SSOCANET SSOCANET - Empowering VANETs with Salp Swarm Optimization-Enhanced Clustering Algorithm
Keywords:
Salp Swarm Optimization Algorithm, Vehicular Clustering., Bio-Inspired Clustering, VANETs, Vehicular ClusteringAbstract
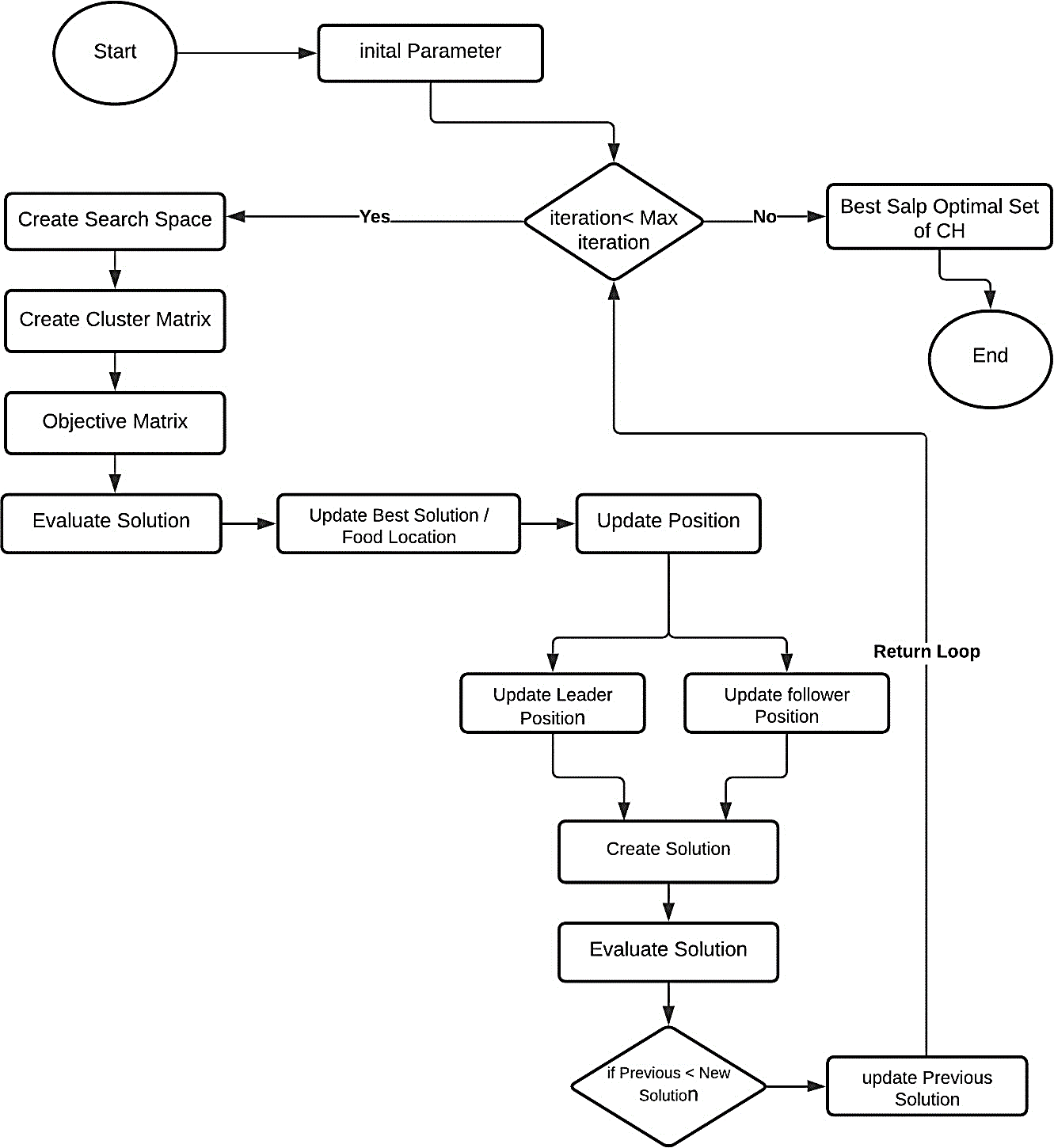
Vehicular Ad hoc networks (VANETs) present significant challenges due to the dynamic nature of vehicle movements, leading to a constantly changing vehicular network topology. This instability results in packet loss, network fragmentation, message reliability, and scalability issues. To address these challenges, clustering has emerged as a promising solution to escalate vehicle communication efficiency. However, determining the optimal number of clusters remains a crucial problem. The proposed solution, the Salp Swarm Optimization-Enhanced Clustering Algorithm for VANET (SSOCANET), leverages the foraging behavior of salps to optimize cluster formation based on multiple objectives. SSOCANET achieves an optimal number of clusters by employing carefully designed objective functions, minimizing communication overhead and end-to-end communication latency in a network. The simulation results demonstrate the superior performance of SSOCANET compared to other clustering approaches, offering a robust solution for VANETs.
References
B. A. Mohammed et al., “Service based VEINS framework for vehicular Ad-hoc network (VANET): A systematic review of state-of-the-art,” Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl., pp. 1–23, May 2024, doi: 10.1007/S12083-024-01692-0/METRICS.
S. A. A. Shah, E. Ahmed, F. Xia, A. Karim, M. Shiraz, and R. M. Noor, “Adaptive Beaconing Approaches for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks: A Survey,” IEEE Syst. J., vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 1263–1277, Jun. 2018, doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2016.2573680.
E. C. Eze, S. J. Zhang, E. J. Liu, and J. C. Eze, “Advances in vehicular ad-hoc networks (VANETs): Challenges and road-map for future development,” Int. J. Autom. Comput., vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 1–18, Feb. 2016, doi: 10.1007/S11633-015-0913-Y/METRICS.
S. Khusro, M. Naeem, M. A. Khan, and I. Alam, “There is no such thing as free Lunch: An Investigation of Bloatware Effects on Smart Devices,” J. Inf. Commun. Technol. Robot. Appl., pp. 20–30, Dec. 2018, Accessed: Jun. 03, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://jictra.com.pk/index.php/jictra/article/view/7
M. Jan, S. Khusro, I. Alam, I. Khan, and B. Niazi, “Interest-Based Content Clustering for Enhancing Searching and Recommendations on Smart TV,” Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput., vol. 2022, 2022, doi: 10.1155/2022/3896840.
A. Ali, F. Aadil, M. F. Khan, M. Maqsood, and S. Lim, “Harris Hawks Optimization-Based Clustering Algorithm for Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks,” IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst., vol. 24, no. 6, pp. 5822–5841, Jun. 2023, doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3257484.
“Role of AI Enabled Smart Meters to Enhance Customer Satisfaction”, [Online]. Available: https://ijcsmc.com/docs/papers/December2022/V11I12202214.pdf
S. K. Panigrahy and H. Emany, “A Survey and Tutorial on Network Optimization for Intelligent Transport System Using the Internet of Vehicles,” Sensors 2023, Vol. 23, Page 555, vol. 23, no. 1, p. 555, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.3390/S23010555.
H. Hartenstein and K. P. Laberteaux, “A tutorial survey on vehicular ad hoc networks,” IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 46, no. 6, pp. 164–171, Jun. 2008, doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2008.4539481.
A. H. Wheeb, R. Nordin, A. A. Samah, M. H. Alsharif, and M. A. Khan, “Topology-Based Routing Protocols and Mobility Models for Flying Ad Hoc Networks: A Contemporary Review and Future Research Directions,” Drones 2022, Vol. 6, Page 9, vol. 6, no. 1, p. 9, Dec. 2021, doi: 10.3390/DRONES6010009.
S. A. Ali Shah et al., “Coverage Differentiation Based Adaptive Tx-Power for Congestion and Awareness Control in VANETs,” Mob. Networks Appl., vol. 23, no. 5, pp. 1194–1205, Oct. 2018, doi: 10.1007/S11036-016-0777-6/METRICS.
S. A. A. Shah, E. Ahmed, J. J. P. C. Rodrigues, I. Ali, and R. Md Noor, “Shapely Value Perspective on Adapting Transmit Power for Periodic Vehicular Communications,” IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst., vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 977–986, Mar. 2018, doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2775965.
S. Yerrathi and V. Pakala, “Enhancing network stability in VANETs using nature inspired algorithm for intelligent transportation system,” PLoS One, vol. 19, no. 1, p. e0296331, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0296331.
A. A. Abbasi and M. Younis, “A survey on clustering algorithms for wireless sensor networks,” Comput. Commun., vol. 30, no. 14–15, pp. 2826–2841, Oct. 2007, doi: 10.1016/J.COMCOM.2007.05.024.
J. Y. Yu and P. H. J. Chong, “A survey of clustering schemes for mobile ad hoc networks,” IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 32–47, Mar. 2005, doi: 10.1109/COMST.2005.1423333.
S. S. Agrawal and R. Rathi, “Topology Control Using Optimized Clustering Scheme in Mobile Ad Hoc Network,” Int. J. Networked Distrib. Comput., pp. 1–12, Feb. 2024, doi: 10.1007/S44227-024-00020-5/FIGURES/9.
W. Shahzad, F. A. Khan, and A. B. Siddiqui, “Clustering in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Using Comprehensive Learning Particle Swarm Optimization (CLPSO),” Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci., vol. 56, pp. 342–349, 2009, doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-10844-0_41.
H. Ali, W. Shahzad, and F. A. Khan, “Energy-efficient clustering in mobile ad-hoc networks using multi-objective particle swarm optimization,” Appl. Soft Comput., vol. 12, no. 7, pp. 1913–1928, Jul. 2012, doi: 10.1016/J.ASOC.2011.05.036.
M. Fahad et al., “Grey wolf optimization based clustering algorithm for vehicular ad-hoc networks,” Comput. Electr. Eng., vol. 70, pp. 853–870, Aug. 2018, doi: 10.1016/J.COMPELECENG.2018.01.002.
J. J. Liang, A. K. Qin, P. N. Suganthan, and S. Baskar, “Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer for global optimization of multimodal functions,” IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput., vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 281–295, Jun. 2006, doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2005.857610.
W. Ahsan et al., “Optimized Node Clustering in VANETs by Using Meta-Heuristic Algorithms,” Electron. 2020, Vol. 9, Page 394, vol. 9, no. 3, p. 394, Feb. 2020, doi: 10.3390/ELECTRONICS9030394.
I. Khan, S. Khusro, and I. Alam, “Smartphone Distractions and its Effect on Driving Performance using Vehicular Lifelog Dataset,” 1st Int. Conf. Electr. Commun. Comput. Eng. ICECCE 2019, Jul. 2019, doi: 10.1109/ICECCE47252.2019.8940697.
D. Singh, S. Nuthakki, A. Naik, S. Mullankandy, P. K. Singh, and Y. Nuthakki, “Revolutionizing Remote Health: The Integral Role of Digital Health and Data Science in Modern Healthcare Delivery,” Cogniz. J. Multidiscip. Stud., vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 20–30, Mar. 2022, doi: 10.47760/COGNIZANCE.2022.V02I03.002.
F. Aadil, K. B. Bajwa, S. Khan, N. M. Chaudary, and A. Akram, “CACONET: Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) Based Clustering Algorithm for VANET,” PLoS One, vol. 11, no. 5, p. e0154080, May 2016, doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0154080.
F. Aadil, “Intelligent clustering in vehicular ad hoc networks,” KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst., vol. 10, no. 8, pp. 3512–3528, 2016.
K. Kandali, L. Bennis, O. El Bannay, and H. Bennis, “An Intelligent Machine Learning Based Routing Scheme for VANET,” IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 74318–74333, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3190964.
L. Abualigah, M. Shehab, M. Alshinwan, and H. Alabool, “Salp swarm algorithm: a comprehensive survey,” Neural Comput. Appl., vol. 32, no. 15, pp. 11195–11215, Aug. 2020, doi: 10.1007/S00521-019-04629-4/METRICS.
D. Aloise, A. Deshpande, P. Hansen, and P. Popat, “NP-hardness of Euclidean sum-of-squares clustering,” Mach. Learn., vol. 75, no. 2, pp. 245–248, May 2009, doi: 10.1007/S10994-009-5103-0/METRICS.
G. Husnain, S. Anwar, and F. Shahzad, “Performance evaluation of CLPSO and MOPSO routing algorithms for optimized clustering in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks,” Proc. 2017 14th Int. Bhurban Conf. Appl. Sci. Technol. IBCAST 2017, pp. 772–778, Mar. 2017, doi: 10.1109/IBCAST.2017.7868141.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 50SEA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















