Preliminary Medical Diagnosis Using Voice-Based Urdu Language Interface
Keywords:
Diagnostic Tree, Knowledge Base, Medical Diagnosis System, Artificial Intelligence, Speech RecognitionAbstract
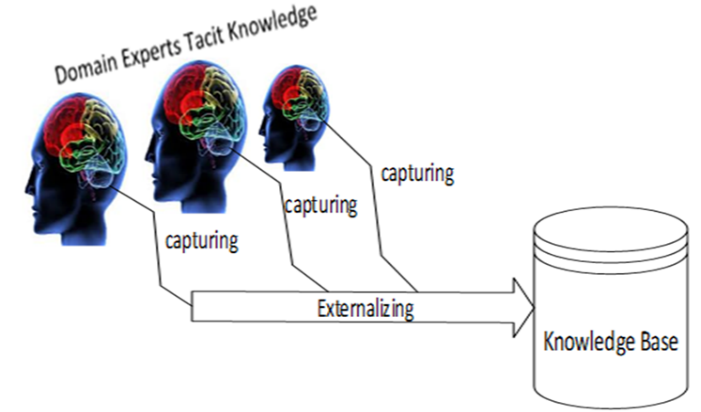
Expert knowledge is stored in the knowledge base through an externalizing process in the form of facts, procedures, heuristics, and rules. The knowledge base helps to refine the present knowledge and insert new knowledge without recompiling a program. Medical diagnosis is one of the first knowledge-based areas in which expert system principles are applied. Almost all knowledge-based medical diagnostic systems take input symptoms in the form of text and rely on the English language. This is a hindrance to illiterate and non-native English speakers of developing countries to utilize the system, and unfortunately, Pakistan is one of them. In this connection, this paper proposed an indexing method for integrating the medical diagnostic knowledge base with a Pakistani National Language-based voice-oriented user interface for accommodating the illiterate.
References
E. Borousan, “Evaluating factors that cause problem in implementation of knowledge management in Iran’s oil and gas industry,” AFRICAN J. Bus. Manag., vol. 6, no. 34, Aug. 2012, doi: 10.5897/AJBM11.1446.
I. J. K. Lindy M. Kregting, Nicolien T. van Ravesteyn, Wolfert Spijker, Tessa Dierks, Clare A. Aitken, H. Amarens Geuzinge, “Effects of a leaflet on breast cancer screening knowledge, explicit attitudes, and implicit associations,” Patient Educ. Couns., vol. 103, no. 12, pp. 2499–2507, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2020.06.032.
M. S. Adam and C. Urquhart, “IT capacity building in developing countries: A model of the Maldivian tourism sector,” Inf. Technol. Dev., vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 315–335, Oct. 2007, doi: 10.1002/ITDJ.20065.
Y. N. Cheah and S. S. R. Abidi, “Augmenting knowledge-based medical systems with tacit healthcare expertise: Towards an intelligent tacit knowledge acquisition info-structure,” Proc. IEEE Symp. Comput. Med. Syst., pp. 264–269, 2001, doi: 10.1109/CBMS.2001.941731.
Protocol for a scoping review to evaluate the extent of utilisation of healthcare services by asthma patients in sub-Saharan African countries, “Protocol for a scoping review to evaluate the extent of utilisation of healthcare services by asthma patients in sub-Saharan African countries,” BMJ Open, vol. 11, no. 8, 2021, [Online]. Available: https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/11/8/e046294
D. S. Aine Carroll, “Use of complexity theory in health and social care: a scoping review protocol,” BMJ Open, vol. 11, no. 7, p. e047633, 2021, [Online]. Available: https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/11/7/e047633
D. L. Hudson, M. E. Cohen, P. W. Banda, and M. S. Blois, “Medical Diagnosis and Treatment Plans Derived from a Hybrid Expert System,” Hybrid Archit. Intell. Syst., pp. 329–344, Sep. 2020, doi: 10.1201/9781003068075-17.
T. Haldin-Herrgard, “Difficulties in diffusion of tacit knowledge in organizations,” J. Intellect. Cap., vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 357–365, Dec. 2000, doi: 10.1108/14691930010359252.
I. Yazici, O. F. Beyca, O. F. Gurcan, H. Zaim, D. Delen, and S. Zaim, “A comparative analysis of machine learning techniques and fuzzy analytic hierarchy process to determine the tacit knowledge criteria,” Ann. Oper. Res. 2020 3081, vol. 308, no. 1, pp. 753–776, Jun. 2020, doi: 10.1007/S10479-020-03697-3.
D.A. Wolfram, “An appraisal of INTERNIST-I,” Artif. Intell. Med., vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 93–116, 1995, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0933-3657(94)00028-Q.
Sajda Qureshi, “Creating cycles of prosperity with human digital development for intelligent global health,” Inf. Technol. Dev., vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 649–659, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/02681102.2022.2135872.
S. Ben Zayed, A. Bin Gani, H. F. Gadelrab, and M. K. Bin Othman, “Operational Management in Emergency Healthcare,” Springer , vol. 297, 2021, doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-53832-3.
S. Ben Zayed, A. Bin Gani, and M. K. Bin Othman, “System Reengineering in Healthcare: Application for Hospital Emergency Departments,” vol. 172, 2019, doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-98104-8.
E. R. Rosyid Ridlo Al Hakim, “Android Based Expert System Application for Diagnose COVID-19 Disease: Cases Study of Banyumas Regency,” J. Intell. Comput. Heal. Informatics, vol. 1, no. 2, 2020, [Online]. Available: https://jurnal.unimus.ac.id/index.php/ICHI/article/view/5958
G. A. Chukwudebe, E. Ekwuwune, and K. I. Nkuma-Udah, “Medical diagnosis expert system for Malaria and related diseases for developing Countries,” 2017 IEEE 3rd Int. Conf. Electro-Technology Natl. Dev. NIGERCON 2017, vol. 2018-January, pp. 24–29, Jul. 2017, doi: 10.1109/NIGERCON.2017.8281875.
J. Munro, “A Review of: ‘Rule-based expert systems: the MYCIN experiments of the Stanford heuristic programming project’ Eds Bruce B. Buchanan and Edward H. Shortliffe Addison-Wesley, 1984, 748 pp, £37.00,” Civ. Eng. Syst., vol. 1, no. 6, pp. 342–343, Dec. 1984, doi: 10.1080/02630258408970370.
“Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach.” Accessed: Jun. 17, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.pearson.com/en-us/subject-catalog/p/artificial-intelligence-a-modern-approach/P200000003500/9780137505135?srsltid=AfmBOoqb0YgCTklkTw235M61b3Yqugl95hJVcNJLb3R0pgY1e_SIT7fA
Poli Venkata Subba Reddy, “Fuzzy logic based on Belief and Disbelief membership functions,” Fuzzy Inf. Eng., vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 405–422, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fiae.2017.12.001.
Sukrit Sondhi, “‘Mobdoc: Mobile Based Medical Diagnostic Tool,’” Quick Company. Accessed: Nov. 13, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.quickcompany.in/patents/mobdoc-mobile-based-medical-diagnostic-tool
Gufran Ahmad Ansari, “An Adoptive Medical Diagnosis System Using Expert System with Applications ,” SCISPACE. Accessed: Nov. 13, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://scispace.com/papers/an-adoptive-medical-diagnosis-system-using-expert-system-3tgperdo6b
S. Kumar and A. Kumar, “Automatic Melanoma Detection System (AMDS): A State-of-the-Art Review,” Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci., vol. 1214 CCIS, pp. 201–212, 2020, doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-7219-7_17.
P.Santosh Kumar Patra, Dipti Prava Sahu, Indrajit Mandal, “An Expert System for Diagnosis of Human Diseases,” Int. J. Comput. Appl., vol. 1, no. 13, 20101, [Online]. Available: https://www.ijcaonline.org/volume1/number13/pxc387439.pdf
J. C. Xinyu Yang, “Clinical use of dendritic cell-derived exosomes for hepatocellular carcinoma immunotherapy: How far we are?,” J. Hepatol., vol. 69, no. 4, pp. 984–986, 2018, [Online]. Available: https://www.journal-of-hepatology.eu/article/S0168-8278(18)32183-4/fulltext
C. Uwaoma and G. Mansingh, “Proposing a decision support system for automated mobile asthma monitoring in remote areas*,” Inf. Technol. Dev., vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 301–314, Apr. 2018, doi: 10.1080/02681102.2017.1310712;CSUBTYPE:STRING:SPECIAL;PAGE:STRING:ARTICLE/CHAPTER.
E. J. Roccella, “Report of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Pregnancy,” Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol., vol. 183, no. 1, 2000, [Online]. Available: https://www.ajog.org/article/S0002-9378(00)40820-3/fulltext
J. Gudu, D. Gichoya, P. Nyongesa, and A. Muumbo, “Development of a Medical Expert System as an ExpertKnowledge Sharing Tool on Diagnosis and Treatment of Hypertension in Pregnancy,” Int. J. Biosci. Biochem. Bioinforma., pp. 297–300, 2012, doi: 10.7763/IJBBB.2012.V2.120.
febbyan teguh, “A guide to expert systems,” Jan. 01, 1986. Accessed: Nov. 13, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.academia.edu/2030055/A_guide_to_expert_systems
E.P.Ephzibah, Dr. V. Sundarapandian, “A NEURO FUZZY EXPERT SYSTEM FOR HEART DISEASE DIAGNOSIS,” Comput. Sci. Eng. An Int. J., vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 17–23, 2012, doi: 10.5121/cseij.2012.2103.
N. A. Mahmoud. Alkhayat., “PREVALENCE OF PARENTAL SELF MEDICATION AND ITS POSSIBLE EFFECT TO THEIR CHILDREN IN AL-MADINAH , KINGDOM OF SAUDI ARABIA,” Int. J. Adv. Res., vol. 5, no. 1, 2017, [Online]. Available: http://www.journalijar.com/article/14702/prevalence-of-parental-self-medication-and--its--possible-effect-to-their-children-in-al-madinah-,-kingdom-of-saudi-arabia./
X.Y. Djam, Y.H. Kimbi, “Fuzzy Expert System for the Management of Hypertension,” Pacific J. Sci. Technol., vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 390–402, 2011, [Online]. Available: https://www.akamai.university/files/theme/AkamaiJournal/PJST12_1_390.pdf
R. O. Guillermo Jorge-Botana, “ Call Routing based on a combination of the Construction-Integration model and Latent Semantic Analysis: a full system,” Informatica. Accessed: Nov. 13, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/266732933_Call_Routing_based_on_a_combination_of_the_Construction-Integration_model_and_Latent_Semantic_Analysis_a_full_system
Y. Han and R. Ellis, “Implicit knowledge, explicit knowledge and general language proficiency,” Lang. Teach. Res., vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 1–23, 1998, doi: 10.1177/136216889800200102;WEBSITE:WEBSITE:SAGE;JOURNAL:JOURNAL:LTRA;ISSUE:ISSUE:DOI.
R. Ellis and C. Roever, “The measurement of implicit and explicit knowledge,” Lang. Learn. J., vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 160–175, 2021, doi: 10.1080/09571736.2018.1504229;REQUESTEDJOURNAL:JOURNAL:RLLJ20;SUBPAGE:STRING:ACCESS.
S. Mertens, “Integrated Declarative Process and Decision Discovery of the Emergency Care Process,” Lect. Notes Bus. Inf. Process., vol. 409, pp. 85–114, 2020, doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-66193-9_4.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 50sea

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















