Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Concentration & its Impacts on Human Health (2010-2022)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33411/ijist/2022040317Keywords:
Nitrogen Dioxide Concentration, Interpolation, Human Health, Climate ChangeAbstract
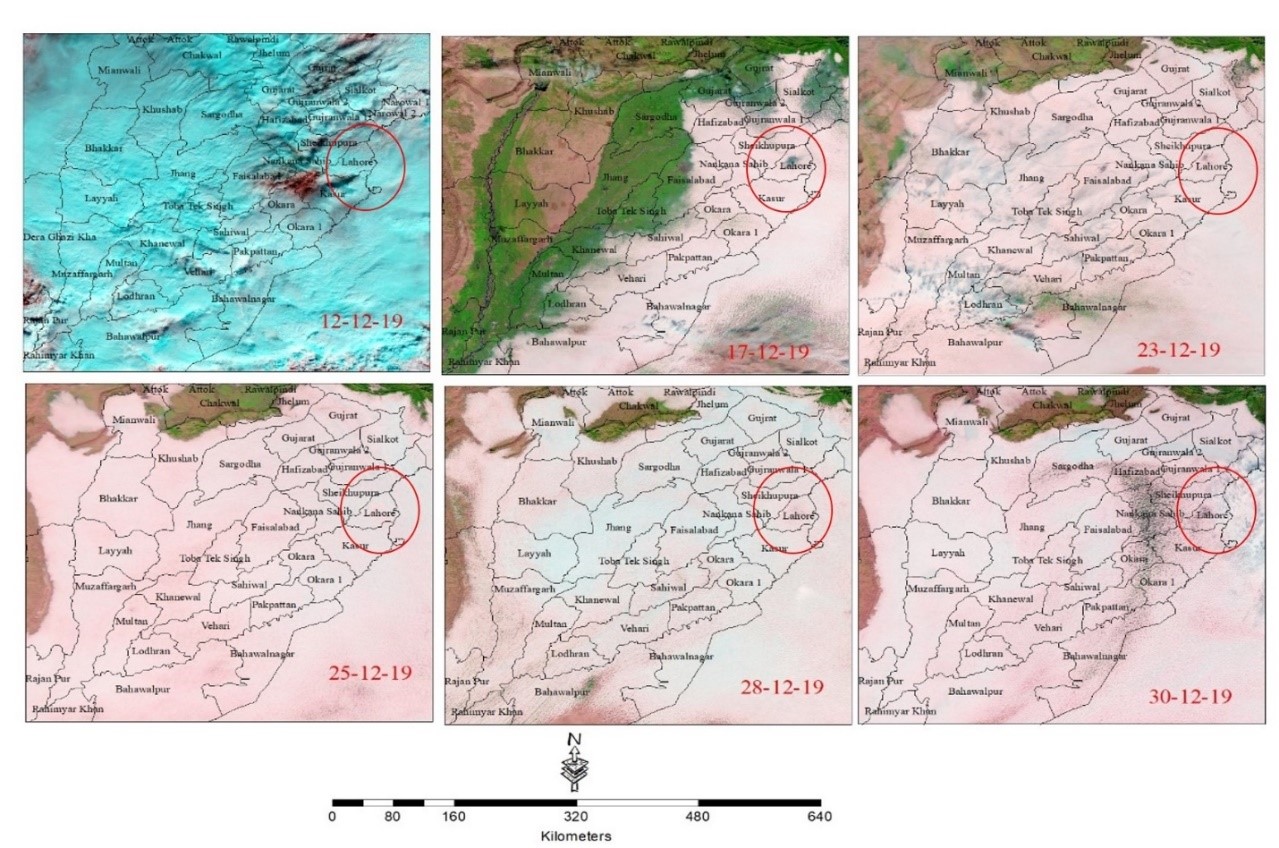
Nitrogen is one of chemical gases which has drastic impact on human health. It is also renowned globally as a major component of climate change. Lahore city has been selected as the study area to conduct this research. The basic objective of this study is to assess the temporal and seasonal change of Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) concentration in the study area and its effects on human health. For this purpose, the two-phase methodology has been adopted. In the first phase, primary and secondary datasets were collected through an online questionnaire and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), respectively, while in the second phase, satellite imageries were acquired from NASA Earth Observatory (NEO). An online questionnaire survey was conducted for a better understanding and assessment of NO2 effects on inhabitants. The interpolation technique was applied to show a temporal change in Concentration of NO2 from 2010-2022 and for seasonal change in 2022. Findings of this research showed that NO2 levels are high during winters as compared to summers. Whereas, temporal analysis from 2010-2019 revealed that high dense columns of NO2 were found in 2019 & 2020 and less dense columns were found in 2019, whereas this concentration declined due to the arrival of COVID from 2020 to the end of 2021. The main reason of this decline is the lack of transport or industrial exhaust due to lockdown by COVID. The results of the questionnaire indicate that people encountered diverse health problems due to long- and short-term exposure to NO2. Moreover, this study helps to display the drastic impacts of NO2 concentration on human health and the natural environment.
References
A. H. Wolfe and J. A. Patz, “Reactive nitrogen and human health: acute and long-term implications,” Ambio, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 120–125, 2002, doi: 10.1579/0044-7447-31.2.120.
J. S. Pandey, R. Kumar, and S. Devotta, “Health risks of NO2, SPM and SO2 in Delhi (India),” Atmos. Environ., vol. 39, no. 36, pp. 6868–6874, Nov. 2005, doi: 10.1016/J.ATMOSENV.2005.08.004.
S. A. Carn et al., “The Unexpected Awakening of Chaitén Volcano, Chile,” Eos (Washington. DC)., vol. 90, no. 24, pp. 205–206, 2009, doi: 10.1029/2009EO240001.
J. G. J. Olivier, A. F. Bouwman, K. W. Van Der Hoek, and J. J. M. Berdowski, “Global air emission inventories for anthropogenic sources of NOx, NH3 and N2O in 1990,” Environ. Pollut., vol. 102, no. 1, pp. 135–148, Jan. 1998, doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(98)80026-2.
D. P. Singh et al., “Study of temporal variation in ambient air quality during Diwali festival in India,” Environ. Monit. Assess., vol. 169, no. 1–4, pp. 1–13, 2010, doi: 10.1007/S10661-009-1145-9.
O. C. Taylor and F. M. Eaton, “Suppression of Plant Growth by Nitrogen Dioxide,” Plant Physiol., vol. 41, no. 1, p. 132, 1966, doi: 10.1104/PP.41.1.132.
Z. Ou Yang, X. Mei, F. Gao, Y. Li, and J. Guo, “Effect of Different Nitrogen Fertilizer Types and Application Measures on Temporal and Spatial Variation of Soil Nitrate-Nitrogen at Cucumber Field,” J. Environ. Prot. (Irvine,. Calif)., vol. 04, no. 01, pp. 129–135, 2013, doi: 10.4236/JEP.2013.41015.
A. A. Gour, S. K. Singh, S. K. Tyagi, and A. Mandal, “Variation in Parameters of Ambient Air Quality in National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi (India),” Atmos. Clim. Sci., vol. 05, no. 01, pp. 13–22, 2015, doi: 10.4236/acs.2015.51002.
N. R. Council, “Rethinking the Ozone Problem in Urban and Regional Air Pollution,” Rethink. Ozone Probl. Urban Reg. Air Pollut., Jan. 1992, doi: 10.17226/1889.
S. G. Ercelebl and H. Toros, “Extreme Value Analysis of Istanbul Air Pollution Data,” CLEAN – Soil, Air, Water, vol. 37, no. 2, pp. 122–131, Feb. 2009, doi: 10.1002/CLEN.200800041.
“Ambient (outdoor) air pollution.”
A. B. Chelani, “Persistence analysis of extreme CO, NO2 and O3 concentrations in ambient air of Delhi,” Atmos. Res., vol. 108, pp. 128–134, May 2012, doi: 10.1016/J.ATMOSRES.2012.02.001.
A. B. Chelani, “Study of extreme CO, NO2 and O3 concentrations at a traffic site in Delhi: Statistical persistence analysis and source identification,” Aerosol Air Qual. Res., vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 377–384, 2013, doi: 10.4209/AAQR.2011.10.0163.
S. Paraschiv, D. E. Constantin, S. L. Paraschiv, and M. Voiculescu, “OMI and ground-based in-situ tropospheric nitrogen dioxide observations over several important European cities during 2005–2014,” Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, vol. 14, no. 11, 2017, doi: 10.3390/ijerph14111415.
M. Sajid, M. Mohsin, T. Jamal, M. Mobeen, A. Rehman, and A. Rafique, “Impact of Land-use Change on Agricultural Production & Accuracy Assessment through Confusion Matrix,” Int. J. Innov. Sci. Technol., vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 233–245, 2022.
F. Sarwar, S. A. Shirazi, and R. W. Aslam, “Assessment and Monitoring of VIIRS-DNB and SQML-L light Pollution in Lahore-Pakistan,” Int. J. Innov. Sci. Technol., vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 94–109, 2022, [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358569889
H. S. Islam, S. M. Mayo, A. U. Rahman, U. Afzal, and M. Ali, “Determination and Mitigation of Urban Heat Island Original Article (UHI) In Lahore (A comparative Study of Landsat 8&9),” Int. J. Innov. Sci. Technol., vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 526–551, 2022.
M. F. Khokhar, H. Mehdi, Z. Abbas, and Z. Javed, “Temporal assessment of NO2 pollution levels in urban centers of Pakistan by employing ground-based and satellite observations,” Aerosol Air Qual. Res., vol. 16, no. 8, pp. 1854–1867, 2016, doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2015.08.0518.
M. F. Khokhar, N. Yasmin, N. Fatima, S. Beirle, and T. Wagner, “Detection of trends and seasonal variation in tropospheric nitrogen dioxide over Pakistan,” Aerosol Air Qual. Res., vol. 15, no. 7, pp. 2508–2524, 2015, doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2015.03.0157.
S. Mazhar, A. Nafeh, and H. A. Jaffari, “Prospects of Biosynthetically produced Nanoparticles in Biocontrol of Pests and Phytopathogens: A Review,” Int. J. Innov. Sci. Technol., vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 552–563, 2022.
M. Kamran, S. R. Ahmad, K. Chohan, A. Akhtar, R. Mansoor, and A. Khan, “Assessment of Water Stress in Rice Fields Incorporating Environmental Parameters,” Int. J. Innov. Sci. Technol., vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 416–424, 2022.
M. Ali and M. Athar, “Impact of transport and industrial emissions on the ambient air quality of Lahore City, Pakistan,” Environ. Monit. Assess., vol. 171, no. 1–4, pp. 353–363, Dec. 2010, doi: 10.1007/S10661-009-1283-0.
M. Rizwan and T. Jamal, “Degradation of Bioplastics under the Influence of Several Environmental conditions,” Int. J. Innov. Sci. Technol., vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 93–101, 2021.
I. Colbeck, Z. A. Nasir, S. Ahmad, and Z. Ali, “Exposure to PM 10, PM 2.5, PM 1 and carbon monoxide on roads in Lahore, Pakistan,” Aerosol Air Qual. Res., vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 689–695, 2011, doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2010.10.0087.
“Preliminary monitoring of tropospheric air quality of Lahore City in Pakistan | Request PDF.”
A. Hamid, S. Akhtar, S. A. Atique, Z. Huma, S. G. M. Uddin, and S. Asghar, “Ambient air quality & noise level monitoring of different areas of lahore (Pakistan) and its health impacts,” Polish J. Environ. Stud., vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 623–629, 2019, doi: 10.15244/pjoes/81702.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 50sea

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






















