Computation of Rotational Flow of the Sun Using Satellite Data and Doppler Shift Calculations
Keywords:
CHASE, Doppler Velocity, Hα Line, Solar Differential Rotation, Solar Dynamics, Voigt FittingAbstract
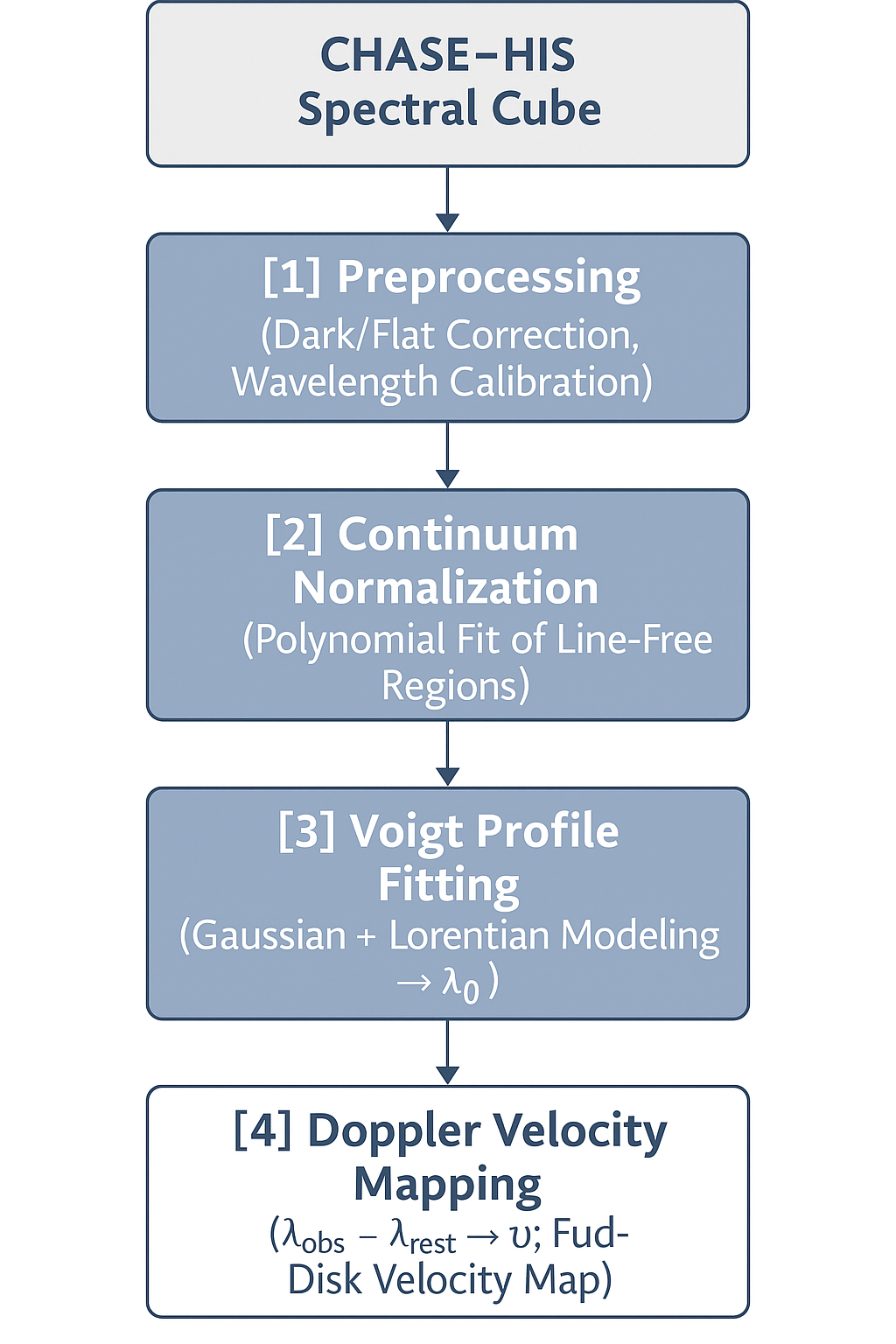
Solar rotational flow governs the Sun’s magnetic activity, space weather variability, and long-term dynamo processes. Traditional tracer-based techniques offer limited precision in mapping these flows, creating the need for direct spectroscopic velocity measurements. This study presents a computational framework for deriving full-disk Doppler velocity maps of the Sun using high-resolution Hα spectra from the Chinese H-alpha Solar Explorer (CHASE) mission. The H-alpha Imaging Spectrograph (HIS) data cube (2304 × 2313 × 46 pixels) was processed through a workflow of preprocessing, continuum normalization, Voigt profile fitting, and pixel-wise Doppler conversion to retrieve line-of-sight velocities. The resulting field of ~5.3 million pixels shows clear differential rotation, with blue shifts up to −7.89 km s⁻¹ on the approaching limb and red shifts up to +2.19 km s⁻¹ on the receding limb, corresponding to equatorial and polar rotation periods of ~25 and ~31 days, respectively. Localized asymmetries in active regions further reveal small-scale velocity perturbations. These results validate CHASE–HIS spectroscopy as a reliable tool for global solar flow diagnostics and highlight the utility of Voigt-based Doppler modeling in resolving fine-scale plasma dynamics. The developed approach bridges spectroscopic and Helio seismic methods, offering a reproducible foundation for future studies on solar dynamo modeling and space weather prediction.
References
M. A. . Seeds and D. E. . Backman, “Foundations of astronomy,” Astron., p. 654, 2011, Accessed: Oct. 25, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://books.google.com/books/about/Foundations_of_Astronomy.html?id=QUhoPgAACAAJ
O. Hathaway, D. H., Upton, L. A., & Colegrove, “Measuring differential rotation and meridional flow with magnetic features,” Sol. Phys., vol. 297, no. 1, p. 14, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-022-01979-7.
B. Mahajan, S., Tripathy, S. C., Jain, K., Hill, F., & Kumar, “Comparative analysis of solar rotational flow measurements: Helioseismology, Doppler imaging, and granule tracking,” Sol. Phys., vol. 299, no. 2, p. 22, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-024-02313-7.
M. J. Thompson, J. Christensen-Dalsgaard, M. S. Miesch, and J. Toomre, “The Internal Rotation of the Sun,” Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys., vol. 41, no. Volume 41, 2003, pp. 599–643, Sep. 2003, doi: 10.1146/ANNUREV.ASTRO.41.011802.094848/CITE/REFWORKS.
R. H. C. Laurent Gizon, “Meridional flow in the Sun’s convection zone is a single cell in each hemisphere,” Science (80-. )., vol. 368, no. 6498, pp. 1469–1472, 2020, [Online]. Available: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.aaz7119
B. M. Q. S. M. Abrarov, “A simple interpolating algorithm for the rapid and accurate calculation of the Voigt function,” J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf., vol. 110, no. 6, pp. 376–383, 2009, doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2009.01.003.
B. Löptien et al., “Global-scale equatorial Rossby waves as an essential component of solar internal dynamics,” Nat. Astron., vol. 2, no. 7, pp. 568–573, Jul. 2018, doi: 10.1038/S41550-018-0460-X;SUBJMETA.
G. D. Z. V. Polito, “Analysis and modelling of recurrent solar flares observed with Hinode/EIS on March 9, 2012,” Astron. Astrophys., vol. 601, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201629703.
A. D. Adrian Doicu, “An Overview of Neural Network Methods for Predicting Uncertainty in Atmospheric Remote Sensing,” Remote Sens, vol. 13, no. 24, p. 5061, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245061.
Q. Jin, C., Wang, J. X., & Song, “Solar differential rotation from SDO/HMI observations,” Astrophys. J., vol. 892, p. 38, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4357/ab7927.
M. Š. T. Roudier, “Photospheric downflows observed with SDO/HMI, HINODE, and an MHD simulation,” Astron. Astrophys., vol. 647, 2021, doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/202040172.
R. K. Snodgrass, H. B., & Ulrich, “Rotation measurements and cross-correlation methods,” Astrophys. J., vol. 351, pp. 309–316, 1990, doi: https://doi.org/10.1086/168467.
D. Permata, S. M., & Herdiwijaya, “Sunspot tracking and solar rotation using SDO/HMI data,” J. Phys. Conf. Ser., vol. 1204, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1204/1/012095.
C. Webb, J. K., Carswell, R. F., & Lee, “Accurate Voigt profile fitting and model selection,” Astron. Astrophys., vol. 647, p. A7, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202039876.
K. Hotta, H., & Kusano, “Magnetohydrodynamic simulations of solar differential rotation,” Nat. Astron., vol. 5, pp. 1100–1106, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-021-01422-7.
X. Yan, “Normalization methods for solar flare spectroscopy: A comparative study,” Sol. Phys., vol. 300, no. 1, p. 45, 2025, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-025-02388-9.
T. Hotta, H., Kusano, K., & Sekii, “Solar differential rotation maintained by magnetic fields and anisotropic turbulence,” Nat. Astron., vol. 6, pp. 832–839, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-022-01638-4.
R. C. Carrington, “On the Distribution of the Solar Spots in Latitude since the Beginning of the Year 1854; with a Map,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 1–3, 1858, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/19.1.1a.
P. Garaud, “Latitudinal shear instability in the solar tachocline,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., vol. 324, no. 1, pp. 68–76, 2001, doi: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04245.x.
François Rincon & Michel Rieutord, “The Sun’s supergranulation,” Living Rev. Sol. Phys., vol. 15, no. 6, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41116-018-0013-5.
and A. G. Abhishek Rajhans, Durgesh Tripathi, Vinay L. Kashyap, James A. Klimchuk, “Center-to-limb Variation of Transition-region Doppler Shifts in Active Regions,” Astrophys. J., vol. 944, no. 2, 2023, doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/acb4ed.
D. Vargas, A., Smith, J., Patel, R., & Lin, “Comparative evaluation of continuum-fitting strategies for astrophysical spectra,” J. Astron. Instrum., vol. 13, no. 1, p. 2450002, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1142/S2251171724500021.
J. F. M. Cretignier, “RASSINE: Interactive tool for normalising stellar spectra,” Astron. Astrophys., vol. 640, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202037722.
P. P. M. Koleva, “ULySS: a full spectrum fitting package,” Astron. Astrophys., vol. 501, no. 3, pp. 1269–1279, 2009, doi: https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200811467.
P. F. M. Scodeggio, “The VVDS Data‐Reduction Pipeline: Introducing VIPGI, the VIMOS Interactive Pipeline and Graphical Interface,” Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacific, vol. 117, no. 837, 2005, doi: 10.1086/496937.
J.-K. Krogager, “VoigtFit: A Python package for Voigt profile fitting,” Astron. Comput., vol. 23, pp. 1–11, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ascom.2018.02.004.
T. T. García, “Voigt profile fitting to quasar absorption lines: an analytic approximation to the Voigt–Hjerting function,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., vol. 369, no. 4, pp. 2025–2035, 2006, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10450.x.
A. Liang, C., & Kravtsov, “Bayesian Voigt profile fitting with affine-invariant MCMC,” J. Open Source Softw., vol. 2, no. 18, p. 336, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.00336.
R. Fenning, S. MacHida, D. Kelliher, A. Khan, and R. Edgecock, “High-order dispersion suppression for FFAG-based optics,” J. Instrum., vol. 7, no. 05, p. P05011, May 2012, doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/7/05/P05011.
V. V. Makarov, “Modeling solar velocity fields from Doppler measurements,” Astrophys. J., vol. 715, no. 1, pp. 265–275, 2010, doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/0004-637X/715/1/265.
M. de la Cruz Rodríguez, J., Kiselman, D., & Carlsson, “Absolute velocity references for solar observations from 3D simulations,” Astron. Astrophys., vol. 528, 2011, doi: https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201015217.
A. A. N. & P. H. S. S. Couvidat, J. Schou, J. T. Hoeksema, R. S. Bogart, R. I. Bush, T. L. Duvall Jr., Y. Liu, “Observables Processing for the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager Instrument on the Solar Dynamics Observatory,” Sol. Phys., vol. 291, pp. 1887–1938, 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-016-0957-3.
H. Pal, P. S., Steinegger, M., Arlt, R., Denker, C., & Balthasar, “Digitized full-disk solar plates from the Einstein Tower (1943–1991): Calibration and access,” Sol. Phys., vol. 295, no. 6, p. 87, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01656-y.
F. Ermolli, I., Giorgi, F., Romano, P., Stangalini, M., Vecchio, A., & Zuccarello, “Rome/PSPT full-disk solar observations: Data and applications,” Sol. Phys., vol. 297, no. 6, p. 87, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-022-02021-6.
C. Xu, Z., Li, H., & Fang, “Spectroscopic diagnostics of solar plasma velocities,” Astron. Astrophys., vol. 664, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202243210.
H. P. Brooks, D. H., Ugarte-Urra, I., & Warren, “Full-Sun coronal Doppler velocity maps with EIS,” Astrophys. J., vol. 799, no. 2, p. 70, 2015, doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/0004-637X/799/2/70.
I. S. D. Sudar, “Steps towards a high precision solar rotation profile: Results from SDO/AIA coronal bright point data,” Astron. Astrophys., vol. 575, 2015, [Online]. Available: https://www.aanda.org/articles/aa/full_html/2015/03/aa24929-14/aa24929-14.html
M. D. Zdenek Hrazdíra, “Iterative Phase Correlation Algorithm for High-precision Subpixel Image Registration,” Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser., vol. 247, no. 1, p. 8, 2020, doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/ab63d7.
H. M. A. Lekshmi B, Dibyendu Nandy, “Asymmetry in Solar Torsional Oscillation and the Sunspot Cycle,” Astrophys. J., vol. 86, no. 121, 2018, [Online]. Available: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-4357/aacbd5/pdf
J. Z. Alexander V. Getling, Alexander G. Kosovichev, “Evolution of Subsurface Zonal and Meridional Flows in Solar Cycle 24 from Helioseismological Data,” Astrophys. J. Lett., vol. 908, no. 2, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2012.15555.
M. Š. T. Roudier, “Large-scale photospheric motions determined from granule tracking and helioseismology from SDO/HMI data,” Astron. Astrophys., vol. 611, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201732014.
R. J.-Š. I. Poljančić Beljan, “Solar differential rotation in the period 1964–2016 determined by the Kanzelhöhe data set,” Astron. Astrophys., vol. 606, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201731047.
S. F. C. Stewart, “Effects of transducer, velocity, Doppler angle, and instrument settings on the accuracy of color Doppler ultrasound,” Ultrasound Med. Biol., vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 551–64, 2001, doi: 10.1016/S0301-5629(01)00357-X.
T. Schöll, M., Egidi, A., & Dudok de Wit, “Processing challenges in solar irradiance composites (SOLID),” Sol. Phys., vol. 291, no. 1, pp. 159–177, 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-015-0830-2.
H. B. Snodgrass, “Solar differential rotation from magnetic features,” Astrophys. J., vol. 270, pp. 288–299, 1983, doi: https://doi.org/10.1086/161124.
R. Howe et al., “Large-scale zonal flows near the solar surface: A comparison of results from local and global helioseismology with direct doppler measurements,” Sol. Phys., vol. 235, no. 1–2, pp. 1–15, 2006, doi: 10.1007/S11207-006-0117-2.
E. B. Zuhal Er, “Dual axis solar angle tracking system without any sensor,” J. Energy Syst., vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 130–139, 2018, doi: 10.30521/jes.456606.
S. Routh, “Image-correlation-based solar flow mapping,” Sol. Phys., 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-024-02189-1.
Z.-C. L. and L. Gizon, “Doppler velocity of m=1 high-latitude inertial mode over the last five sunspot cycles,” arXiv:2409.06896v2, 2025, [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/html/2409.06896v2
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 50sea

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















